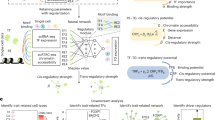
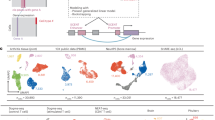
Abstract
Opioid use disorder is a highly heterogeneous disease driven by a variety of genetic and environmental risk factors which have yet to be fully elucidated. Opioid overdose, the most severe outcome of opioid use disorder, remains the leading cause of accidental death in the United States. We interrogated the effects of opioid overdose on the brain using ChIP-seq to quantify patterns of H3K27 acetylation in dorsolateral prefrontal cortical neurons isolated from 51 opioid-overdose cases and 51 accidental death controls. Among opioid cases, we observed global hypoacetylation and identified 388 putative enhancers consistently depleted for H3K27ac. Machine learning on H3K27ac patterns predicted case-control status with high accuracy. We focused on case-specific regulatory alterations, revealing 81,399 hypoacetylation events, uncovering vast inter-patient heterogeneity. We developed a strategy to decode this heterogeneity based on convergence analysis, which leveraged promoter-capture Hi-C to identify five genes over-burdened by alterations in their regulatory network or “plexus”: ASTN2, KCNMA1, DUSP4, GABBR2, ENOX1. These convergent loci are enriched for opioid use disorder risk genes and heritability for generalized anxiety, number of sexual partners, and years of education. Overall, our multi-pronged approach uncovers neurobiological aspects of opioid use disorder and captures genetic and environmental factors perpetuating the opioid epidemic.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
ChIP and RNA seq data are available through dbgap accession number: phs002724.v1.p1.
Code availability
Code for the machine learning and VEL analyses are available through: https://github.com/corradin-lab/DLPFC-opioid-overdose. Convergence analysis code is available through: https://axiotl.com/ and https://convergence.axiotl.com/.
References
Center for Disease Control. Increase in fatal drug overdoses across the United States driven by synthetic opioids before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Publication Number CDCHAN-00438 December. Available at https://emergency cdc gov/han/2020/han00438 asp (Accessed February 14, 2021). 2020.
Zhou H, Rentsch CT, Cheng Z, Kember RL, Nunez YZ, Sherva RM, et al. Association of OPRM1 functional coding variant with opioid use disorder: A genome-wide association study. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020; Available from: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.1206.
Hancock DB, Markunas CA, Bierut LJ, Johnson EO. Human genetics of addiction: New insights and future directions. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2018;20:8.
Sullivan PF, Agrawal A, Bulik CM, Andreassen OA, Børglum AD, Breen G, et al. Psychiatric genomics: An update and an agenda. AJP 2018;175:15–27.
Koob GF, Volkow ND. Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010;35:217–38.
Browne CJ, Godino A, Salery M, Nestler EJ. Epigenetic mechanisms of opioid addiction. Biol Psychiatry 2020;87:22–33.
Goldstein RZ, Volkow ND. Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: Neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12:652–69.
Maurano MT, Humbert R, Rynes E, Thurman RE, Haugen E, Wang H, et al. Systematic localization of common disease-associated variation in regulatory DNA. Science 2012;337:1190–5. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222794.
Trynka G, Sandor C, Han B, Xu H, Stranger BE, Liu XS, et al. Chromatin marks identify critical cell types for fine mapping complex trait variants. Nat Genet. 2013;45:124–30.
Finucane HK, Bulik-Sullivan B, Gusev A, Trynka G, Reshef Y, Loh P-R, et al. Partitioning heritability by functional annotation using genome-wide association summary statistics. Nat Genet. 2015;47:1228–35.
Jung I, Schmitt A, Diao Y, Lee AJ, Liu T, Yang D, et al. A compendium of promoter-centered long-range chromatin interactions in the human genome. Nat Genet. 2019;51:1442–9.
Akhtar-Zaidi B, Cowper-Sal-lari R, Corradin O, Saiakhova A, Bartels CF, Balasubramanian D, et al. Epigenomic enhancer profiling defines a signature of colon cancer. Science 2012;336:736–9.
Cohen AJ, Saiakhova A, Corradin O, Luppino JM, Lovrenert K, Bartels CF, et al. Hotspots of aberrant enhancer activity punctuate the colorectal cancer epigenome. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1–13.
Morrow JJ, Bayles I, Funnell APW, Miller TE, Saiakhova A, Lizardo MM, et al. Positively selected enhancer elements endow osteosarcoma cells with metastatic competence. Nat Med. 2018;24:176–85.
Blackwood CA, McCoy MT, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL. Oxycodone self-administration activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase/ mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase (MAPK-MSK) signaling pathway in the rat dorsal striatum. Sci Rep. 2021;11:2567.
Qiao X, Zhu Y, Dang W, Wang R, Sun M, Chen Y, et al. Dual-specificity phosphatase 15 (DUSP15) in the nucleus accumbens is a novel negative regulator of morphine-associated contextual memory. Addict Biol. 2021;26:e12884.
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD, Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, et al. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W90–7.
Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, Duan Q, Wang Z, Meirelles GV, et al. Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinforma. 2013;14:128.
Al-Hasani R, Bruchas MR. Molecular mechanisms of opioid receptor-dependent signaling and behavior. Anesthesiology 2011;115:1363–81.
Brynildsen JK, Mace KD, Cornblath EJ, Weidler C, Pasqualetti F, Bassett DS, et al. Gene coexpression patterns predict opiate-induced brain-state transitions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:19556–65.
Chen T, Guestrin C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2016. 785–94. (KDD ’16).
McInnes L, Healy J, Melville J. UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction. arXiv [stat.ML]. 2018. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03426.
Watanabe K, Taskesen E, van Bochoven A, Posthuma D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1826.
Sallari RC, Sinnott-Armstrong NA, French JD, Kron KJ, Ho J, Moore JH, et al. Convergence of dispersed regulatory mutations predicts driver genes in prostate cancer. biorxrv. 2017; Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/097451.
Bailey SD, Desai K, Kron KJ, Mazrooei P, Sinnott-Armstrong NA, Treloar AE, et al. Noncoding somatic and inherited single-nucleotide variants converge to promote ESR1 expression in breast cancer. Nat Genet. 2016;48:1260–6.
Lutz P-E, Almeida D, Filliol D, Jollant F, Kieffer BL, Turecki G. Increased functional coupling of the mu opioid receptor in the anterior insula of depressed individuals. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021;46:920–7.
Mendez EF, Wei H, Hu R, Stertz L, Fries GR, Wu X, et al. Angiogenic gene networks are dysregulated in opioid use disorder: evidence from multi-omics and imaging of postmortem human brain. Mol Psychiatry. 2021; Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01259-y.
Martins SS, Fenton MC, Keyes KM, Blanco C, Zhu H, Storr CL. Mood and anxiety disorders and their association with non-medical prescription opioid use and prescription opioid-use disorder: longitudinal evidence from the National Epidemiologic Study on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Vol. 42, Psychological Med. 2012. 1261–72. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291711002145.
Polimanti R, Walters RK, Johnson EC, McClintick JN, Adkins AE, Adkins DE, et al. Leveraging genome-wide data to investigate differences between opioid use vs. opioid dependence in 41,176 individuals from the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/765065.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:15545–50.
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson K-F, Subramanian A, Sihag S, Lehar J, et al. PGC-1α-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet. 2003;34:267–73.
Bettinger JC, Davies AG. The role of the BK channel in ethanol response behaviors: Evidence from model organism and human studies. Front Physiol. 2014;5:346.
Wolen AR, Phillips CA, Langston MA, Putman AH, Vorster PJ, Bruce NA, et al. Genetic dissection of acute ethanol responsive gene networks in prefrontal cortex: Functional and mechanistic implications. PLoS One. 2012;7:e33575.
Abdul Rahman NZ, Greenwood SM, Brett RR, Tossell K, Ungless MA, Plevin R, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase Phosphatase-2 deletion impairs synaptic plasticity and hippocampal-dependent memory. J Neurosci. 2016;36:2348–54.
Cui W-Y, Seneviratne C, Gu J, Li MD. Genetics of GABAergic signaling in nicotine and alcohol dependence. Hum Genet. 2012;131:843–55.
Ribeiro AF, Correia D, Torres AA, Boas GRV, Rueda AVL, Camarini R, et al. A transcriptional study in mice with different ethanol-drinking profiles: Possible involvement of the GABA(B) receptor. Pharm Biochem Behav. 2012;102:224–32.
Behesti H, Fore TR, Wu P, Horn Z, Leppert M, Hull C, et al. ASTN2 modulates synaptic strength by trafficking and degradation of surface proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E9717–26.
Inoue R, Nishizawa D, Hasegawa J, Nakayama K, Fukuda K-I, Ichinohe T, et al. Effects of rs958804 and rs7858836 single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the ASTN2 gene on pain-related phenotypes in patients who underwent laparoscopic colectomy and mandibular sagittal split ramus osteotomy. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2021;41:82–90.
Hillis SD, Anda RF, Felitti VJ, Marchbanks PA. Adverse childhood experiences and sexual risk behaviors in women: A retrospective cohort study. Fam Plann Perspect. 2001;33:206–11.
Montez JK, Hayward MD. Cumulative childhood adversity, educational attainment, and active life expectancy among U.S. adults. Demography 2014;51:413–35.
Murthy S, Gould E. How early life adversity influences defensive circuitry. Trends Neurosci. 2020;43:200–12.
Levis SC, Bentzley BS, Molet J, Bolton JL, Perrone CR, Baram TZ, et al. On the early life origins of vulnerability to opioid addiction. Mol Psychiatry. 2019; Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-019-0628-5.
Enoch M-A. The role of early life stress as a predictor for alcohol and drug dependence. Psychopharmacology 2011;214:17–31.
Widom CS, Marmorstein NR, White HR. Childhood victimization and illicit drug use in middle adulthood. Psychol Addict Behav. 2006;20:394–403.
Vaiserman AM, Koliada AK. Early-life adversity and long-term neurobehavioral outcomes: Epigenome as a bridge? Hum Genomics 2017;11:34.
Barnett Burns S, Almeida D, Turecki G. The Epigenetics of Early Life Adversity: Current Limitations and Possible Solutions. In: Grayson DR, editor. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science. Academic Press; 2018. 343–425.
Leza L, Siria S, López-Goñi JJ, Fernández-Montalvo J. Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) and substance use disorder (SUD): A scoping review. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021;221:108563.
Dasgupta N, Beletsky L, Ciccarone D. Opioid crisis: No easy fix to its social and economic determinants. Am J Public Health. 2018;108:182–6.
Altekruse SF, Cosgrove CM, Altekruse WC, Jenkins RA, Blanco C. Socioeconomic risk factors for fatal opioid overdoses in the United States: Findings from the Mortality Disparities in American Communities Study (MDAC). PLoS One 2020;15:e0227966.
Case A, Deaton A, Stone AA. Decoding the mystery of American pain reveals a warning for the future. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:24785–9.
Kundakovic M, Jiang Y, Kavanagh DH, Dincer A, Brown L, Pothula V, et al. Practical guidelines for high-resolution epigenomic profiling of nucleosomal histones in postmortem human brain tissue. Biol. Psychiatry 2017;81:162–70.
Martin M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011;17:10–2.
Li H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv [q-bio.GN]. 2013. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1303.3997.
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009;25:2078–9.
Zhang Y, Liu T, Meyer CA, Eeckhoute J, Johnson DS, Bernstein BE, et al. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 2008;9:R137.
Ramírez F, Ryan DP, Grüning B, Bhardwaj V, Kilpert F, Richter AS, et al. deepTools2: A next generation web server for deep-sequencing data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W160–5.
Thorvaldsdóttir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform. 2013;14:178–92.
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, et al. Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004;5:R80.
Carroll TS, Liang Z, Salama R, Stark R, de Santiago I. Impact of artifact removal on ChIP quality metrics in ChIP-seq and ChIP-exo data. Front Genet. 2014;5:75.
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014;30:2114–20.
Patro R, Duggal G, Love MI, Irizarry RA, Kingsford C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat Methods 2017;14:417–9.
Srivastava A, Malik L, Sarkar H, Zakeri M, Almodaresi F, Soneson C, et al. Alignment and mapping methodology influence transcript abundance estimation. Genome Biol. 2020;21:239.
Love MI, Hogenesch JB, Irizarry RA. Modeling of RNA-seq fragment sequence bias reduces systematic errors in transcript abundance estimation. Nat Biotechnol. 2016;34:1287–91.
Soneson C, Love MI, Robinson MD. Differential analyses for RNA-seq: Transcript-level estimates improve gene-level inferences. F1000Res. 2015;4. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc4712774/.
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15:550.
Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, Jaffe AE, Storey JD. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics 2012;28:882–3.
Lundberg SM, Erion G, Chen H, DeGrave A, Prutkin JM, Nair B, et al. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for Trees. Nat Mach Intell 2020;2:56–67.
Bulik-Sullivan BK, Loh P-R, Finucane HK, Ripke S, Yang J. Schizophrenia working group of the psychiatric genomics consortium, et al. LD Score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet. 2015;47:291–5.
1000 Genomes Project Consortium, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Garrison EP, Kang HM, et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015;526:68–74.
Demontis D, Walters RK, Martin J, Mattheisen M, Als TD, Agerbo E, et al. Discovery of the first genome-wide significant risk loci for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Nat Genet. 2019;51:63–75.
Zhou H, Sealock JM, Sanchez-Roige S, Clarke T-K, Levey DF, Cheng Z, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of problematic alcohol use in 435,563 individuals yields insights into biology and relationships with other traits. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23:809–18.
Boraska V, Franklin CS, Floyd JAB, Thornton LM, Huckins LM, Southam L, et al. A genome-wide association study of anorexia nervosa. Mol Psychiatry 2014;19:1085–94.
Stahl EA, Breen G, Forstner AJ, McQuillin A, Ripke S, Trubetskoy V, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 30 loci associated with bipolar disorder. Nat Genet. 2019;51:793–803.
Speliotes EK, Willer CJ, Berndt SI, Monda KL, Thorleifsson G, Jackson AU, et al. Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat Genet. 2010;42:937–48.
Dubois PCA, Trynka G, Franke L, Hunt KA, Romanos J, Curtotti A, et al. Multiple common variants for celiac disease influencing immune gene expression. Nat Genet. 2010;42:295–302.
Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, Duerr RH, McGovern DP, Hui KY, et al. Host–microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2012;491:119–24.
Howard DM, Adams MJ, Clarke T-K, Hafferty JD, Gibson J, Shirali M, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:343–52.
Manning AK, Hivert M-F, Scott RA, Grimsby JL, Bouatia-Naji N, Chen H, et al. A genome-wide approach accounting for body mass index identifies genetic variants influencing fasting glycemic traits and insulin resistance. Nat Genet. 2012;44:659–69.
Levey DF, Gelernter J, Polimanti R, Zhou H, Cheng Z, Aslan M, et al. Reproducible genetic risk loci for anxiety: Results from ∼200,000 participants in the Million Veteran Program. AJP. 2020;177:223–32.
Allen HL, Estrada K, Lettre G, Berndt SI, Weedon MN, Rivadeneira F, et al. Hundreds of variants clustered in genomic loci and biological pathways affect human height. Nature 2010;467:832–8.
Okbay A, Baselmans BML, De Neve J-E, Turley P, Nivard MG, Fontana MA, et al. Genetic variants associated with subjective well-being, depressive symptoms, and neuroticism identified through genome-wide analyses. Nat Genet. 2016;48:624–33.
Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature 2014;511:421–7.
Liu M, Jiang Y, Wedow R, Li Y, Brazel DM, Chen F, et al. Association studies of up to 1.2 million individuals yield new insights into the genetic etiology of tobacco and alcohol use. Nat Genet. 2019;51:237–44.
Teslovich TM, Musunuru K, Smith AV, Edmondson AC, Stylianou IM, Koseki M, et al. Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature 2010;466:707–13.
Bradfield JP, Qu H-Q, Wang K, Zhang H, Sleiman PM, Kim CE, et al. A genome-wide meta-analysis of six type 1 diabetes cohorts identifies multiple associated Loci. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002293.
Rietveld CA, Medland SE, Derringer J, Yang J, Esko T, Martin NW, et al. GWAS of 126,559 individuals identifies genetic variants associated with educational attainment. Science 2013;340:1467–71.
Okbay A, Beauchamp JP, Fontana MA, Lee JJ, Pers TH, Rietveld CA, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 74 loci associated with educational attainment. Nature 2016;533:539–42.
Linnér RK, Biroli P, Kong E, Meddens SFW, Wedow R, Fontana MA, et al. Genome-wide association analyses of risk tolerance and risky behaviors in over 1 million individuals identify hundreds of loci and shared genetic influences. Nat Genet 2019;51:245–57.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the families of the subjects used in this study. We would also like to acknowledge the teams of technicians at the Miami Brain Endowment Bank. This work was supported by NIH National Institute of Drug Abuse R01 DA043980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This work was conceptualized and written by PCS, SA, EOJ, DCM, DBH, RS, and OC. ChIP-seq and RNA-seq experiments were completed by SA, BSK, GBH, LC, KL, MI, HC, and CFB. Data analysis was performed by, OC, RS, ATH, BCQ, KL, and YS. Discussion and feedback were provided by CH and BEG.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Peter Scacheri received compensation as a consultant for Kronos Bio.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corradin, O., Sallari, R., Hoang, A.T. et al. Convergence of case-specific epigenetic alterations identify a confluence of genetic vulnerabilities tied to opioid overdose. Mol Psychiatry 27, 2158–2170 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01477-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01477-y
This article is cited by
-
Epigenetic alterations identify a confluence of genetic vulnerabilities tied to opioid overdose
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Single nucleus transcriptomics of ventral midbrain identifies glial activation associated with chronic opioid use disorder
Nature Communications (2023)