Abstract
There is increasing interest in developing drugs that act at α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) to treat alcohol use disorder. The smoking cessation agent varenicline, a partial agonist of α4β2 nAChRs, reduces alcohol intake, but its use can be limited by side effects at high therapeutic doses. There are two stoichiometric forms of α4β2 nAChRs, (α4)3(β2)2 and (α4)2(β2)3. Here we investigated the hypothesis that NS9283, a positive allosteric modulator selective for the (α4)3(β2)2 form, reduces ethanol consumption. NS9283 increased the potency of varenicline to activate and desensitize (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs in vitro without affecting other known targets of varenicline. In male and female C57BL/6J mice, NS9283 (10 mg/kg) reduced ethanol intake in a two-bottle choice, intermittent drinking procedure without affecting saccharin intake, ethanol-induced incoordination or ethanol-induced loss of the righting reflex. Subthreshold doses of NS9283 (2.5 mg/kg) plus varenicline (0.1 mg/kg) synergistically reduced ethanol intake in both sexes. Finally, despite having no aversive valence of its own, NS9283 enhanced ethanol-conditioned place aversion. We conclude that compounds targeting the (α4)3(β2)2 subtype of nAChRs can reduce alcohol consumption, and when administered in combination with varenicline, may allow use of lower varenicline doses to decrease varenicline side effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a major public health problem and currently, only three drugs are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for AUD treatment: disulfiram, naltrexone and acamprosate. Unfortunately, these medications have limited efficacy [1], so there is a need to identify new medications for AUD. The most effective FDA-approved smoking cessation aid, varenicline, has recently gained attention as a treatment for AUD. It reduces ethanol intake in rodents and decreases drinking and alcohol craving in human smokers and nonsmokers [2,3,4]. Since the efficacy of varenicline correlates with its plasma level [5], higher doses may increase its efficacy. However, dosing is limited by dose-dependent side effects such as insomnia, irritability and gastrointestinal symptoms [5,6,7].
Varenicline is a partial agonist for α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). At high prescribed doses, it activates two other subtypes of nAChRs (α3β4 and α7) as well as 5HT3A receptors, which may explain several of its side effects [8, 9]. Understanding mechanisms by which α4β2 nAChRs reduce ethanol consumption could help in rational design of compounds with improved efficacy and side effect profiles. α4β2 nAChRs are pentamers that assemble in two subunit stoichiometries: (α4)2(β2)3 and (α4)3(β2)2. Both bind similar agonists [10], but show differences in agonist sensitivity, calcium permeability and rates of desensitization [11, 12]. Pharmacological and genetic studies suggest that α4β2 nAChRs contribute to ethanol drinking and ethanol’s sedative-hypnotic effects [13,14,15]. However, it is unknown if one or both of the stoichiometric forms are involved in these responses. Here we used an (α4)3(β2)2-selective ligand, NS9283 [16, 17], to study the role of this subtype in ethanol drinking and intoxication. NS9283 potentiates agonist activation of nAChR but alone does not activate these receptors [18]. Our results suggest that drugs targeting (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs could be useful for treating AUD and could be combined with low doses of varenicline to reduce varenicline side effects.
Methods and materials
Animals
Adult female and male C57BL/6J and DBA/2 mice (The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME) were housed in a reverse light−dark circle room with food and water available ad libitum. Mice were at least 9 weeks old at the start of experimental procedures. We used C57BL/6J mice for all experiments except place conditioning experiments for which we used DBA/2J mice. All procedures were conducted in accordance with guidelines of the National Institute of Health and The University of Texas at Austin Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Chemicals
NS9283 was synthesized as described [19] or purchased from Tocris Bioscience (Minneapolis, MN, USA). For cell assays, NS9283 stock was prepared at 10 mM in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and diluted in assay buffer before each experiment. For animal experiments, NS9283 was solubilized in a 5:1 solution of Tween-80 and DMSO with sonication, and then diluted to the final concentration in sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS; v/v/v DMSO/Tween-80/PBS: 2/10/88). Varenicline stock was prepared in water, aliquoted and frozen at −80 °C before use. NS9283 was injected intraperitoneally at 10 ml/kg and varenicline at 5 ml/kg. Control vehicle was injected in the same volume. Doses were calculated from the base forms of the drugs. All chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) unless otherwise noted.
nAChR functional assay in vitro
cDNA encoding the human 5HT3A receptor was obtained from hORFeome V7.1 (catalog ID 3803). The 5HT3A cDNA was amplified using primers GTCGACAAGCTTGCCACCATGCTGCTGTGGGTCCAGC and CAGCGTGGATCCTCAAGCGTACTGCCAGATGG. The 1437 bp DNA fragment was purified and digested by HindIII and BamHI, and then cloned into pcDNA3.0 (+) hygro plasmid. Cells (8 × 106) were transfected with 20 μg cDNA and 50 μl Fugene HD (Promega) in a 10-cm dish. HEK293 cells stably expressing human (α4)2(β2)3, (α4)3(β2)2, α3β4 or α7 nAChRs were generated previously [20, 21]. The effects of varenicline on activating and desensitizing nicotinic and 5HT3A receptors were evaluated by a fluorescent-based assay using a FlexStation 3 (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA) as previously described [17]. All assays were performed at 37 °C in triplicate or quadruplicate.
Pharmacokinetics
NS9383 was formulated in DMSO:Tween-80:saline (ratio 2:10:88) and administered i.p. at 2.5 mg/kg (n = 3) or 10 mg/kg (n = 3). Blood and brains were collected 1 h later. Blood samples were centrifuged to generate plasma. Each brain was disrupted in potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4; 2 µl per 1 mg tissue) on ice using brief sonication pulses. Compounds were detected with an ABSciex 5500 Triple Quad LC-MS/MS (SCIEX, Redwood City, CA, USA) using an MRM(+) method: (249/130, m/z), with carbamazepine (238/195.1, m/z) as an internal standard.
Intermittent access ethanol consumption
Male and female mice were singly housed and allowed to habituate to their individual cages containing two bottles of tap water for 5 days. Mice were then given access to one bottle of water and one bottle of ethanol at increasing concentrations of 3, 6, and 10% (v/v) over three drinking sessions, and, thereafter, were provided a bottle of water and a bottle containing 15% or 20% (v/v) ethanol every Monday, Wednesday and Friday [22]. Ethanol bottles were placed in the home cage at 1300 hours and left in place for 24 h. Bottle positions were alternated before each ethanol session to account for side preferences. A drip cage was present during each experiment to control for spillage from ethanol and water bottles. Intraperitoneal injections began after ethanol consumption stabilized (i.e., <10% change over three consecutive ethanol-drinking sessions). Mice were habituated using one sham injection and two vehicle injections. Drugs or vehicle were administered 40 min before presentation of ethanol bottles using a within-subjects, counterbalanced design. One male mouse was excluded from the analysis because it consumed less than 1 g/kg in 3 h before drug testing. All results are from at least two cohorts of mice.
Saccharin consumption
After 6 days of habituation to the reverse light−dark circle, ethanol-naïve male mice were provided one bottle of tap water and one bottle of 0.015% saccharin (0.075 mM). Bottles were weighed daily and positions were alternated to account for side preferences. Mice were habituated to intraperitoneal injections as described. Vehicle or drugs were administered using a within-subjects, counterbalanced design.
Locomotor activity
Nine-week-old ethanol-naïve male mice were injected with vehicle, NS9283 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) or NS9283 with varenicline (2.5/0.1 mg/kg, i.p.) using a between-subjects, counterbalanced design. After injection, each mouse was placed in an open-field arena (Med Associates Inc) for 60 min with lights off and the total distance traveled was recorded.
Elevated plus maze
Four days after the locomotor test, mice were administered vehicle, NS9283 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) or NS9283 with varenicline (2.5/0.1 mg/kg, i.p.) using a between-subjects, counterbalanced design 40 min before being placed in an elevated plus maze (EPM) for 5 min [23] in a quiet room under dim light. Open and closed arm entries and time spent in the closed arms were measured using Datavyu (http://datavyu.org/). Arm entries were scored when all four paws and the full body of the mouse crossed the entrance of an arm.
Ethanol-induced loss of the righting reflex (LORR)
Four days after the EPM test, mice were injected with vehicle or NS9283 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) and placed back in their home cages. Forty minutes later, mice were administered ethanol (3.6 g/kg i.p.) and placed individually on their backs. The time at which the mouse lost the righting reflex was recorded. The mouse was considered to have recovered when it could right itself three times within 30 s.
Accelerating rotarod
Three weeks after the LORR test, male mice were trained for three sessions over 2 days on a rotarod apparatus that was set to accelerate from 0 to 15 rpm over 210 s. Mice were tested in up to five trials per session and needed to successfully stay on the rotarod for the entire 210 s in at least one of the trials to be included in the study. In order to determine if the drug treatments affected rotarod performance, we injected mice with vehicle or test drugs (varenicline, NS9283 or varenicline with NS9283) using a between-subjects, counterbalanced design and 30 min later tested them on the rotarod for up to three trials before the ethanol injection. Vehicle and drug treatment tests were separated by 1 week. Two vehicle-treated mice and one NS9283 (2.5 mg/kg) plus varenicline (0.1 mg/kg)-treated mouse were excluded due to failure to stay on the rotarod for 210 s in one of the three trails. Forty-five minutes after drug administration, mice received ethanol (2 g/kg i.p.) and were tested again on the rotarod at 15-min intervals. Mice that could remain longer than 5 s on the rotarod, 5 min after ethanol injection, were excluded from the study because of a presumed failed ethanol injection. We recorded the latency to fall off the rotarod.
Place conditioning with NS9283
Naïve mice were habituated to the vivarium for 1 week and then trained in a standard conditioned place preference (CPP) procedure. CPP was conducted using open-field activity chambers (ENV-510, Med Associates) equipped with infrared beams, two-chamber place preference inserts, and a software interface (activity monitor, Med Associates). On day 1, drug naïve mice were allowed to freely explore both chambers for 30 min. Each mouse was then randomly assigned in a counterbalanced fashion to receive NS9283 or vehicle in either chamber using an unbiased design. Mice were trained in twice daily 30-min sessions with 4 h between each session. Half of the mice received two conditioning sessions of NS9283 on days 2 and 4 and the other half on days 3 and 5. On day 6, mice were allowed free access to both chambers for 30 min to record time spent in NS9283- and vehicle-paired sides.
Place conditioning with ethanol
Ethanol CPP and conditioned place aversion (CPA) were performed using DBA/2J mice [24] and an unbiased and counterbalanced design as previously described [25], with the two-chambered apparatus described above. On day 1, ethanol-naïve mice were allowed to freely explore both chambers for 30 min. The use of ethanol as an unconditioned stimulus to generate either a place preference or place aversion is dependent upon the timing of the ethanol injection relative to conditioned stimulus exposure [24]. For place preference experiments, mice were injected with ethanol or saline immediately prior to being placed in the conditioning chamber. For place aversion experiments, mice were injected with ethanol or saline immediately after being removed from the conditioning chamber. The ethanol-paired compartment was assigned randomly across subjects. Mice were trained in eight daily 5-min sessions, with saline on days 2, 4, 6 and 8, and ethanol on days 3, 5, 7 and 9. On day 10, mice were administered NS9283 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle in the home cage and then 40 min later were allowed free access to both chambers for 30 min to record time spent in ethanol- and saline-paired sides.
Ethanol clearance
One week after the LORR or accelerating rotarod tests, mice were injected intraperitoneally with vehicle, NS9283 (10 mg/kg), or NS9283 (2.5 mg/kg) plus varenicline (0.1 mg/kg) using a between-subjects, counterbalanced design. After 40 min, mice were injected with 4 g/kg ethanol intraperitoneally. At 30, 60, 120, and 180 min after injection, 20 μl of tail vein blood were collected from each mouse. Blood ethanol concentrations were measured using a β-NAD enzymatic assay [26].
Statistical analysis
For the nAChR functional assay, the concentration−response relationship was analyzed by a nonlinear least squares curve fitting method using Kaleidagraph (Abelbeck/Synergy, Reading, PA): I(x) = Imax [xnHill/(xnHill + θ50nHill)], where I(x) is the peak current measured at the drug concentration x, Imax is the maximum current peak at the saturating drug concentration relative to ACh, θ50 (EC50 for activation or IC50 for desensitization) is the drug concentration required to achieve half of the maximum response, and nHill is the Hill coefficient. In vivo results were analyzed using Prism 7.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA). Data were first tested for normality using a D’Agostino−Pearson omnibus normality test, and if normally distributed were analyzed by a two-tailed t test or ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett’s or Sidak’s multiple comparisons tests. Data for rotarod tests were compared by calculating the area over the curve (AOC) and below the maximal time of 210 s for each treatment condition and comparing results by two-tailed t tests. Data that were not normally distributed were log transformed before parametric analysis. All data are presented as mean ± SE values.
Results
NS9283 increases potency and selectivity of varenicline in vitro
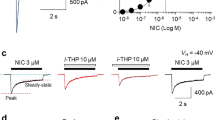
We first investigated whether NS9283 selectively increases actions of varenicline at (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs and not at other receptors known to be affected by varenicline. Varenicline was tenfold more potent at desensitizing than activating both (α4)3(β2)2 and (α4)2(β2)3 nAChRs (Fig. 1, Supplementary Table 1), which is consistent with varenicline being a partial agonist. NS9283 increased the potency of varenicline by 235-fold in activating (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs, and to a lesser extent (tenfold) in desensitizing them. NS9283 also slightly increased varenicline efficacy. NS9283 had no effect on other nAChRs [(α4)2(β2)3, α3β4, α7] or 5HT3A receptors. These results indicate that NS9283 selectively increases the effects of low concentrations of varenicline on (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs.
NS9283 selectively promotes activation and desensitization of (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs by varenicline. The different receptor subtypes were expressed in HEK293 cells and assayed with a membrane potential sensitive dye. In activation experiments, varenicline was added acutely whereas in desensitization studies, varenicline was preincubated with cells for 6 h prior to acute application of ACh [300 μM for (α4)3(β2)2, 10 μM for (α4)2(β2)3, 300 μM for α3β4, 100 μM for α7]. For desensitization studies with cells expressing 5HT3A receptors, varenicline was preincubated for 1 h prior to acute application of 5HT (3 μM). These preincubation times were chosen to ensure complete desensitization without significant upregulation of nAChRs or downregulation of 5HT3A receptors
NS9283 alone or in combination with a low-dose of varenicline reduces ethanol consumption
We next investigated whether NS9283 could reduce alcohol consumption by using a two-bottle choice, every other day access procedure, which produces high levels of intake in C57BL/6J mice [22]. We found that over 24 h male mice consumed ~14 g/kg and female mice consumed ~22 g/kg of 15% (v/v) ethanol, whereas male mice consumed ~15 g/kg and female mice consumed ~27 g/kg of 20% (v/v) ethanol (Supplementary Fig. 1). Because the half-lives of NS9283 (0.5 h) and varenicline (1.4 h) in mice are short [18, 27], we measured their effects 3 h after the beginning of an ethanol-drinking session. To determine amounts of NS9283 in plasma and brain during these studies we measured drug levels 1 h following i.p. administration of 2.5 mg/kg (n = 3) or 10 mg/kg (n = 3) NS9283. The 2.5 mg/kg dose resulted in levels of 1.94 ± 0.72 µM in plasma and 2.05 ± 0.48 µM in brain. The 10 mg/kg dose resulted in levels of 4.51 ± 1.42 µM in plasma and 3.49 ± 0.98 µM in brain.
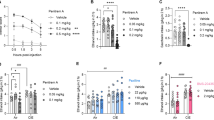
Since NS9283 potentiates activation of (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs by endogenous ACh [18], we investigated whether it reduced ethanol drinking when administered alone (Fig. 2). NS9283 reduced 3-h ethanol (15% v/v) consumption [Ftreatment (2, 68) = 8.601, p = 0.0005; Ftreatment × sex (2, 68) = 2.064, p = 0.1348] and preference [Ftreatment (2, 68) = 12.75, p < 0.0001; Ftreatment × sex (2, 68) = 0.587, p = 0.5588] in male and female mice. Consumption was reduced by the 5 mg/kg dose (p = 0.0014) and by the 10 mg/kg dose (p = 0.0026) compared with vehicle (Sidak’s test). Preference was also reduced by the 5 mg/kg dose (p = 0.0004) and by the 10 mg/kg dose (p = < 0.0001) compared with vehicle (Sidak’s test). Ethanol consumption was greater in female than in male mice [Fsex (1, 34) = 17, p = 0.0002], while ethanol preference was similar in both sexes [Fsex (1, 34) = 2.337, p = 0.1356]. NS9283 also increased water intake, and this effect did not differ by sex [Ftreatment (2, 68) = 6.753, p = 0.0021; Fsex (1, 34) = 0.3596, p = 0.5527; Ftreatment × sex (2, 68) = 0.04726, p = 0.9539]. Water intake was increased by both the 5 mg/kg (p = 0.0046) and the 10 mg/kg dose (p = 0.0097) compared with vehicle (Sidak’s test).
We next investigated whether subthreshold doses of varenicline and NS9283 could synergistically reduce ethanol intake (Fig. 3). Although varenicline (0.1 mg/kg) and NS9283 (2.5 mg/kg) did not alter 3-h ethanol intake when given individually, together they reduced ethanol consumption in both sexes [Ftreatment (3, 69) = 5.988; p = 0.0011; Fsex (1, 23) = 11.57, p = 0.0024; Ftreatment × sex (3,69) = 1.063, p = 0.3705; p = 0.0016 for varenicline + NS9283 compared with vehicle control, Sidak’s test]. None of these treatments altered ethanol preference [Ftreatment (3, 69) = 1.124; p = 0.3455; Fsex (1, 23) = 6.196, p = 0.0205; Ftreatment x sex (3,69) = 0.8717, p = 0.4601] or water intake [Ftreatment (3, 69) = 0.9016; p = 0.4450; Fsex (1, 23) = 5.704, p = 0.0255; Ftreatment x sex (3,69) = 0.5939, p = 0.6211].
Low doses of NS9283 and varenicline reduce ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice in the first 3 h of a drinking session. At low doses, NS9283 plus varenicline reduced 20% (v/v) ethanol consumption (a) in both male (n = 12) and female (n = 13) mice, without altering ethanol preference (b) or water intake (c)
NS9283 does not alter ethanol intoxication or clearance
Varenicline can reduce ethanol drinking if administered at a high dose [28]. It may reduce ethanol intake, in part, because it enhances the intoxicating effects of ethanol [15, 29]. Therefore, we investigated whether the combination of low-dose varenicline and NS9283 alters ethanol intoxication (Fig. 4). Ethanol-induced incoordination on the accelerating rotarod was prolonged by administration of 2 mg/kg varenicline (AOC = 17,208 ± 1301 min-s) compared with vehicle [AOC = 11,700 ± 933 min-s; t(20) = 3.52, p = 0.0022; Fig. 4a]. Administration of 2 mg/kg varenicline also increased the duration of the ethanol-induced LORR [t (18) = 4.6, p = 0.0002; Fig. 4d]. Administration of 10 mg/kg NS9283 alone did not alter the effect of ethanol on rotarod performance [vehicle AOC = 12,670 ± 1132, n = 9; NS9283 AOC = 12,401 ± 1038, n = 11; t(18) = 0.1749, p = 0.8631; Fig. 4b] or the duration of the ethanol-induced LORR [t(11) = 0.012; p = 0.990; Fig. 4e]. The combination of 2.5 mg/kg NS9283 and 0.1 mg/kg varenicline also did not alter the effect of ethanol on rotarod performance [vehicle AOC = 13,723 ± 1021, n = 9; NS9283 + varenicline AOC = 12,249 ± 1183, n = 10; t(17) = 0.9329, p = 0.5841; Fig. 4c] or the duration of the ethanol-induced LORR [t(12) = 0.254, p = 0.804; Fig. 4f].
NS9283 does not alter ethanol intoxication or clearance in C57BL/6J mice. In rotarod experiments, varenicline (2 mg/kg) decreased the latency to fall after injection of 2 g/kg ethanol, unlike NS9283 (10 mg/kg) or low-dose NS9283 and varenicline (a−c, n = 9−12). Varenicline increased the duration of LORR after injection of 3.6 g/kg ethanol (d, n = 9−11, ***p = 0.0002), unlike 10 mg/kg NS9283 (e, n = 6−7) or a combination of low doses of NS9283 and varenicline (f, n = 7). NS9283 alone (10 mg/kg) or in combination (2.5 mg/kg) with varenicline (0.1 mg/kg) did not alter ethanol clearance (g, h, n = 8−9)
Varenicline does not alter ethanol metabolism [29]. Similarly, neither NS9283 nor low-dose NS9283 plus varenicline changed ethanol clearance [NS9283: Ftime × treatment (3, 42) = 0.61, p = 0.61; Combination: Ftime × treatment (3, 48) = 0.89, p = 0.45; Fig. 4g, h].
NS9283 does not affect saccharin consumption, anxiety, or locomotor activity
Because varenicline reduces saccharin consumption in mice [29], we tested the effects of NS9283 alone or in combination with varenicline on saccharin consumption. Unlike varenicline, NS9283 (10 mg/kg) alone had no effect on saccharin consumption, but the combination of a low dose of NS9283 (2.5 mg/kg) plus varenicline (0.1 mg/kg) decreased saccharin consumption [t(9) = 2.607, p = 0.028, n = 10; Supplementary Fig. 2a, b].
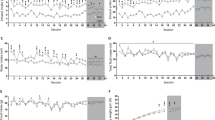
In the intermittent drinking protocol, drinking days alternate with days of withdrawal, which can be anxiogenic [30]. To examine whether NS9283 might decrease ethanol intake because it is anxiolytic, we measured its effect on anxiety-like behavior. NS9283 alone or in combination with varenicline did not alter the percentage of time or distance traveled in the center of the open field (Supplementary Fig. 2c−f), or the percentage of entries into or time spent in the open arms of the EPM (Supplementary Fig. 2h−k), indicating that NS9283 is not anxiolytic.
We also considered whether NS9283 reduced ethanol intake by causing sedation. To examine this possibility, we examined activity in the open field and EPM. NS9283 alone or in combination with varenicline also did not reduce the total distance traveled in an open field (Supplementary Fig. 2f−g) or the number of closed arm entries in the elevated plus maze (Supplementary Fig. 2l−m), indicating that the effects of NS9283 on ethanol intake were not due to impaired locomotion.
NS9283 enhances ethanol place aversion
One behavioral mechanism by which NS9283 could reduce ethanol intake is by reducing the rewarding or accentuating aversive responses to ethanol. We first investigated whether NS9283 itself was rewarding. C57BL/6J mice were conditioned with NS9283, and despite some variability in preference, on average there was no evidence for NS9283-conditioned place preference [t(13) = 0.3975, p = 0.6975, n = 14; Fig. 5a]. We next measured the effect of NS9283 on ethanol CPP and CPA. Since C57BL/6J show weak place conditioning to ethanol [31], we used DBA/2J mice instead, because they show robust place conditioning responses to ethanol [24]. NS9283 did not alter the expression of ethanol-induced CPP [Fdrug (1,22) = 0.804, p = 0.3797; Ftest (1,22) = 40.34; p < 0.0001; Fdrug × test (1,22) = 1.671, p = 02095; Fig. 5b]. However, NS9283 enhanced expression of CPA for ethanol [Fdrug (1,16) = 5.448, p = 0.033; Ftest (1,16) = 96.72; p < 0.0001; Fdrug × test (1,16) = 8.032, p = 0.0120; Fig. 5c].
NS9283 increases ethanol-conditioned place aversion. a NS9283 (10 mg/kg) alone did not induce CPP or CPA in C57BL/6J mice. b Following conditioning sessions with 1.5 g/kg ethanol, male DBA/2J mice in both vehicle and NS9283 (10 mg/kg) treatment groups developed CPP for ethanol and the magnitude of CPP was not different between these treatment groups. **p = 0.0034, ****p < 0.0001 by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. c Following conditioning sessions with 2.0 g/kg ethanol, male DBA/2J mice in vehicle and NS9283 (10 mg/kg) treatment groups developed CPA for ethanol, and the magnitude of CPA was greater in the group treated with NS9283. CPA data were not initially normally distributed and therefore were normalized by log transformation prior to ANOVA. **p = 0.0022, ***p = 0.0003, ****p < 0.0001 by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test
Discussion
NS9283 reduces ethanol consumption
We used NS9283, an agonist that is selective for (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs, to study the role of these receptors in ethanol-related behaviors. NS9283 increased the potency of varenicline’s effects on (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs but not on other nAChRs or 5-HT3A receptors activated by high doses of varenicline. When administered in vivo, a high dose of NS9283 (10 mg/kg) as well as subthreshold doses of NS9283 (2.5 mg/kg) plus varenicline (0.1 mg/kg) reduced ethanol consumption in mice to an extent similar to that reported previously for 2 mg/kg varenicline alone [28]. Although varenicline can increase ethanol-induced incoordination and LORR duration [15, 29], we found that NS9283 alone, or in combination with 0.1 mg/kg varenicline did not alter these signs of ethanol intoxication. NS9283 appeared to accentuate the memory of ethanol’s aversive properties, without altering memory of ethanol’s rewarding effects. NS9283 did not alter ethanol-induced sedation, anxiety-like behavior or ethanol clearance. These findings suggest that (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs are a potential drug target for reducing ethanol consumption.
NS9283 pharmacokinetics
Administration of 2.5 or 10 mg/kg NS9283 led to brain concentrations that are well above the EC50 (0.42 µM) measured for enhancement of nicotine-induced Ca2+ responses in HEK293 cells expressing α4β2 nAChRs [18]. Although the drinking study lasted 3 h, it is important to note that the 3-h time point reflects the end of the study. Since the half-life of NS9283 in mice is 30 min [18], then at 2 h of drinking (~2.5 h after injection) the brain concentration would have been ~0.44 µM (reduced by 3 half-lives) which is at the EC50 in HEK293 cells [18], and at 3 h would have been ~0.11 µM. Therefore, we think that there was sufficient NS9283 in the brain during most of the 3-h drinking session to have affected ethanol consumption via an action at α4β2 receptors. However, the effect was small and we were not able to test a higher NS9283 dose because of its limited solubility.
Targeting (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs to reduce ethanol consumption and avoid varenicline side effects
Previous pharmacological and genetic manipulations of α4β2 nAChRs have yielded inconsistent results about their role in ethanol consumption. Studies using traditional agonists and antagonists suggest that activation of α4β2 nAChRs reduces ethanol intake in rats and mice [14, 32,33,34]. However, global knockout of the α4 subunit decreased ethanol intake and reward in mice [13, 35]. Mice with a gain-of-function mutation in α4 showed no difference in ethanol consumption compared with wild-type littermates [13], but were more sensitive to the rewarding effect of ethanol [35] and to varenicline-mediated decreases in ethanol intake [13]. Although these pharmacological and genetic manipulations are predicted to target both stoichiometric forms of α4β2 nAChRs, it is not known if both forms would be altered to a similar extent. Additionally, gene targeted mice carry mutations throughout development that likely evoke compensatory changes and complicate interpretation of behavioral results. Our novel findings using a selective positive modulator indicate that activation of (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs is sufficient to reduce ethanol consumption.
Studies using pharmacological agents and knockout mice suggest that activating α4-containing nAChRs increases the hypnotic effect of ethanol [15, 34]. However, we found that selective activation of (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs does not increase ethanol-induced ataxia or LORR. This result suggests that activation of (α4)2(β2)3, rather than (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs, is responsible for varenicline enhancement of ethanol intoxication. This speculation is supported by evidence that sazetidine, a full agonist for (α4)2(β2)3 nAChRs, with minimal activity at (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs, is more effective than nicotine or varenicline at prolonging the ethanol-induced LORR [15]. Although a recent clinical study found that varenicline did not make alcoholics feel more intoxicated, the sample size may have been too small to detect this side effect [36].
Nausea and sleep disorders are the two major side effects that limit clinical use of varenicline [6]. Nausea may result from activation of 5HT3A receptors, which occurs at varenicline doses that activate (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs. This side effect is unlikely with NS9283 because we showed that it did not affect 5HT3A receptors in vitro, and it also did not cause vomiting in ferrets administered a nAChR partial agonist [37]. Inhibiting α7 nAChRs may disrupt sleep [38, 39], but we found that NS9283 did not alter activation or desensitization of α7 nAChRs. Thus, it is possible that NS9283 used with low doses of varenicline might reduce the likelihood of both sleep disorders and nausea that are associated with higher varenicline doses. Because NS9283 does not affect α3β4 nAChRs, its use may also avoid other varenicline-induced side effects such as constipation, urinary retention and dryness of the mouth and skin [40].
NS9283 limitations
The selectivity of NS9283 makes it a lead compound for future study, but we also note its limitations. Firstly, NS9283 not only potentiates activation, but also increases desensitization of (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs. However, its effect on activation is 23-fold greater than its effect on desensitization, suggesting that NS9283 primarily alters ethanol intake via activation of (α4)3(β2)2 nAChRs. Secondly, mice metabolize NS9283 rapidly and the human pharmacokinetic profile of NS9283 is not yet known. Thirdly, use of NS9283 may not overcome all side effects associated with varenicline such as its inhibitory effect on intake of sweet (e.g. saccharin-containing) solutions. Finally, in addition to (α4)3(β2)2, NS9283 potentiates (α2)3(β2)2 and (α2)3(β4)2 nAChRs [18]. Although we cannot exclude the possibility that NS9283 reduced ethanol consumption by acting at these other subtypes, we note that expression of the α2 subunit is low in rodents [41] and studies of β4-null mice suggest that these receptors are not involved in ethanol drinking or intoxication [42, 43].
Summary
In conclusion, we found evidence that suggests promoting activation of the (α4)3(β2)2 stoichiometric form of α4β2 nAChRs is a new strategy to reduce ethanol consumption, and when used in combination with the partial α4β2 agonist varenicline, may allow use of lower varenicline doses, thereby mitigating side effects. Ongoing work is directed towards improving the half-lives of (α4)3(β2)2 selective drugs and investigating effects of single and repeated dosing on ethanol consumption in binge and dependent drinking behavioral models.
Funding and disclosure
This work was supported by The University of Texas at Austin start-up funds to ROM, DA030929 to TMK and JL, and NSF fellowship DGE 1110007 to MBP. The authors declare no competing interests.
References
Litten RZ, Egli M, Heilig M, Cui C, Fertig JB, Ryan ML. et al. Medications development to treat alcohol dependence: a vision for the next decade. Addict Biol. 2012;17:513–27.
Litten RZ, Wilford BB, Falk DE, Ryan ML, Fertig JB. Potential medications for the treatment of alcohol use disorder: an evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety. Subst Abus. 2016;37:286–98.
McKee SA, Harrison EL, O’Malley SS, Krishnan-Sarin S, Shi J, Tetrault JM. et al. Varenicline reduces alcohol self-administration in heavy-drinking smokers. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;66:185–90.
O’Malley SS, Zweben A, Fucito LM, Wu R, Piepmeier ME, Ockert DM, et al. Effect of varenicline combined with medical management on alcohol use disorder with comorbid cigarette smoking: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:129–38.
Verplaetse TL, Pittman BP, Shi JM, Tetrault JM, Coppola S, McKee SA. Effect of lowering the dose of varenicline on alcohol self-administration in drinkers with alcohol use disorders. J Addict Med. 2016;10:166–73.
Litten RZ, Ryan ML, Fertig JB, Falk DE, Johnson B, Dunn KE. et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial assessing the efficacy of varenicline tartrate for alcohol dependence. J Addict Med. 2013;7:277–86.
Anthenelli RM, Benowitz NL, West R, St Aubin L, McRae T, Lawrence D. et al. Neuropsychiatric safety and efficacy of varenicline, bupropion, and nicotine patch in smokers with and without psychiatric disorders (EAGLES): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Lancet. 2016;387:2507–20.
Campling BG, Kuryatov A, Lindstrom J. Acute activation, desensitization and smoldering activation of human acetylcholine receptors. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e79653
Lummis SC, Thompson AJ, Bencherif M, Lester HA. Varenicline is a potent agonist of the human 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor. J Pharm Exp Ther. 2011;339:125–31.
Wang J, Lindstrom J. Orthosteric and allosteric potentiation of heteromeric neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175:1805–21.
Nelson ME, Kuryatov A, Choi CH, Zhou Y, Lindstrom J. Alternate stoichiometries of alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;63:332–41.
Tapia L, Kuryatov A, Lindstrom J. Ca2+ permeability of the (alpha4)3(beta2)2 stoichiometry greatly exceeds that of (alpha4)2(beta2)3 human acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;71:769–76.
Hendrickson LM, Zhao-Shea R, Pang X, Gardner PD, Tapper AR. Activation ofalpha4* nAChRs is necessary and sufficient for varenicline-induced reduction of alcohol consumption. J Neurosci. 2010;30:10169–76.
Hendrickson LM, Zhao-Shea R, Tapper AR. Modulation of ethanol drinking-in-the-dark by mecamylamine and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology. 2009;204:563–72.
Slater CA, Jackson A, Muldoon PP, Dawson A, O’Brien M, Soll LG. et al. Nicotine enhances the hypnotic and hypothermic effects of alcohol in the mouse. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016;40:62–72.
Harpsoe K, Ahring PK, Christensen JK, Jensen ML, Peters D, Balle T. Unraveling the high- and low-sensitivity agonist responses of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Neurosci. 2011;31:10759–66.
Wang J, Kuryatov A, Sriram A, Jin Z, Kamenecka TM, Kenny PJ, et al. An accessory agonist binding site promotes activation of alpha4beta2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:13907–18.
Timmermann DB, Sandager-Nielsen K, Dyhring T, Smith M, Jacobsen AM, Nielsen EO, et al. Augmentation of cognitive function by NS9283, a stoichiometry-dependent positive allosteric modulator of alpha2- and alpha4-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;167:164–82.
Jin Z, Khan P, Shin Y, Wang J, Lin L, Cameron MD, et al. Synthesis and activity of substituted heteroaromatics as positive allosteric modulators for alpha4beta2alpha5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014;24:674–78.
Wang J, Kuryatov A, Jin Z, Norleans J, Kamenecka TM, Kenny PJ, et al. A novel alpha2/alpha4 subtype-selective positive allosteric modulator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors acting from the C-tail of an alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:28834–46.
Kuryatov A, Mukherjee J, Lindstrom J. Chemical chaperones exceed the chaperone effects of RIC-3 in promoting assembly of functional alpha7 AChRs. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e62246.
Hwa LS, Chu A, Levinson SA, Kayyali TM, DeBold JF, Miczek KA. Persistent escalation of alcohol drinking in C57BL/6J mice with intermittent access to 20% ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011;35:1938–47.
Chen J, Rinaldo L, Lim SJ, Young H, Messing RO, Choi DS. The type 1 equilibrative nucleoside transporter regulates anxiety-like behavior in mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2007;6:776–83.
Cunningham CL, Gremel CM, Groblewski PA. Drug-induced conditioned place preference and aversion in mice. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:1662–70.
Newton PM, Messing RO. Increased sensitivity to the aversive effects of ethanol in PKCepsilon null mice revealed by place conditioning. Behav Neurosci. 2007;121:439–42.
Zapata A, Gonzales RA, Shippenberg TS. Repeated ethanol intoxication induces behavioral sensitization in the absence of a sensitized accumbens dopamine response in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31:396–405.
Obach RS, Reed-Hagen AE, Krueger SS, Obach BJ, O’Connell TN, Zandi KS, et al. Metabolism and disposition of varenicline, a selective alpha4beta2 acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, in vivo and in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006;34:121–30.
Kamens HM, Andersen J, Picciotto MR. Modulation of ethanol consumption by genetic and pharmacological manipulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in mice. Psychopharmacology. 2010;208:613–26.
Kamens HM, Andersen J, Picciotto MR. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist varenicline increases the ataxic and sedative-hypnotic effects of acute ethanol administration in C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010;34:2053–60.
Kang S, Li J, Zuo W, Fu R, Gregor D, Krnjevic K, et al. Ethanol withdrawal drives anxiety-related behaviors by reducing M-type potassium channel activity in the Lateral Habenula. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017;42:1813–24.
Cunningham CL, Niehus DR, Malott DH, Prather LK. Genetic differences in the rewarding and activating effects of morphine and ethanol. Psychopharmacology. 1992;107:385–93.
Steensland P, Simms JA, Holgate J, Richards JK, Bartlett SE. Varenicline, an alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, selectively decreases ethanol consumption and seeking. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:12518–23.
Sotomayor-Zarate R, Gysling K, Busto UE, Cassels BK, Tampier L, Quintanilla ME. Varenicline and cytisine: two nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands reduce ethanol intake in University of Chile bibulous rats. Psychopharmacology. 2013;227:287–98.
Dawson A, Miles MF, Damaj MI. The beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit differentially influences ethanol behavioral effects in the mouse. Alcohol. 2013;47:85–94.
Liu L, Hendrickson LM, Guildford MJ, Zhao-Shea R, Gardner PD, Tapper AR. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors containing the alpha4 subunit modulate alcohol reward. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;73:738–46.
Verplaetse TL, Pittman BP, Shi JM, Tetrault JM, Coppola S, McKee SA. Effect of varenicline combined with high-dose alcohol on craving, subjective intoxication, perceptual motor response, and executive cognitive function in adults with alcohol use disorders: preliminary findings. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016;40:1567–76.
Lee CH, Zhu C, Malysz J, Campbell T, Shaughnessy T, Honore P, et al. alpha4beta2 neuronal nicotinic receptor positive allosteric modulation: an approach for improving the therapeutic index of alpha4beta2 nAChR agonists in pain. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;82:959–66.
Pocivavsek A, Baratta AM, Mong JA, Viechweg SS. Acute kynurenine challenge disrupts sleep-wake architecture and impairs contextual memory in adult rats. Sleep. 2017;40:zsx141.
Ni KM, Hou XJ, Yang CH, Dong P, Li Y, Zhang Y, et al. Selectively driving cholinergic fibers optically in the thalamic reticular nucleus promotes sleep. Elife. 2016;5:e10382.
Shytle RD, Penny E, Silver AA, Goldman J, Sanberg PR. Mecamylamine (Inversine): an old antihypertensive with new research directions. J Hum Hypertens. 2002;16:453–57.
Wang J, Kuryatov A, Lindstrom J. Expression of clonedalpha6* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2015;96(Pt B):194–204.
Kamens HM, Silva C, McCarthy R, Cox RJ, Ehringer MA. No evidence of a role of the beta4 subunit of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in alcohol-related behaviors. BMC Res Notes. 2017;10:151.
Patkar OL, Belmer A, Tarren JR, Holgate JY, Bartlett SE. The effect of varenicline on binge-like ethanol consumption in mice is beta4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-independent. Neurosci Lett. 2016;633:235–39.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Rajani Maiya for advice on experiments, Dr. Jody Mayfield for editing the manuscript, and Kristina Tipton for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Blasio, A., Chapman, H.L. et al. Promoting activity of (α4)3(β2)2 nicotinic cholinergic receptors reduces ethanol consumption. Neuropsychopharmacol. 45, 301–308 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-019-0475-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-019-0475-8