Abstract
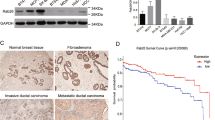
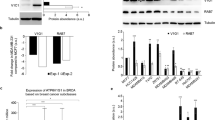
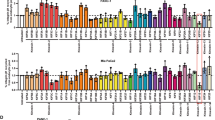
The small GTPase Rab34 regulates spatial distribution of the lysosomes, secretion, and macropinocytosis. In this study, we found that Rab34 is over-expressed in aggressive breast cancer cells, implying a potential role of Rab34 in breast cancer. Silencing Rab34 by shRNA inhibits cell migration, invasion, and adhesion of breast cancer cells. Rab34 specifically binds to the cytoplasmic tail of integrin β3, and depletion of Rab34 promotes the degradation of integrin β3. Interestingly, EGF induces the translocation of Rab34 to the membrane ruffle, which is greatly enhanced by the expression of Src kinase. Accordingly, Rab34 is tyrosine phosphorylated by Src at Y247 residue. A mutant mimicking phosphorylated form of Rab34 (Rab34Y247D) promotes cell migration and invasion. Importantly, the tyrosine phosphorylation of Rab34 is inhibited in cells in suspension, and increased with the cells re-adhesion. In addition, Rab34Y247D promotes cell adhesion, and enhances integrin β3 endocytosis and recycling. The results uncover a role of Rab34 in migration and invasion of breast cancer cells and its involvement in cancer metastasis, and provide a novel mechanism of tyrosine phosphorylation of Rab34 in regulating cell migration, invasion, and adhesion through modulating the endocytosis, stability, and recycling of integrin β3.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hawes CR, Brandizzi F, Andreeva AV. Endomembranes and vesicle trafficking. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 1999;2:454–61.
Spang A. The life cycle of a transport vesicle. Cell Mol life Sci. 2008;65:2781–9.
Salisbury JL, Condeelis JS, Satir P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: machinery and regulation of the clathrin-coated vesicle pathway. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;24:1–62.
Mosesson Y, Mills GB, Yarden Y. Derailed endocytosis: an emerging feature of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:835–50.
Balzac F, Avolio M, Degani S, Kaverina I, Torti M, Silengo L, et al. E-cadherin endocytosis regulates the activity of Rap1: a traffic light GTPase at the crossroads between cadherin and integrin function. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:4765–83.
Voulgari A, Pintzas A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: mechanisms, markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1796:75–90.
Stenmark H. Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:513–25.
Harris KP, Littleton JT. Vesicle trafficking: a Rab family profile. Curr Biol. 2011;21:R841–843.
Bhuin T, Roy JK. Rab proteins: the key regulators of intracellular vesicle transport. Exp Cell Res. 2014;328:1–19.
Cheng KW, Lahad JP, Gray JW, Mills GB. Emerging role of RAB GTPases in cancer and human disease. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2516–9.
Cheng KW, Lahad JP, Kuo WL, Lapuk A, Yamada K, Auersperg N, et al. The RAB25 small GTPase determines aggressiveness of ovarian and breast cancers. Nat Med. 2004;10:1251–6.
Caswell PT, Spence HJ, Parsons M, White DP, Clark K, Cheng KW, et al. Rab25 associates with alpha5beta1 integrin to promote invasive migration in 3D microenvironments. Dev Cell. 2007;13:496–510.
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Marrero-Diaz R, Megias D, Genis L, Garcia-Grande A, Garcia MA, et al. MT1-MMP proinvasive activity is regulated by a novel Rab8-dependent exocytic pathway. EMBO J. 2007;26:1499–510.
Wang T, Zhang M, Ma Z, Guo K, Tergaonkar V, Zeng Q, et al. A role of Rab7 in stabilizing EGFR-Her2 and in sustaining Akt survival signal. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227:2788–97.
Edinger AL, Cinalli RM, Thompson CB. Rab7 prevents growth factor-independent survival by inhibiting cell-autonomous nutrient transporter expression. Dev Cell. 2003;5:571–82.
Igarashi T, Araki K, Yokobori T, Altan B, Yamanaka T, Ishii N, et al. Association of RAB5 overexpression in pancreatic cancer with cancer progression and poor prognosis via E-cadherin suppression. Oncotarget. 2017;8:12290–12300.
Bin Z, Dedong H, Xiangjie F, Hongwei X, Qinghui Y. The microRNA-367 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by directly repressing Rab23. Genet Test Mol Biomark. 2015;19:69–74.
Stein MP, Dong J, Wandinger-Ness A. Rab proteins and endocytic trafficking: potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55:1421–37.
Starling GP, Yip YY, Sanger A, Morton PE, Eden ER, Dodding MP. Folliculin directs the formation of a Rab34-RILP complex to control the nutrient-dependent dynamic distribution of lysosomes. EMBO Rep. 2016;17:823–41.
Wang T, Hong W. Interorganellar regulation of lysosome positioning by the Golgi apparatus through Rab34 interaction with Rab-interacting lysosomal protein. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13:4317–32.
Speight P, Silverman M. Diacylglycerol-activated Hmunc13 serves as an effector of the GTPase Rab34. Traffic. 2005;6:858–65.
Goldenberg NM, Grinstein S, Silverman M. Golgi-bound Rab34 is a novel member of the secretory pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18:4762–71.
Sun P, Yamamoto H, Suetsugu S, Miki H, Takenawa T, Endo T. Small GTPase Rah/Rab34 is associated with membrane ruffles and macropinosomes and promotes macropinosome formation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:4063–71.
Zhang X, Liang X, Gu J, Chang D, Zhang J, Chen Z, et al. Investigation and intervention of autophagy to guide cancer treatment with nanogels. Nanoscale. 2017;9:150–63.
Zhang J, Zhang X, Liu G, Chang D, Liang X, Zhu X, et al. Intracellular trafficking network of protein nanocapsules: endocytosis, exocytosis and autophagy. Theranostics. 2016;6:2099–113.
Coyne CB, Shen L, Turner JR, Bergelson JM. Coxsackievirus entry across epithelial tight junctions requires occludin and the small GTPases Rab34 and Rab5. Cell Host Microbe. 2007;2:181–92.
Wang HJ, Gao Y, Chen L, Li YL, Jiang CL. RAB34 was a progression- and prognosis-associated biomarker in gliomas. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:1573–8.
Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J, Baehner FL, Fevr T, et al. A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:515–27.
Chavez KJ, Garimella SV, Lipkowitz S. Triple negative breast cancer cell lines: one tool in the search for better treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Breast Dis. 2010;32:35–48.
Caswell PT, Chan M, Lindsay AJ, McCaffrey MW, Boettiger D, Norman JC. Rab-coupling protein coordinates recycling of alpha5beta1 integrin and EGFR1 to promote cell migration in 3D microenvironments. J Cell Biol. 2008;183:143–55.
Subramani D, Alahari SK. Integrin-mediated function of Rab GTPases in cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:312.
Gu Z, Noss EH, Hsu VW, Brenner MB. Integrins traffic rapidly via circular dorsal ruffles and macropinocytosis during stimulated cell migration. J Cell Biol. 2011;193:61–70.
Amyere M, Mettlen M, Van Der Smissen P, Platek A, Payrastre B, Veithen A, et al. Origin, originality, functions, subversions and molecular signalling of macropinocytosis. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002;291:487–94.
Mettlen M, Platek A, Van Der Smissen P, Carpentier S, Amyere M, Lanzetti L, et al. Src triggers circular ruffling and macropinocytosis at the apical surface of polarized MDCK cells. Traffic. 2006;7:589–603.
Di Florio A, Capurso G, Milione M, Panzuto F, Geremia R, Delle Fave G, et al. Src family kinase activity regulates adhesion, spreading and migration of pancreatic endocrine tumour cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007;14:111–24.
Arias-Salgado EG, Lizano S, Sarkar S, Brugge JS, Ginsberg MH, Shattil SJ. Src kinase activation by direct interaction with the integrin beta cytoplasmic domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:13298–302.
Wright PK. Targeting vesicle trafficking: an important approach to cancer chemotherapy. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2008;3:137–47.
Agola JO, Jim PA, Ward HH, Basuray S, Wandinger-Ness A. Rab GTPases as regulators of endocytosis, targets of disease and therapeutic opportunities. Clin Genet. 2011;80:305–18.
Xiao R, Xi XD, Chen Z, Chen SJ, Meng G. Structural framework of c-Src activation by integrin beta3. Blood. 2013;121:700–6.
Alanko J, Mai A, Jacquemet G, Schauer K, Kaukonen R, Saari M, et al. Integrin endosomal signalling suppresses anoikis. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17:1412–21.
Alanko J, Ivaska J. Endosomes: emerging platforms for integrin-mediated FAK signalling. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26:391–8.
Tang BL, Ng EL. Rabs and cancer cell motility. Cell Motil Cytoskelet. 2009;66:365–70.
Porther N, Barbieri MA. The role of endocytic Rab GTPases in regulation of growth factor signaling and the migration and invasion of tumor cells. Small GTPases. 2015;6:135–44.
Pellinen T, Arjonen A, Vuoriluoto K, Kallio K, Fransen JA, Ivaska J. Small GTPase Rab21 regulates cell adhesion and controls endosomal traffic of beta1-integrins. J Cell Biol. 2006;173:767–80.
Chodniewicz D, Klemke RL. Guiding cell migration through directed extension and stabilization of pseudopodia. Exp Cell Res. 2004;301:31–37.
Gardel ML, Schneider IC, Aratyn-Schaus Y, Waterman CM. Mechanical integration of actin and adhesion dynamics in cell migration. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010;26:315–33.
Iwamoto DV, Calderwood DA. Regulation of integrin-mediated adhesions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015;36:41–47.
Mitra SK, Schlaepfer DD. Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:516–23.
Valdembri D, Serini G. Regulation of adhesion site dynamics by integrin traffic. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24:582–91.
Ihemelandu CU, Naab TJ, Mezghebe HM, Makambi KH, Siram SM, Leffall LD Jr, et al. Basal cell-like (triple-negative) breast cancer, a predictor of distant metastasis in African American women. Am J Surg. 2008;195:153–8.
Redig AJ, McAllister SS. Breast cancer as a systemic disease: a view of metastasis. J Intern Med. 2013;274:113–26.
Lee U, Frankenberger C, Yun J, Bevilacqua E, Caldas C, Chin SF, et al. A prognostic gene signature for metastasis-free survival of triple negative breast cancer patients. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e82125.
Luo H, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Ning B, Guo J, et al. Down-regulated miR-9 and miR-433 in human gastric carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009;28:82.
Lin X, Zhang J, Chen L, Chen Y, Xu X, Hong W, et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Rab7 by Src kinase. Cell Signal. 2017;35:84–94.
Wang T, Wong KK, Hong W. A unique region of RILP distinguishes it from its related proteins in its regulation of lysosomal morphology and interaction with Rab7 and Rab34. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:815–26.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.31371353 and No.31671478) and International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (No.2013DFG32730). The cDNA of integrin β1 and integrin β3 were kindly provided by Dr. Jiahuai Han (State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology, Xiamen University, China).
Author contributions
SL and XX conducted most of the experiments and analyzed the results. CY and ZY conducted experiments on cell metastasis in vivo. TR and FR completed assays on cancer tissues. QH, JL, and ZY provided technical supports. HW involved in the ideas and paper writing. WT conceived the idea for the project, experiments design, and wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Xu, X., Chen, Y. et al. Rab34 regulates adhesion, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 37, 3698–3714 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0202-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0202-7
This article is cited by
-
Endocytosis in cancer and cancer therapy
Nature Reviews Cancer (2023)
-
Numb exon 9 inclusion regulates Integrinβ5 surface expression and promotes breast cancer metastasis
Oncogene (2022)
-
Rab26 suppresses migration and invasion of breast cancer cells through mediating autophagic degradation of phosphorylated Src
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Integrin trafficking in cells and tissues
Nature Cell Biology (2019)