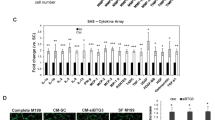
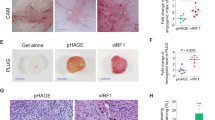
Abstract
Latent transforming growth factor β (TGFβ)-binding proteins (LTBPs) are important for the secretion, activation, and function of mature TGFβ, especially so in cancer cell physiology. However, specific roles of the LTBPs remain understudied in the context of the primary tumor microenvironment. Herein, we investigated the role of LTBP3 in the distinct processes involved in cancer metastasis. By using three human tumor cell lines of different tissue origin (epidermoid HEp-3 and prostate PC-3 carcinomas and HT-1080 fibrosarcoma) and several metastasis models conducted in both mammalian and avian settings, we show that LTBP3 is involved in the early dissemination of primary cancer cells, namely in the intravasation step of the metastatic cascade. Knockdown of LTBP3 in all tested cell lines led to significant inhibition of tumor cell intravasation, but did not affect primary tumor growth. LTBP3 was dispensable in the late steps of carcinoma cell metastasis that follow tumor cell intravasation, including vascular arrest, extravasation, and tissue colonization. However, LTBP3 depletion diminished the angiogenesis-inducing potential of HEp-3 cells in vivo, which was restorable by exogenous delivery of LTBP3 protein. A similar compensatory approach rescued the dampened intravasation of LTBP3-deficient HEp-3 cells, suggesting that LTBP3 regulates the induction of the intravasation-supporting angiogenic vasculature within developing primary tumors. Using our recently developed microtumor model, we confirmed that LTBP3 loss resulted in the development of intratumoral vessels with an abnormal microarchitecture incompatible with efficient intravasation of HEp-3 carcinoma cells. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that LTBP3 represents a novel oncotarget that has distinctive functions in the regulation of angiogenesis-dependent tumor cell intravasation, a critical process during early cancer dissemination. Our experimental data are also consistent with the survival prognostic value of LTBP3 expression in early-stage head and neck squamous cell carcinomas, further indicating a specific role for LTBP3 in cancer progression toward metastatic disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moustakas A, Heldin P. TGFbeta and matrix-regulated epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840:2621–34.
Dongre A, Rashidian M, Reinhardt F, Bagnato A, Keckesova Z, Ploegh HL, et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to immunosuppression in breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2017;77:3982–9. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-1116-3292.
Shibue T, Weinberg RA. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14:611–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.1044.
Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971;285:1182–6.
Folkman J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. 2002;29:15–18.
Chung AS, Ferrara N. Developmental and pathological angiogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:563–84.
Deryugina EI, Kiosses WB. Intratumoral cancer cell intravasation can occur independent of invasion into the adjacent stroma. Cell Rep. 2017;19:601–16.
Weinberg RA. Mechanisms of malignant progression. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:1092–5.
Bos PD, Zhang XH, Nadal C, Shu W, Gomis RR, Nguyen DX, et al. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Nature. 2009;459:1005–9.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Yilmaz M, Christofori G. EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastas- Rev. 2009;28:15–33.
Massague J, Batlle E, Gomis RR. Understanding the molecular mechanisms driving metastasis. Mol Oncol. 2017;11:3–4.
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP. Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastas- Rev. 2006;25:9–34.
Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massague J. Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:274–84.
Ikushima H, Miyazono K. TGFbeta signalling: a complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:415–24.
Wakefield LM, Hill CS. Beyond TGFbeta: roles of other TGFbeta superfamily members in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:328–41.
Derynck R, Muthusamy BP, Saeteurn KY. Signaling pathway cooperation in TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014;31:56–66.
Principe DR, Doll JA, Bauer J, Jung B, Munshi HG, Bartholin L, et al. TGF-beta: duality of function between tumor prevention and carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106:djt369.
Bachman KE, Park BH. Duel nature of TGF-beta signaling: tumor suppressor vs. tumor promoter. Curr Opin Oncol. 2005;17:49–54.
Lebrun J-J. The dual role of TGFbeta in human cancer: from tumor suppression to cancer metastasis. ISRN Mol Biol. 2012;2012:381428.
Neuzillet C, Tijeras-Raballand A, Cohen R, Cros J, Faivre S, Raymond E, et al. Targeting the TGFbeta pathway for cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;147:22–31.
Miyazono K, Heldin CH. Structure, function and possible clinical application of transforming growth factor-beta. J Dermatol. 1992;19:644–7.
Saharinen J, Keski-Oja J. Specific sequence motif of 8-Cys repeats of TGF-beta binding proteins, LTBPs, creates a hydrophobic interaction surface for binding of small latent TGF-beta. Mol Biol Cell. 2000;11:2691–704.
Lack J, O’Leary JM, Knott V, Yuan X, Rifkin DB, Handford PA, et al. Solution structure of the third TB domain from LTBP1 provides insight into assembly of the large latent complex that sequesters latent TGF-beta. J Mol Biol. 2003;334:281–91.
Chandramouli A, Simundza J, Pinderhughes A, Cowin P. Choreographing metastasis to the tune of LTBP. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011;16:67–80.
Fontana L, Chen Y, Prijatelj P, Sakai T, Fassler R, Sakai LY, et al. Fibronectin is required for integrin alphavbeta6-mediated activation of latent TGF-beta complexes containing LTBP1. FASEB J. 2005;19:1798–808.
Yoshinaga K, Obata H, Jurukovski V, Mazzieri R, Chen Y, Zilberberg L, et al. Perturbation of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 association with latent TGF-beta binding protein yields inflammation and tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:18758–63.
Shi M, Zhu J, Wang R, Chen X, Mi L, Walz T, et al. Latent TGF-beta structure and activation. Nature. 2011;474:343–9.
Dabovic B, Robertson IB, Zilberberg L, Vassallo M, Davis EC, Rifkin DB. Function of latent TGFbeta binding protein 4 and fibulin 5 in elastogenesis and lung development. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230:226–36.
Gleizes PE, Beavis RC, Mazzieri R, Shen B, Rifkin DB. Identification and characterization of an eight-cysteine repeat of the latent transforming growth factor-beta binding protein-1 that mediates bonding to the latent transforming growth factor-beta1. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:29891–6.
Isogai M, Saitou Y, Takahashi N, Itabashi T, Terada M, Satoh H, et al. The 50-kDa protein of Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus interferes with intracellular and intercellular targeting and tubule-inducing activity of the 39-kDa protein of Grapevine berry inner necrosis virus. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003;16:188–95.
Loeys BL, Chen J, Neptune ER, Judge DP, Podowski M, Holm T, et al. A syndrome of altered cardiovascular, craniofacial, neurocognitive and skeletal development caused by mutations in TGFBR1 or TGFBR2. Nat Genet. 2005;37:275–81.
Lindsay ME, Schepers D, Bolar NA, Doyle JJ, Gallo E, Fert-Bober J, et al. Loss-of-function mutations in TGFB2 cause a syndromic presentation of thoracic aortic aneurysm. Nat Genet. 2012;44:922–7.
Schepers D, Doyle AJ, Oswald G, Sparks E, Myers L, Willems PJ, et al. The SMAD-binding domain of SKI: a hotspot for de novo mutations causing Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015;23:224–8.
Inoue T, Ohbayashi T, Fujikawa Y, Yoshida H, Akama TO, Noda K, et al. Latent TGF-beta binding protein-2 is essential for the development of ciliary zonule microfibrils. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:5672–82.
Eklov S, Funa K, Nordgren H, Olofsson A, Kanzaki T, Miyazono K, et al. Lack of the latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein in malignant, but not benign prostatic tissue. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3193–7.
Henriksen R, Gobl A, Wilander E, Oberg K, Miyazono K, Funa K. Expression and prognostic significance of TGF-beta isotypes, latent TGF-beta 1 binding protein, TGF-beta type I and type II receptors, and endoglin in normal ovary and ovarian neoplasms. Lab Invest. 1995;73:213–20.
Roth-Eichhorn S, Heitmann B, Flemming P, Kubicka S, Trautwein C. Evidence for the decreased expression of the latent TGF-beta binding protein and its splice form in human liver tumours. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2001;36:1204–10.
Vehvilainen P, Koli K, Myllarniemi M, Lindholm P, Soini Y, Salmenkivi K, et al. Latent TGF-beta binding proteins (LTBPs) 1 and 3 differentially regulate transforming growth factor-beta activity in malignant mesothelioma. Hum Pathol. 2011;42:269–78.
Naba A, Clauser KR, Lamar JM, Carr SA, Hynes RO. Extracellular matrix signatures of human mammary carcinoma identify novel metastasis promoters. Elife. 2014;3:e01308.
Wan F, Peng L, Zhu C, Zhang X, Chen F, Liu T. Knockdown of latent transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta)-binding protein 2 (LTBP2) inhibits invasion and tumorigenesis in thyroid carcinoma cells. Oncol Res. 2017;25:503–10.
Kim J, Yu W, Kovalski K, Ossowski L. Requirement for specific proteases in cancer cell intravasation as revealed by a novel semiquantitative PCR-based assay. Cell. 1998;94:353–62.
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP. Chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane model systems to study and visualize human tumor cell metastasis. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008;130:1119–30.
Conn EM, Botkjaer KA, Kupriyanova TA, Andreasen PA, Deryugina EI, Quigley JP. Comparative analysis of metastasis variants derived from human prostate carcinoma cells: roles in intravasation of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis and uPA-mediated invasion. Am J Pathol. 2009;175:1638–52.
Juncker-Jensen A, Deryugina EI, Rimann I, Zajac E, Kupriyanova TA, Engelholm LH, et al. Tumor MMP-1 activates endothelial PAR1 to facilitate vascular intravasation and metastatic dissemination. Cancer Res. 2013;73:4196–211.
Minder P, Zajac E, Quigley JP, Deryugina EI. EGFR regulates the development and microarchitecture of intratumoral angiogenic vasculature capable of sustaining cancer cell intravasation. Neoplasia. 2015;17:634–49.
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP. Chapter 2. Chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane models to quantify angiogenesis induced by inflammatory and tumor cells or purified effector molecules. Methods Enzymol. 2008;444:21–41.
Deryugina EI. Chorioallantoic membrane microtumor model to study the mechanisms of tumor angiogenesis, vascular permeability, and tumor cell intravasation. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1430:283–98.
Jilani SM, Murphy TJ, Thai SNM, Eichmann A, Alva JA, Iruela-Arispe ML. Selective binding of lectins to embryonic chicken vasculature. J Histochem Cytochem. 2003;51:597–604.
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP. Tumor angiogenesis: MMP-mediated induction of intravasation- and metastasis-sustaining neovasculature. Matrix Biol. 2015;44-46:94–112.
Tanaka T, Nakayama H, Yoshitake Y, Irie A, Nagata M, Kawahara K, et al. Selective inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB by nuclear factor-kappaB essential modulator-binding domain peptide suppresses the metastasis of highly metastatic oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2012;103:455–63.
Vincent-Chong VK, Salahshourifar I, Woo KM, Anwar A, Razali R, Gudimella R, et al. Genome wide profiling in oral squamous cell carcinoma identifies a four genetic marker signature of prognostic significance. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0174865.
Chen Y, Dabovic B, Annes JP, Rifkin DB. Latent TGF-beta binding protein-3 (LTBP3) requires binding to TGF-beta for secretion. FEBS Lett. 2002;517:277–80.
Penttinen C, Saharinen J, Weikkolainen K, Hyytiainen M, Keski-Oja J. Secretion of human latent TGF-beta-binding protein-3 (LTBP3) is dependent on co-expression of TGF-beta. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:3457–68.
Chen H, Cai W, Chu ESH, Tang J, Wong CC, Wong SH, et al. Hepatic cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression induced spontaneous hepatocellular carcinoma formation in mice. Oncogene. 2017;36:4415–26.
Akhurst RJ, Hata A. Targeting the TGFbeta signalling pathway in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11:790–811.
Connolly EC, Freimuth J, Akhurst RJ. Complexities of TGF-beta targeted cancer therapy. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8:964–78.
Deryugina EI, Zijlstra A, Partridge JJ, Kupriyanova TA, Madsen MA, Papagiannakopoulos T, et al. Unexpected effect of matrix metalloproteinase down-regulation on vascular intravasation and metastasis of human fibrosarcoma cells selected in vivo for high rates of dissemination. Cancer Res. 2005;65:10959–69.
Dell RB, Holleran S, Ramakrishnan R. Sample size determination. ILAR J. 2002;43:207–13.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants R01CA157792 (E.I.D.), R01CA105412 (J.P.Q.), and R01CA034282 (D.R.) from the National Institutes of Health. This is manuscript no. 29589 from TSRI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deryugina, E.I., Zajac, E., Zilberberg, L. et al. LTBP3 promotes early metastatic events during cancer cell dissemination. Oncogene 37, 1815–1829 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0075-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0075-1
This article is cited by
-
ROCK2-RNA interaction map reveals multiple biological mechanisms underlying tumor progression in renal cell carcinoma
Human Cell (2023)
-
Integrated analysis of 1804 samples of six centers to construct and validate a robust immune-related prognostic signature associated with stromal cell abundance in tumor microenvironment for gastric cancer
World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2022)
-
Exploring the biological function of immune cell-related genes in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 infection based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA)
BMC Medical Genomics (2022)
-
LTBP1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer-associated fibroblasts transformation
Journal of Translational Medicine (2020)
-
Combination of laser microdissection, 2D-DIGE and MALDI-TOF MS to identify protein biomarkers to predict colorectal cancer spread
Clinical Proteomics (2019)