Abstract
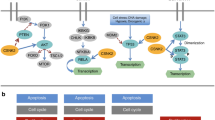
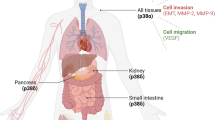
Protein kinase D2 (PKD2) is a serine/threonine kinase that belongs to the PKD family of calcium–calmodulin kinases, which comprises three isoforms: PKD1, PKD2, and PKD3. PKD2 is activated by many stimuli including growth factors, phorbol esters, and G-protein-coupled receptor agonists. PKD2 participation to uncontrolled growth, survival, neovascularization, metastasis, and invasion has been documented in various tumor types including pancreatic, colorectal, gastric, hepatic, lung, prostate, and breast cancer, as well as glioma multiforme and leukemia. This review discusses the versatile functions of PKD2 from the perspective of cancer hallmarks as described by Hanahan and Weinberg. The PKD2 status, signaling pathways affected in different tumor types and the molecular mechanisms that lead to tumorigenesis and tumor progression are presented. The latest developments of small-molecule inhibitors selective for PKD/PKD2, as well as the need for further chemotherapies that prevent, slow down, or eliminate tumors are also discussed in this review.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 2002;298:1912–34.
Huse M, Kuriyan J. The conformational plasticity of protein kinases. Cell 2002;109:275–82.
Nolen B, Taylor S, Ghosh G. Regulation of protein kinases; controlling activity through activation segment conformation. Mol Cell. 2004;15:661–75.
Cohen P. Protein kinases-the major drug targets of the twenty-first century? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:309–15.
Zhang J, Yang PL, Gray NS. Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2009;9:28–39.
Matthews SA, Navarro MN, Sinclair LV, Emslie E, Feijoo-Carnero C, Cantrell DA. Unique functions for protein kinase D1 and protein kinase D2 in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 2010;432:153–63.
Valverde AM, Sinnett-Smith J, Van Lint J, Rozengurt E. Molecular cloning and characterization of protein kinase D: a target for diacylglycerol and phorbol esters with a distinctive catalytic domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994;91:8572–76.
Johannes FJ, Prestle J, Dieterich S, Oberhagemann P, Link G, Pfizenmaier K. Characterization of activators and inhibitors of protein kinase C mu. Eur J Biochem. 1995;227:303–7.
Nishikawa K, Toker A, Johannes FJ, Songyang Z, Cantley LC. Determination of the specific substrate sequence motifs of protein kinase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:952–60.
Sturany S, Van Lint J, Muller F, Wilda M, Hameister H, Hocker M, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human protein kinase D2. A novel member of the protein kinase D family of serine threonine kinases. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:3310–18.
Hayashi A, Seki N, Hattori A, Kozuma S, Saito T. PKCnu, a new member of the protein kinase C family, composes a fourth subfamily with PKCmu. Biochim Biophys Acta 1999;1450:99–106.
Rykx A, De Kimpe L, Mikhalap S, et al. Protein kinase D: a family affair. FEBS Lett. 2003;546:81–86.
Storz P, Toker A. Protein kinase D mediates a stress-induced NF-kB activation and survival pathway. EMBO J. 2003;22:109–20.
Iglesias T, Matthews S, Rozengurt E. Dissimilar phorbol ester binding properties of the individual cysteine-rich motifs of protein kinase D. FEBS Lett. 1998;437:19–23.
Auer A, von Blume J, Sturany S, von Wichert G, Van Lint J, Vandenheede J, et al. Role of the regulatory domain of protein kinase D2 in phorbol ester binding, catalytic activity, and nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;9:4375–85.
Sturany S, Van Lint J, Gilchrist A, Vandenheede JR, Adler G, Seufferlein T. Mechanism of activation of protein kinase D2(PKD2) by the CCK(B)/gastrin receptor. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:29431–36.
von Blume J, Knippschild U, Dequiedt F, Giamas G, Beck A, Auer A, et al. Phosphorylation at Ser244 by CK1 determines nuclear localization and substrate targeting of PKD2. EMBO J. 2007;26:4619–33.
Cobbaut M, Derua R, Döppler H, Lou HJ, et al. Differential regulation of PKD isoforms in oxidative stress conditions through phosphorylation of a conserved Tyr in the P+1 loop. Sci Rep. 2017;7:887.
Zugaza JL, Sinnett-Smith J, Van Lint J, Rozengurt E. Protein kinase D (PKD) activation in intact cells through a protein kinase C-dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1996;15:6220–30.
Baron CL, Malhotra V. Role of diacylglycerol in PKD recruitment to the TGN and protein transport to the plasma membrane. Science 2002;295:325–28.
Azoitei N, Pusapati GV, Kleger A, Möller P, Küfer R, Genze F, et al. Protein kinase D2 is a crucial regulator of tumor cell – endothelial cell communication in gastrointestinal tumors. Gut 2010;59:1316–30.
von Wichert G, Jehle PM, Hoeflich A, Koschnick S, Dralle H, Wolf E, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I is an autocrine regulator of chromogranin A secretion and growth in human neuroendocrine tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4573–81.
Bossard C, Bresson D, Polishchuk RS, Malhotra V. Dimeric PKD regulates membrane fission to form transport carriers at the TGN. J Cell Biol. 2007;179:1123–31.
Li J, O’Connor KL, Hellmich MR, Greeley GH Jr, Townsend CM Jr, Evers BM. The role of protein kinase D in neurotensin secretion mediated by protein kinase C-alpha/-delta and Rho/Rho kinase. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:28466–74.
von Wichert G, Edenfeld T, von Blume J, Krisp H, Krndija D, Schmid H, et al. Protein kinase D2 regulates chromogranin A secretion in human BON neuroendocrine tumour cells. Cell Signal. 2008;20:925–34.
Yeaman C, Ayala MI, Wright JR, Bard F, Bossard C, Ang A, et al. Protein kinase D regulates basolateral membrane protein exit from trans-Golgi network. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:106–12.
Mihailovic T, Marx M, Auer A, Van Lint J, Schmid M, Weber C, et al. Protein kinase D2 mediates activation of nuclear factor kappaB by Bcr-Abl in Bcr-Abl+human myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:8939–44.
Storz P, Döppler H, Toker A. Activation loop phosphorylation controls protein kinase D-dependent activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;66:870–79.
Steiner TS, Ivison SM, Yao Y, Kifayet A. Protein kinase D1 and D2 are involved in chemokine release induced by toll-like receptors 2, 4, and 5. Cell Immunol. 2010;264:135–42.
Sumara G, Formentini I, Collins S, Sumara I, Windak R, Bodenmiller B, et al. Regulation of PKD by the MAPK p38delta in insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis. Cell 2009;136:235–48.
Wang QJ. PKD at the crossroads of DAG and PKC signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:317–23.
Rey O, Yuan J, Rozengurt E. Intracellular redistribution of protein kinase D2 in response to G-protein-coupled receptor agonists. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;302:817–24.
Oancea E, Meyer T. Protein kinase C as a molecular machine for decoding calcium and diacylglycerol signals. Cell 1998;95:307–18.
Rey O, Sinnett-Smith J, Zhukova E, Rozengurt E. Regulated nucleocytoplasmic transport of protein kinase D in response to G protein-coupled receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:49228–35.
Liljedahl M, Maeda Y, Colanzi A, Ayala I, Van Lint J, Malhotra V. Protein kinase D regulates the fission of cell surface destined transport carriers from the trans-Golgi network. Cell 2001;104:409–20.
Hausser A, Link G, Hoene M, Russo C, Selchow O, Pfizenmaier K. Phospho-specific binding of 14-3-3 proteins to phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III beta protects from dephosphorylation and stabilizes lipid kinase activity. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:3613–21.
Fugmann T, Hausser A, Schöffler P, Schmid S, Pfizenmaier K, Olayioye MA. Regulation of secretory transport by protein kinase D-mediated phosphorylation of the ceramide transfer protein. J Cell Biol. 2007;17:15–22.
Nhek S, Ngo M, Yang X, Ng MM, Field SJ, Asara JM, et al. Regulation of oxysterol-binding protein Golgi localization through protein kinase D-mediated phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21:2327–37.
Eiseler T, Wille C, Koehler C, Illing A, Seufferlein T. Protein kinase D2 assembles a multiprotein complex at the trans-Golgi network to regulate matrix metalloproteinase secretion. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:462–77.
Sidorenko SP, Law CL, Klaus SJ, Chandran KA, Takata M, Kurosaki T, et al. Protein kinase C mu (PKC mu) associates with the B cell antigen receptor complex and regulates lymphocyte signaling. Immunity 1996;5:353–63.
Marklund U, Lightfoot K, Cantrell D. Intracellular location and cell context-dependent function of protein kinase D. Immunity 2003;19:491–501.
Matthews SA, Dayalu R, Thompson LJ, Scharenberg AM. Regulation of protein kinase Cnu by the B-cell antigen receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:9086–91.
Spitaler M, Emslie E, Wood CD, Cantrell D. Diacylglycerol and protein kinase D localization during T lymphocyte activation. Immunity 2006;24:535–46.
Hollenbach M, Stoll SJ, Jörgens K, Seufferlein T, Kroll J. Different regulation of physiological and tumor angiogenesis in zebrafish by protein kinase D1 (PKD1). PLoS ONE 2013;8:e68033.
Müller M, Schröer J, Azoitei N, Eiseler T, Bergmann W, Köhntop R, et al. A time frame permissive for protein kinase D2 activity to direct angiogenesis in mouse embryonic stem cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11742.
Geng J, Zhao Z, Kang W, Wang W, Liu G, Sun Y, et al. Hypertrophic response to angiotensin II is mediated by protein kinase D-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 pathway in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;388:517–22.
Fielitz J, Kim MS, Shelton JM, Qi X, Hill JA, Richardson JA, et al. Requirement of protein kinase D1 for pathological cardiac remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008;105:3059–63.
Kim Y, Phan D, van Rooij E, Wang DZ, McAnally J, Qi X, et al. The MEF2D transcription factor mediates stress-dependent cardiac remodeling in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:124–32.
Avkiran M, Rowland AJ, Cuello F, Haworth RS. Protein kinase d in the cardiovascular system: emerging roles in health and disease. Circ Res. 2008;102:157–63.
Kleger A, Loebnitz C, Pusapati GV, Armacki M, Müller M, Tümpel S, et al. Protein kinase D2 is an essential regulator of murine myoblast differentiation. PLoS ONE 2011;6:e14599.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000;100:57–70.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011;144:646–74.
Pearson MA, Fabbro D. Targeting protein kinases in cancer therapy: a success? Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2004;4:1113–24.
Guha S, Rey O, Rozengurt E. Neurotensin induces protein kinase C-dependent protein kinase D activation and DNA synthesis in human pancreatic carcinoma cell line PANC-1. Cancer Res. 2002;62:1632–40.
Wille C, Köhler C, Armacki M, Jamali A, Gössele U, Pfizenmaier K, et al. Protein kinase D2 induces invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating matrix metalloproteinases. Mol Biol Cell. 2014;25:324–36.
Wei N, Chu E, Wipf P, Schmitz JC. Protein kinase D as a potential chemotherapeutic target for colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:1130–41.
Chen J, Deng F, Singh SV, Wang QJ. Protein kinase D3 (PKD3) contributes to prostate cancer cell growth and survival through a PKC epsilon/PKD3 pathway downstream of Akt and ERK 1/2. Cancer Res. 2008;68:3844–53.
Zou Z, Zeng F, Xu W, Wang C, Ke Z, Wang QJ, et al. PKD2 and PKD3 promote prostate cancer cell invasion by modulating NF-κB- and HDAC1-mediated expression and activation of uPA. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:4800–11.
Shabelnik MY, Kovalevska LM, Yurchenko MY, Shlapatska LM, Rzepetsky Y, Sidorenko SP. Differential expression of PKD1 and PKD2 in gastric cancer and analysis of PKD1 and PKD2 function in the model system. Exp Oncol. 2011;33:206–11.
Hao Q, McKenzie R, Gan H, Tang H. Protein kinases D2 and D3 are novel growth regulators in HCC1806 triple-negative breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:393–99.
Alpsoy A, Gündüz U. Protein kinase D2 silencing reduced motility of doxorubicin-resistant MCF7 cells. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:4417–26.
Zhu Y, Cheng Y, Guo Y, Chen J, Chen F, Luo R, et al. Protein kinase D2 contributes to TNF-α-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition and invasion via the PI3K/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016;7:5327–41.
Azoitei N, Kleger A, Schoo N, Thal DR, Brunner C, Pusapati GV, et al. Protein kinase D2 is a novel regulator of glioblastoma growth and tumor formation. Neuro Oncol. 2011;13:710–24.
Bernhart E, Damm S, Wintersperger A, DeVaney T, Zimmer A, Raynham T, et al. Protein kinase D2 regulates migration and invasion of U87MG glioblastoma cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319:2037–48.
Bernhart E, Damm S, Heffeter P, Wintersperger A, Asslaber M, Frank S, et al. Silencing of protein kinase D2 induces glioma cell senescence via p53-dependent and -independent pathways. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16:933–45.
Wang Y, Waldron RT, Dhaka A, Patel A, Riley MM, Rozengurt E, et al. The RAS effector RIN1 directly competes with RAF and is regulated by 14-3-3 proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:916–26.
Wei N, Chu E, Wipf P, Schmitz JC. Protein kinase D as a potential chemotherapeutic target for colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:1130–41.
Hao Q, Wang L, Zhao ZJ, Tang H. Identification of protein kinase D2 as a pivotal regulator of endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2009;28:799–806.
Zhou X, Xue P, Yang M, Shi H, Lu D, Wang Z, et al. Protein kinase D2 promotes the proliferation of glioma cells by regulating Golgi phosphoprotein 3. Cancer Lett. 2014;355:121–29.
Scott KL, Kabbarah O, Liang MC, Ivanova E, Anagnostou V, Wu J, et al. GOLPH3 modulates mTOR signalling and rapamycin sensitivity in cancer. Nature 2009;459:1085–90.
Chiu T, Rozengurt E. PKD in intestinal epithelial cells: rapid activation by phorbol esters, LPA, and angiotensin through PKC. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;280:929–42.
Chiu T, Rozengurt E. CCK2 (CCK(B)/gastrin) receptor mediates rapid protein kinase D (PKD) activation through a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. FEBS Lett. 2001;489:101–6.
Qiang YW, Yao L, Tosato G, Rudikoff S. Insulin-like growth factor I induces migration and invasion of human multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2004;103:301–8.
Qin L, Zeng H, Zhao D. Requirement of protein kinase D tyrosine phosphorylation for VEGF-A165-induced angiogenesis through its interaction and regulation of phospholipase Cgamma phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:32550–58.
Wong C, Jin ZG. Protein kinase C-dependent protein kinase D activation modulates ERK signal pathway and endothelial cell proliferation by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:33262–69.
Lowe SW, Cepero E, Evan G. Intrinsic tumour suppression. Nature 2004;432:307–15.
Adams JM, Cory S. The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 2007;26:1324–37.
Trauzold A, Schmiedel S, Sipos B, Wermann H, Westphal S, Röder C, et al. PKCmu prevents CD95-mediated apoptosis and enhances proliferation in pancreatic tumour cells. Oncogene 2003;22:8939–47.
Storz P, Döppler H, Toker A. Protein kinase C delta selectively regulates protein kinase D-dependent activation of NF-kappaB in oxidative stress signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:2614–26.
Storz P, Döppler H, Toker A. Protein kinase D mediates mitochondrion-to-nucleus signaling and detoxification from mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:8520–30.
Finkel T, Holbrook NJ. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000;408:239–47.
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, et al. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 1999;96:857–68.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 2002;296:550–53.
Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, ten Dijke P, Saitoh M, Moriguchi T, et al. Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science 1997;275:90–94.
Zhang W, Zheng S, Storz P, Min W. Protein kinase D specifically mediates apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-JNK signaling induced by H2O2 but not tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:19036–44.
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Kimchi A. DAP kinase regulates JNK signaling by binding and activating protein kinase D under oxidative stress. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:1908–15.
Chen J, Giridhar KV, Zhang L, Xu S, Wang QJ. A protein kinase C/protein kinase D pathway protects LNCaP prostate cancer cells from phorbol ester-induced apoptosis by promoting ERK1/2 and NF-kB activities. Carcinogenesis 2011;32:1198–206.
Azoitei N, Diepold K, Brunner C, Rouhi A, Genze F, Becher A, et al. HSP90 supports tumor growth and angiogenesis through PRKD2 protein stabilization. Cancer Res. 2014;74:7125–36.
Klymkowsky MW, Savagner P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a cancer researcher’s conceptual friend and foe. Am J Pathol. 2009;174:1588–93.
Polyak K, Weinberg RA. Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer 2009;9:265–73.
Yilmaz M, Christofori G. EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastas Rev. 2009;28:15–33.
Barrallo-Gimeno A, Nieto MA. The Snail genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: implications in development and cancer. Development 2005;132:3151–61.
Eiseler T, Köhler C, Nimmagadda SC, Jamali A, Funk N, Joodi G, et al. Protein kinase D1 mediates anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of tumor cells via the zinc finger transcription factor Snail1. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:32367–80.
Jaggi M, Rao PS, Smith DJ, Wheelock MJ, Johnson KR, Hemstreet GP, et al. E-cadherin phosphorylation by protein kinase D1 is associated with altered cellular aggregation and motility in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:483–92.
Durand N, Borges S, Storz P. Protein kinase D enzymes as regulators of EMT and cancer cell invasion. J Clin Med. 2016;5:pii: E20.
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010;141:52–67.
Soria G, Ofri-Shahak M, Haas I, Yaal-Hahoshen N, Leider-Trejo L, Leibovich-Rivkin T, et al. Inflammatory mediators in breast cancer: coordinated expression of TNFα & IL-1β with CCL2 & CCL5 and effects on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. BMC Cancer 2011;11:130.
Yan C, Grimm WA, Garner WL, Qin L, Travis T, Tan N, et al. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human skin wound healing is induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha through bone morphogenic protein-2. Am J Pathol. 2010;176:2247–58.
Van Lint J, Rykx A, Maeda Y, Vantus T, Sturany S, Malhotra V, et al. Protein kinase D: an intracellular traffic regulator on the move. Trends Cell Biol. 2002;12:193–200.
Eiseler T, Döppler H, Yan IK, Goodison S, Storz P. Protein kinase D1 regulates matrix metalloproteinase expression and inhibits breast cancer cell invasion. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11:R13.
Borges S, Perez EA, Thompson EA, Radisky DC, Geiger XJ, Storz P. Effective targeting of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancers with the protein kinase D inhibitor CRT0066101. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14:1306–16.
Liu ZC, Chen XH, Song HX, Wang HS, Zhang G, Wang H, et al. Snail regulated by PKC/GSK-3β pathway is crucial for EGF-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of cancer cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;358:491–502.
Wille C, Seufferlein T, Eiseler T. Protein kinase D family kinases: roads start to segregate. Bioarchitecture 2014;4:111–15.
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH, Itoh T, Tamaki K, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:737–44.
Bergers G, Benjamin LE. Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2003;3:401–10.
Yoo J, Rodriguez Perez CE, Nie W, Sinnett-Smith J, Rozengurt E. Protein kinase D1 mediates synergistic MMP-3 expression induced by TNF-α and bradykinin in human colonic myofibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;413:30–35.
Armacki M, Joodi G, Nimmagadda SC, de Kimpe L, Pusapati GV, Vandoninck S, et al. A novel splice variant of calcium and integrin-binding protein 1 mediates protein kinase D2-stimulated tumour growth by regulating angiogenesis. Oncogene 2014;33:1167–80.
Janssens K, De Kimpe L, Balsamo M, Vandoninck S, Vandenheede JR, Gertler F, et al. Characterization of EVL-I as a protein kinase D substrate. Cell Signal. 2009;21:282–92.
Egeblad M, Werb Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2002;2:161–74.
Eiseler T, Hausser A, De Kimpe L, Van Lint J, Pfizenmaier K. Protein kinase D controls actin polymerization and cell motility through phosphorylation of cortactin. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:18672–83.
Baeriswyl V, Christofori G. The angiogenic switch in carcinogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2009;19:329–37.
Mac Gabhann F, Popel AS. Systems biology of vascular endothelial growth factors. Microcirculation 2008;15:715–38.
Sipos B, Weber D, Ungefroren H, Kalthoff H, Zühlsdorff A, Luther C, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor mediated angiogenic potential of pancreatic ductal carcinomas enhanced by hypoxia: an in vitro and in vivo study. Int J Cancer 2002;102:592–600.
Ijichi S, Kusaka T, Isobe K, Islam F, Okubo K, Okada H, et al. Quantification of cerebral hemoglobin as a function of oxygenation using near-infrared time-resolved spectroscopy in a piglet model of hypoxia. J Biomed Opt. 2005;10:024026.
Barbara M, Pilar de la P, Feda A, Abdel Kareem A. The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia (Auckl) 2015;3:83–92.
Chouaib S, Messai Y, Sophie C, Bernard E, Meriem H. Hypoxia promotes tumor growth in linking angiogenesis to immune escape. Front Immunol. 2012;3:21.
Eales KL, Hollinshead KER, Tennant DA. Hypoxia and metabolic adaptation of cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2016;5:e190.
Young TA, Wang H, Munk S, Hammoudi DS, Young DS, Mandelcorn MS, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and secretion by retinal pigment epithelial cells in high glucose and hypoxia is protein kinase C-dependent. Exp Eye Res. 2005;80:651–62.
Dequiedt F, Van Lint J, Lecomte E, Van Duppen V, Seufferlein T, Vandenheede JR, et al. Phosphorylation of histone deacetylase 7 by protein kinase D mediates T cell receptor-induced Nur77 expression and apoptosis. J Exp Med. 2005;201:793–804.
Zeng H, Qin L, Zhao D, Tan X, Manseau EJ, Van Hoang M, et al. Orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 regulates VEGF-A-induced angiogenesis through its transcriptional activity. J Exp Med. 2006;203:719–29.
Miwa D, Sakaue T, Inoue H, Takemori N, Kurokawa M, Fukuda S, et al. Protein kinase D2 and heat shock protein 90 beta are required for BCL6-associated zinc finger protein mRNA stabilization induced by vascular endothelial growth factor-A. Angiogenesis 2013;16:675–88.
Dou GR, Wang YC, Hu XB, Hou LH, Wang CM, Xu JF, et al. RBP-J, the transcription factor downstream of Notch receptors, is essential for the maintenance of vascular homeostasis in adult mice. FASEB J. 2008;22:1606–17.
Hellström M, Phng LK, Hofmann JJ, Wallgard E, Coultas L, Lindblom P, et al. Dll4 signalling through Notch1 regulates formation of tip cells during angiogenesis. Nature 2007;445:776–80.
Jakobsson L, Franco CA, Bentley K, Collins RT, Ponsioen B, Aspalter IM, et al. Endothelial cells dynamically compete for the tip cell position during angiogenic sprouting. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:943–53.
Benedito R, Roca C, Sörensen I, Adams S, Gossler A, Fruttiger M, et al. The notch ligands Dll4 and Jagged1 have opposing effects on angiogenesis. Cell 2009;137:1124–35.
Isaacs JS, Jung YJ, Mimnaugh EG, Martinez A, Cuttitta F, Neckers LM. Hsp90 regulates a von Hippel Lindau-independent hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha-degradative pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:29936–44.
Neckers L, Neckers K. Heat-shock protein 90 inhibitors as novel cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 2002;7:277–88.
Minet E, Mottet D, Michel G, Roland I, Raes M, Remacle J, et al. Hypoxia-induced activation of HIF-1: role of HIF-1alpha-Hsp90 interaction. FEBS Lett. 1999;460:251–56.
Choi JW, Park SC, Kang GH, Liu JO, Youn HD. Nur77 activated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha overproduces proopiomelanocortin in von Hippel-Lindau-mutated renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2004;64:35–39.
Yoo YG, Yeo MG, Kim DK, Park H, Lee MO. Novel function of orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 in stabilizing hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:53365–73.
Culver C, Sundqvist A, Mudie S, Melvin A, Xirodimas D, Rocha S. Mechanism of hypoxia-induced NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:4901–21.
Pfeifhofer C, Gruber T, Letschka T, Thuille N, Lutz-Nicoladoni C, Hermann-Kleiter N, et al. Defective IgG2a/2b class switching in PKC alpha-/- mice. J Immunol. 2006;176:6004–11.
Pfeifhofer C, Kofler K, Gruber T, Tabrizi NG, Lutz C, Maly K, et al. Protein kinase C theta affects Ca2 + mobilization and NFAT cell activation in primary mouse T cells. J Exp Med. 2003;197:1525–35.
Gruber T, Hermann-Kleiter N, Pfeifhofer-Obermair C, Lutz-Nicoladoni C, Thuille N, Letschka T, et al. PKC theta cooperates with PKC alpha in alloimmune responses of T cells in vivo. Mol Immunol. 2009;46:2071–79.
Zheng H, Qian J, Baker DP, Fuchs SY. Tyrosine phosphorylation of protein kinase D2 mediates ligand-inducible elimination of the Type 1 interferon receptor. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:35733–41.
Chen J, Feng Y, Lu L, Wang H, Dai L, Li Y, et al. Interferon-γ-induced PD-L1 surface expression on human oral squamous carcinoma via PKD2 signal pathway. Immunobiology 2012;217:385–93.
Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:503–10.
Bryceson YT, Ljunggren HG, Long EO. Minimal requirement for induction of natural cytotoxicity and intersection of activation signals by inhibitory receptors. Blood 2009;114:2657–66.
Scheiter M, Bulitta B, van Ham M, Klawonn F, König S, Jänsch L. Protein kinase inhibitors CK59 and CID755673 alter primary human NK cell effector functions. Front Immunol. 2013;4:66.
Sharlow ER, Giridhar KV, LaValle CR, Chen J, Leimgruber S, Barrett R, et al. Potent and selective disruption of protein kinase D functionality by a benzoxoloazepinolone. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:33516–26.
Patel S, Ngounou Wetie AG, Darie CC, Clarkson BD. Cancer secretomes and their place in supplementing other hallmarks of cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;806:409–42.
Malhotra V, Campelo F. PKD regulates membrane fission to generate TGN to cell surface transport carriers. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011;3:pii: a005280.
Diaz Anel AM, Malhotra V. PKCeta is required for beta1gamma2/beta3gamma2- and PKD-mediated transport to the cell surface and the organization of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 2005;169:83–91.
Goginashvili A, Zhang Z, Erbs E, Spiegelhalter C, Kessler P, Mihlan M, et al. Insulin granules. Insulin secretory granules control autophagy in pancreatic β cells. Science 2015;347:878–82.
Ochi N, Tanasanvimon S, Matsuo Y, Tong Z, Sung B, Aggarwal BB, et al. Protein kinase D1 promotes anchorage-independent growth, invasion, and angiogenesis by human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226:1074–81.
Steiner TS, Ivison SM, Yao Y, Kifayet A. Protein kinase D1 and D2 are involved in chemokine release induced by toll-like receptors 2, 4, and 5. Cell Immunol. 2010;264:135–42.
Hao Q, Wang L, Tang H. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces protein kinase D-dependent production of proinflammatory cytokines in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;296:821–27.
Fanelli MF, Chinen LT Sr, Begnami MD, Costa WL Jr, Fregnami JH, et al. The influence of CD44v6, TGF-α, COX-2, MMP-7, and MMP-9 on clinical evolution of patients with gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:21.
Egeblad M, Werb Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2002;2:161–74.
LaValle CR, Zhang L, Xu S, Eiseman JL, Wang QJ. Inducible silencing of protein kinase D3 inhibits secretion of tumor-promoting factors in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11:1389–99.
Fugmann T, et al Regulation of secretory transport by protein kinase D-mediated phosphorylation of the ceramide transfer protein. J Cell Biol. 2011;178:15–22.
Hausser A, et al Protein kinase D regulates vesicular transport by phosphorylating and activating phosphatidylinositol-4 kinase IIIbeta at the Golgi complex. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:880–86.
Pusapati GV, et al Role of the second cysteine-rich domain and Pro275 in protein kinase D2 interaction with ADP-ribosylation factor 1, trans-Golgi network recruitment, and protein transport. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21:1011–22.
Donaldson JG, Honda A. Localization and function of Arf family GTPases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005;33:639–42.
Bonifacino JS, Glick BS. The mechanisms of vesicle budding and fusion. Cell 2004;116:153–66.
D’Souza-Schorey C, Chavrier P. ARF proteins: roles in membrane traffic and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:347–58.
Koch, et al. ADP ribosylation factor-dependent phospholipase D2 activation is required for agonist-induced mu-opioid receptor endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:9979–85.
Mitchell, et al. ADP-ribosylation factor-dependent phospholipase D activation by the M3 muscarinic receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:33818–30.
Aikawa, et al ARF6 regulates a plasma membrane pool of phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate required for regulated endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 2003;16:647–59.
Aicart-Ramos C, He SD, Land M, Rubin CS. A novel conserved domain mediates dimerization of protein kinase D (PKD) isoforms: dimerization is essential for PKD-dependent regulation of secretion and innate immunity. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:23516–31.
McDonald PC, Chafe SC, Dedhar S. Overcoming hypoxia-mediated tumor progression: combinatorial approaches targeting pH regulation, angiogenesis and immune dysfunction. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016;4:27–32.
Marchiq I, Pouysségur J. Hypoxia, cancer metabolism and the therapeutic benefit of targeting lactate/H(+) symporters. J Mol Med. (Berl) 2016;94:155–71.
Pouysségur J, Dayan F, Mazure NM. Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature 2006;441:437–43.
Semenza GL. Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics. Oncogene 2010;29:625–34.
Kroemer G, Pouyssegur J. Tumor cell metabolism: cancer’s Achilles’ heel. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:472–82.
George KM, Frantz MC, Bravo-Altamirano K, Lavalle CR, Tandon M, Leimgruber S, et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of PKD inhibitors. Pharmaceutics 2011;3:186–28.
Monovich L, Vega RB, Meredith E, Miranda K, Rao C, Capparelli M, et al. A novel kinase inhibitor establishes a predominant role for protein kinase D as a cardiac class IIa histone deacetylase kinase. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:631–37.
Meredith EL, Beattie K, Burgis R, Capparelli M, Chapo J, Dipietro L, et al. Identiication of potent and selective amidobipyridyl inhibitors of protein kinase D. J Med Chem. 2010;53:5422–38.
Meredith EL, Ardayfio O, Beattie K, Dobler MR, Enyedy I, Gaul C, et al. Identification of orally available naphthyridine protein kinase D inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2010;53:5400–21.
Gamber GG, Meredith E, Zhu Q, Yan W, Rao C, Capparelli M, et al. 3,5-diarylazoles as novel and selective inhibitors of protein kinase D. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011;21:1447–51.
Tandon M, Salamoun JM, Carder EJ, Farber E, Xu S, Deng F, et al. SD-208, a novel protein kinase D inhibitor, blocks prostate cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth in vivo by inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest. PLoS ONE 2015;10:e0119346.
Evans IM, Bagherzadeh A, Charles M, Raynham T, Ireson C, Boakes A, et al. Characterization of the biological effects of a novel protein kinase D inhibitor in endothelial cells. Biochem J. 2010;429:565–72.
Tandon M, Johnson J, Li Z, Xu S, Wipf P, Wang QJ. New pyrazolopyrimidine inhibitors of protein kinase d as potent anticancer agents for prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013;8:e75601.
Moulick K, Ahn JH, Zong H, Rodina A, Cerchietti L, Gomes DaGama EM, et al. Affinity-based proteomics reveal cancer-specific networks coordinated by Hsp90. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7:818–26.
Wang Y, Trepel JB, Neckers LM, Giaccone G. STA-9090, a small molecule HSP90 inhibitor for the potential treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2010;11:1466–76.
Jackson LN, Li J, Chen LA, Townsend CM, Evers BM. Overexpression of wild-type PKD2 leads to increased proliferation and invasion of BON endocrine cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;348:945–49.
Biswas MH, Du C, Zhang C, Straubhaar J, Languino LR, Balaji KC. Protein kinase D1 inhibits cell proliferation through matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:2095–100.
Du C, Zhang C, Hassan S, Biswas MH, Balaji KC. Protein kinase D1 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through phosphorylation of snail. Cancer Res. 2010;70:7810–19.
Huck B, Duss S, Hausser A, Olayioye MA. Elevated protein kinase D3 (PKD3) expression supports proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer cells and contributes to mTORC1-S6K1 pathway activation. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:3138–47.
Funding
This work was supported by the German Research Foundation (grants AZ.96/1-1 and AZ.96/1-3 to NA, grant SE.676/10-1 to TS), the German Cancer Aid (grant 109373 to TS), FP7 grant 259770 – LUNGTARGET (to JVL and TS) and IWT - Agentschap voor Innovatie door Wetenschap en Technologie (to MC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azoitei, N., Cobbaut, M., Becher, A. et al. Protein kinase D2: a versatile player in cancer biology. Oncogene 37, 1263–1278 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0052-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0052-8
This article is cited by
-
RGCC-mediated PLK1 activity drives breast cancer lung metastasis by phosphorylating AMPKα2 to activate oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid oxidation
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
Potential role for protein kinase D inhibitors in prostate cancer
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
Test yourself: soft tissue mass in elbow
Skeletal Radiology (2023)