Abstract
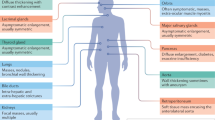
Erdheim–Chester disease (ECD) is a rare non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis with a putative neoplastic and inflammatory nature. The disease is driven by mutations in proto-oncogenes such as BRAF and MEK, while immune-mediated mechanisms contribute to disease development and progression. The clinical presentation of ECD is highly heterogeneous, ranging from smouldering unifocal forms to multiorgan life-threatening disease. Almost any organ can be involved, but the most common lesions include long-bone involvement, retroperitoneal fibrosis, interstitial lung disease, pericardial and myocardial infiltration, CNS, retro-orbital, and large-vessel involvement. These manifestations may mimic those of neoplastic and systemic immune-mediated diseases. Overlap with these conditions represents an emerging challenge for the clinician. A variety of treatments are efficacious for ECD, targeting both the MAPK-pathway and the immune-mediated pathomechanisms. The traditional approach is based on immunomodulatory agents (interferon-α), but recent alternatives—including anti-cytokine therapies (IL1- and TNFα-blockers) and immunosuppressants (mTOR-inhibitors)—showed promising results. However, since the detection of MAPK pathway activation in most patients and the dramatic efficacy of BRAF and MEK inhibitors, these targeted treatments represent the first-line approach in patients with severe disease forms. High rates of radiologic responses do not often mean clinical remission, especially for CNS involvement, which often results in chronic disability. This review will outline the main clinical features of ECD, with emphasis on the emerging challenges in pathogenesis and management, and on the role of recent targeted approaches.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emile J-F, Abla O, Fraitag S, Horne A, Haroche J, Donadieu J, et al. Revised classification of histiocytoses and neoplasms of the macrophage-dendritic cell lineages. Blood. 2016;127:2672–81.
Haroche J, Cohen-Aubart F, Rollins BJ, Donadieu J, Charlotte F, Idbaih A, et al. Histiocytoses: emerging neoplasia behind inflammation. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:e113–25.
Haroche J, Charlotte F, Arnaud L, von Deimling A, Hélias-Rodzewicz Z, Hervier B, et al. High prevalence of BRAF V600E mutations in Erdheim–Chester disease but not in other non-Langerhans cell histiocytoses. Blood. 2012;120:2700–3.
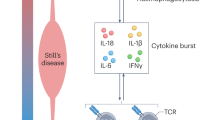
Stoppacciaro A, Ferrarini M, Salmaggi C, Colarossi C, Praderio L, Tresoldi M, et al. Immunohistochemical evidence of a cytokine and chemokine network in three patients with Erdheim–Chester disease: implications for pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:4018–22.
Arnaud L, Gorochov G, Charlotte F, Lvovschi V, Parizot C, Larsen M, et al. Systemic perturbation of cytokine and chemokine networks in Erdheim–Chester disease: a single-center series of 37 patients. Blood. 2011;117:2783–90.
Haroche J, Cohen-Aubart F, Emile J-F, Maksud P, Drier A, Tolédano D, et al. Reproducible and sustained efficacy of targeted therapy with vemurafenib in patients with BRAF V600E-mutated Erdheim–Chester disease. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:411–8.
Diamond EL, Durham BH, Ulaner GA, Drill E, Buthorn J, Ki M, et al. Efficacy of MEK inhibition in patients with histiocytic neoplasms. Nature. 2019;567:521–4.
Goyal G, Heaney ML, Collin M, Cohen Aubart F, Vaglio A, Durham B, et al. Erdheim–Chester disease: consensus recommendations for the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment in the molecular era. Blood. 2020;135:1929–45.
Hervier B, Haroche J, Arnaud L, Charlotte F, Donadieu J, Neel A, et al. Association of both Langerhans cell histiocytosis and Erdheim–Chester disease linked to the BRAFV600E mutation. Blood. 2014;124:1119–26.
Estrada-Veras JI, O’Brien KJ, Boyd LC, Dave RH, Durham BH, Xi L, et al. The clinical spectrum of Erdheim–Chester disease: an observational cohort study. Blood Adv. 2017;1:357–66.
Badalian-Very G, Vergilio J-A, Degar BA, MacConaill LE, Brandner B, Calicchio ML, et al. Recurrent BRAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2010;116:1919–23.
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–54.
Melloul S, Hélias-Rodzewicz Z, Cohen-Aubart F, Charlotte F, Fraitag S, Terrones N, et al. Highly sensitive methods are required to detect mutations in histiocytoses. Haematologica. 2019;104:e97–9.
Emile J-F, Diamond EL, Hélias-Rodzewicz Z, Cohen-Aubart F, Charlotte F, Hyman DM, et al. Recurrent RAS and PIK3CA mutations in Erdheim–Chester disease. Blood. 2014;124:3016–9.
Diamond EL, Durham BH, Haroche J, Yao Z, Ma J, Parikh SA, et al. Diverse and targetable kinase alterations drive histiocytic neoplasms. Cancer Disco. 2016;6:154–65.
Gianfreda D, Nicastro M, Galetti M, Alberici F, Corradi D, Becchi G, et al. Sirolimus plus prednisone for Erdheim–Chester disease: an open-label trial. Blood. 2015;126:1163–71.
Durham BH, Lopez Rodrigo E, Picarsic J, Abramson D, Rotemberg V, De Munck S, et al. Activating mutations in CSF1R and additional receptor tyrosine kinases in histiocytic neoplasms. Nat Med. 2019;25:1839–42.
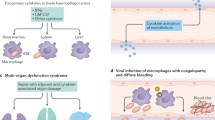
Durham BH, Roos-Weil D, Baillou C, Cohen-Aubart F, Yoshimi A, Miyara M, et al. Functional evidence for derivation of systemic histiocytic neoplasms from hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Blood. 2017;130:176–80.
Milne P, Bigley V, Bacon CM, Néel A, McGovern N, Bomken S, et al. Hematopoietic origin of Langerhans cell histiocytosis and Erdheim–Chester disease in adults. Blood. 2017;130:167–75.
Berres ML, Lim KP, Peters T, Price J, Takizawa H, Salmon H, et al. BRAF-V600E expression in precursor versus differentiated dendritic cells defines clinically distinct LCH risk groups. J Exp Med. 2014;211:669–83.
Mass E, Jacome-Galarza CE, Blank T, Lazarov T, Durham BH, Ozkaya N, et al. A somatic mutation in erythro-myeloid progenitors causes neurodegenerative disease. Nature. 2017;549:389–93.
Haroche J, Amoura Z, Wechsler B, Veyssier-Belot C, Charlotte F, Piette J-C. Maladie d’Erdheim–Chester. La Presse Médicale. 2007;36:1663–8.
Dagna L, Girlanda S, Langheim S, Rizzo N, Bozzolo EP, Sabbadini MG, et al. Erdheim–Chester disease: report on a case and new insights on its immunopathogenesis. Rheumatology. 2010;49:1203–6.
Pacini G, Cavalli G, Tomelleri A, De Luca G, Pacini G, Ferrarini M, et al. The fibrogenic chemokine CCL18 is associated with disease severity in Erdheim–Chester disease. Oncoimmunology. 2018;7:e1440929.
Cangi MG, Biavasco R, Cavalli G, Grassini G, Dal-Cin E, Campochiaro C, et al. BRAF V600E -mutation is invariably present and associated to oncogene-induced senescence in Erdheim–Chester disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1596–602.
Michaloglou C, Vredeveld LCW, Soengas MS, Denoyelle C, Kuilman T, van der Horst CMAM, et al. BRAFE600-associated senescence-like cell cycle arrest of human naevi. Nature. 2005;436:720–4.
Haroche J, Amoura Z, Trad SG, Wechsler B, Cluzel P, Grenier PA, et al. Variability in the efficacy of interferon-α in Erdheim–Chester disease by patient and site of involvement: results in eight patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:3330–6.
Cohen-Aubart F, Emile J-F, Carrat F, Helias-Rodzewicz Z, Taly V, Charlotte F, et al. Phenotypes and survival in Erdheim–Chester disease: results from a 165-patient cohort. Am J Hematol. 2018;93:E114–7.
Tran T-A, Fabre M, Pariente D, Craiu I, Haroche J, Charlotte F, et al. Erdheim–Chester disease in childhood: a challenging diagnosis and treatment. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2009;31:782–6.
Tezol O, Citak EC, Ayhan YS, Balci Y, Koc ZP, Yuyucu Karabulut Y. Effective high-dose interferon-α therapy in a 13-year-old girl with Erdheim–Chester disease. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2020;42:326–31.
Hao X, Feng R, Bi Y, Liu Y, Li C, Lu T, et al. Dramatic efficacy of dabrafenib in Erdheim–Chester disease (ECD): a pediatric patient with multiple large intracranial ECD lesions hidden by refractory Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2019;23:48–53.
Picarsic J, Pysher T, Zhou H, Fluchel M, Pettit T, Whitehead M, et al. BRAF V600E mutation in Juvenile Xanthogranuloma family neoplasms of the central nervous system (CNS-JXG): a revised diagnostic algorithm to include pediatric Erdheim–Chester disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7:168.
Cavalli G, Guglielmi B, Berti A, Campochiaro C, Sabbadini MG, Dagna L. The multifaceted clinical presentations and manifestations of Erdheim–Chester disease: comprehensive review of the literature and of 10 new cases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72:1691–5.
Arnaud L, Hervier B, Néel A, Hamidou MA, Kahn J-E, Wechsler B, et al. CNS involvement and treatment with interferon-α are independent prognostic factors in Erdheim–Chester disease: a multicenter survival analysis of 53 patients. Blood. 2011;117:2778–82.
Lachenal F, Cotton F, Desmurs-Clavel H, Haroche J, Taillia H, Magy N, et al. Neurological manifestations and neuroradiological presentation of Erdheim–Chester disease: report of 6 cases and systematic review of the literature. J Neurol. 2006;253:1267–77.
Bhatia A, Hatzoglou V, Ulaner G, Rampal R, Hyman DM, Abdel-Wahab O, et al. Neurologic and oncologic features of Erdheim–Chester disease: a 30-patient series. Neuro-oncology 2020; https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noaa008.
Parks NE, Goyal G, Go RS, Mandrekar J, Tobin WO. Neuroradiologic manifestations of Erdheim–Chester disease. Neurol Clin Pr. 2018;8:15–20.
Cives M, Simone V, Rizzo FM, Dicuonzo F, Cristallo Lacalamita M, Ingravallo G, et al. Erdheim–Chester disease: a systematic review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015;95:1–11.
Drier A, Haroche J, Savatovsky J, Godenèche G, Dormont D, Chiras J, et al. Cerebral, facial, and orbital involvement in Erdheim–Chester disease: CT and MR imaging findings. Radiology. 2010;255:586–94.
Diamond EL, Hatzoglou V, Patel S, Abdel-Wahab O, Rampal R, Hyman DM, et al. Diffuse reduction of cerebral grey matter volumes in Erdheim–Chester disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016;11:109.
Haroche J, Cohen Aubart F, Amoura Z. Erdheim–Chester disease. Blood. 2020;135:1311–8.
Merritt H, Pfeiffer ML, Richani K, Phillips ME. Erdheim–Chester disease with orbital involvement: case report and ophthalmic literature review. Orbit. 2016;35:221–6.
Marinelli JP, Peters PA, Vaglio A, Van Gompel JJ, Lane JI, Carlson ML. Skull base manifestations of Erdheim–Chester disease: a case series and systematic review. Neurosurgery. 2019;85:E693–701.
Courtillot C, Laugier Robiolle S, Cohen Aubart F, Leban M, Renard-Penna R, Drier A, et al. Endocrine manifestations in a monocentric cohort of 64 patients with Erdheim–Chester disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:305–13.
Sedrak P, Ketonen L, Hou P, Guha-Thakurta N, Williams MD, Kurzrock R, et al. Erdheim–Chester disease of the central nervous system: new manifestations of a rare disease. Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:2126–31.
Herndon J, Nadeau AM, Davidge-Pitts CJ, Young WF, Bancos I. Primary adrenal insufficiency due to bilateral infiltrative disease. Endocrine. 2018;62:721–8.
Gianfreda D, Palumbo AA, Rossi E, Buttarelli L, Manari G, Martini C, et al. Cardiac involvement in Erdheim–Chester disease: an MRI study. Blood. 2016;128:2468–71.
Vaglio A, Corradi D, Maestri R, Callegari S, Buzio C, Salvarani C. Pericarditis heralding Erdheim–Chester disease. Circulation. 2008;118:e511–2.
Gupta A, Kelly B, McGuigan JE. Erdheim–Chester disease with prominent pericardial involvement: clinical, radiologic, and histologic findings. Am J Med Sci. 2002;324:96–100.
Diamond EL, Dagna L, Hyman DM, Cavalli G, Janku F, Estrada-Veras J, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and clinical management of Erdheim–Chester disease. Blood. 2014;124:483–92.
Haroche J, Cluzel P, Toledano D, Montalescot G, Touitou D, Grenier PA, et al. Cardiac involvement in Erdheim–Chester disease: magnetic resonance and computed tomographic scan imaging in a monocentric series of 37 patients. Circulation. 2009;119:e597–8.
Berti A, Ferrarini M, Ferrero E, Dagna L. Cardiovascular manifestations of Erdheim–Chester disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015;33:S-155-63.
Vaideeswar P, Vaz WF. Erdheim–Chester disease with extensive coronary arterial involvement. Pathology. 2011;43:375–8.
Haroche J, Amoura Z, Dion E, Wechsler B, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Cacoub P, et al. Cardiovascular Involvement, an overlooked feature of Erdheim–Chester disease: report of 6 new cases and a literature review. Medicine. 2004;83:371–92.
Villatoro-Villar M, Bold MS, Warrington KJ, Crowson CS, Goyal G, Shah M, et al. Arterial involvement in Erdheim–Chester disease: a retrospective cohort study. Medicine. 2018;97:e13452.
Vaglio A, Pipitone N, Salvarani C. Chronic periaortitis: a large-vessel vasculitis? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23:1–6.
Arnaud L, Pierre I, Beigelman-Aubry C, Capron F, Brun A-L, Rigolet A, et al. Pulmonary involvement in Erdheim–Chester disease: a single-center study of thirty-four patients and a review of the literature. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:3504–12.
Brun A-L, Touitou-Gottenberg D, Haroche J, Toledano D, Cluzel P, Beigelman-Aubry C, et al. Erdheim–Chester disease: CT findings of thoracic involvement. Eur Radio. 2010;20:2579–87.
Mirmomen SM, Sirajuddin A, Nikpanah M, Symons R, Paschall AK, Papageorgiou I, et al. Thoracic involvement in Erdheim–Chester disease: computed tomography imaging findings and their association with the BRAFV600E mutation. Eur Radio. 2018;28:4635–42.
Haroutunian SG, O’Brien KJ, Estrada-Veras JI, Yao J, Boyd LC, Mathur K, et al. Clinical and histopathologic features of interstitial lung disease in Erdheim–Chester disease. J Clin Med. 2018;7:243.
Nikpanah M, Kim L, Mirmomen SM, Symons R, Papageorgiou I, Gahl WA, et al. Abdominal involvement in Erdheim–Chester disease (ECD): MRI and CT imaging findings and their association with BRAFV600E mutation. Eur Radio. 2018;28:3751–9.
Vaglio A, Maritati F. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. JASN. 2016;27:1880–9.
Purysko AS, Westphalen AC, Remer EM, Coppa CP, Leão Filho HM, Herts BR. Imaging manifestations of hematologic diseases with renal and perinephric involvement. RadioGraphics. 2016;36:1038–54.
Yelfimov DA, Lightner DJ, Tollefson MK. Urologic manifestations of Erdheim–Chester disease. Urology. 2014;84:218–21.
Haroche J, Amoura Z, Touraine P, Seilhean D, Graef C, Birmelé B, et al. Bilateral adrenal infiltration in Erdheim–Chester disease. Report of seven cases and literature review. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:2007–12.
Dion E, Graef C, Miquel A, Haroche J, Wechsler B, Amoura Z, et al. Bone involvement in Erdheim–Chester disease: imaging findings including periostitis and partial epiphyseal involvement. Radiology. 2006;238:632–9.
Chasset F, Barete S, Charlotte F, Cohen-Aubart F, Arnaud L, Le Pelletier F, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of Erdheim–Chester disease (ECD): Clinical, pathological, and molecular features in a monocentric series of 40 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:513–20.
Goyal G, Ravindran A, Liu Y, He R, Shah MV, Bennani NN, et al. Bone marrow findings in Erdheim–Chester disease: increased prevalence of chronic myeloid neoplasms. Haematologica. 2020;105:e84–6.
Shah MV, Call TG, Hook CC, Johnston PB, Letendre L, Colgan JP, et al. Clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome of patients with Erdheim–Chester disease: the mayo clinic experience. Blood. 2014;124:1405.
Sheu S-Y. Erdheim–Chester disease: case report with multisystemic manifestations including testes, thyroid, and lymph nodes, and a review of literature. J Clin Pathol. 2004;57:1225–8.
Roverano S, Gallo J, Ortiz A, Migliore N, Eletti M, Paira S. Erdheim–Chester disease: description of eight cases. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35:1625–9.
Cohen Aubart F, Emile JF, Carrat F, Charlotte F, Benameur N, Donadieu J, et al. Targeted therapies in 54 patients with Erdheim–Chester disease, including follow-up after interruption (the LOVE study). Blood. 2017;130:1377–80.
Razanamahery J, Diamond EL, Cohen-Aubart F, Plate K-H, Lourida G, Charlotte F, et al. Erdheim–Chester disease with concomitant Rosai–Dorfman like lesions: a distinct entity mainly driven by MAP2K1. Haematologica. 2020;105:e5–8.
Papo M, Diamond EL, Cohen-Aubart F, Emile J-F, Roos-Weil D, Gupta N, et al. High prevalence of myeloid neoplasms in adults with non–Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2017;130:1007–13.
Roeser A, Cohen-Aubart F, Breillat P, Miyara M, Emile J-F, Charlotte F, et al. Autoimmunity associated with Erdheim–Chester disease improves with BRAF/MEK inhibitors. Haematologica. 2019;104:e502–5.
Gianfreda D, Musetti C, Nicastro M, Maritati F, Cobelli R, Corradi D, et al. Erdheim–Chester disease as a mimic of IgG4-related disease: a case report and a review of a single-center cohort. Medicine. 2016;95:e3625.
García-Gómez FJ, Acevedo-Báñez I, Martínez-Castillo R, Tirado-Hospital JL, Cuenca-Cuenca JI, Pachón-Garrudo VM, et al. The role of 18FDG, 18FDOPA PET/CT and 99mTc bone scintigraphy imaging in Erdheim–Chester disease. Eur J Radio. 2015;84:1586–92.
Hyman DM, Diamond EL, Vibat CRT, Hassaine L, Poole JC, Patel M, et al. Prospective blinded study of BRAF V600E mutation detection in cell-free DNA of patients with systemic histiocytic disorders. Cancer Disco. 2015;5:64–71.
Janku F, Diamond EL, Goodman AM, Raghavan VK, Barnes TG, Kato S, et al. Molecular profiling of tumor tissue and plasma cell-free DNA from patients with non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019;18:1149–57.
Rossi GM, Rocco R, Accorsi Buttini E, Marvisi C, Vaglio A. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis and its overlap with IgG4-related disease. Intern Emerg Med. 2017;12:287–99.
Wallace ZS, Zhang Y, Perugino CA, Naden R, Choi HK, Stone JH. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease: an analysis of two international cross-sectional cohorts. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:406–12.
Corradi D, Nicastro M, Vaglio A. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease: some missing pieces in a still unsolved complex puzzle. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2016;25:90–2.
Salvarani C, Cantini F, Hunder GG. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant-cell arteritis. Lancet. 2008;372:12.
Amoura A, Haroche J, Emile J‐F, Barete S, Helias‐Rodzewicz Z, Charlotte F, et al. Sarcoidosis occurring during BRAF/MEK inhibitors is associated with paradoxical ERK activation in Erdheim‐Chester patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:e348–50.
Veyssier-Belot C, Cacoub P, Caparros-Lefebvre D, Wechsler J, Brun B, Remy M, et al. Erdheim–Chester disease. Clinical and radiologic characteristics of 59 cases. Medicine. 1996;75:157–69.
Diamond EL, Subbiah V, Lockhart AC, Blay J-Y, Puzanov I, Chau I, et al. Vemurafenib for BRAF V600–mutant Erdheim–Chester disease and Langerhans cell histiocytosis: analysis of data from the histology-independent, phase 2, open-label VE-BASKET study. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:384–8.
Hyman DM, Puzanov I, Subbiah V, Faris JE, Chau I, Blay J-Y, et al. Vemurafenib in multiple nonmelanoma cancers with BRAF V600 mutations. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:726–36.
Bhatia A, Ulaner G, Rampal R, Hyman DM, Abdel-Wahab O, Durham BH, et al. Single-agent dabrafenib for BRAF V600E-mutated histiocytosis. Haematologica. 2018;103:e177–80.
Nordmann TM, Juengling FD, Recher M, Berger CT, Kalbermatten D, Wicki A, et al. Trametinib following disease reactivation under dabrafenib in Erdheim–Chester disease with both BRAF and KRAS mutations. Blood. 2017;129:879–82.
Al Bayati A, Plate T, Al Bayati M, Yan Y, Lavi ES, Rosenblatt JD. Dabrafenib and trametinib treatment for Erdheim–Chester disease with brain stem involvement. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018;2:303–8.
Hervier B, Arnaud L, Charlotte F, Wechsler B, Piette JC, Amoura Z, et al. Treatment of Erdheim–Chester disease with long-term high-dose interferon-α. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;41:907–13.
Pegoraro F, Maniscalco V, Peyronel F, Westenend PJ, Hendriksz TR, Roperto RM, et al. mTOR-inhibition in patients with Erdheim–Chester disease: a long-term follow-up study. Blood. 2020;135:1994–7.
Cohen-Aubart F, Maksud P, Saadoun D, Drier A, Charlotte F, Cluzel P, et al. Variability in the efficacy of the IL1 receptor antagonist anakinra for treating Erdheim–Chester disease. Blood. 2016;127:1509–12.
Goyal G, Shah MV, Call TG, Litzow MR, Wolanskyj-Spinner AP, Koster MJ, et al. Efficacy of biological agents in the treatment of Erdheim–Chester disease. Br J Haematol. 2018;183:520–4.
Campochiaro C, Cavalli G, Farina N, Tomelleri A, Luca GD, Dagna L. Efficacy and improved tolerability of combination therapy with interleukin-1 blockade and MAPK pathway inhibitors for the treatment of Erdheim–Chester disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216610.
Cohen-Aubart F, Maksud P, Emile J-F, Benameur N, Charlotte F, Cluzel P, et al. Efficacy of infliximab in the treatment of Erdheim–Chester disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:1387–90.
Dagna L, Corti A, Langheim S, Guglielmi B, De Cobelli F, Doglioni C, et al. Tumor necrosis factor α as a master regulator of inflammation in Erdheim–Chester disease: rationale for the treatment of patients with infliximab. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:e286–90.
Tran T-A, Pariente D, Guitton C, Delwail A, Barat-Houari M, Meinzer U. Treatment of Erdheim–Chester disease with canakinumab. Rheumatol (Oxf). 2014;53:2312–4.
Berti A, Cavalli G, Guglielmi B, Biavasco R, Campochiaro C, Tomelleri A, et al. Tocilizumab in patients with multisystem Erdheim–Chester disease. OncoImmunology. 2017;6:e1318237.
Goyal G, Shah MV, Call TG, Litzow MR, Hogan WJ, Go RS. Clinical and radiologic responses to cladribine for the treatment of Erdheim–Chester disease. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1253–6.
Goyal G, Shah MV, Call TG, Hook CC, Hogan WJ, Go RS. Clinical and radiological responses to oral methotrexate alone or in combination with other agents in Erdheim–Chester disease. Blood. Cancer J. 2017;7:647.
Vaglio A, Diamond EL. Erdheim–Chester disease: the “targeted” revolution. Blood. 2017;130:1282–4.
Diamond EL, Reiner AS, Buthorn JJ, Shuk E, Applebaum AJ, Hyman DM, et al. A scale for patient-reported symptom assessment for patients with Erdheim–Chester disease. Blood Adv. 2019;3:934–8.
Sieni E, Barba C, Mortilla M, Savelli S, Grisotto L, Di Giacomo G, et al. Early diagnosis and monitoring of neurodegenerative Langerhans cell histiocytosis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0131635.
Sanchez JE, Mora C, Macia M, Navarro JF. Erdheim–Chester disease as cause of end-stage renal failure: a case report and review of the literature. Int Urol Nephrol. 2010;42:1107–12.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank Dr. Annamaria Buccoliero for providing some of the histological images and Prof. Carlo Salvarani for reviewing the table on differential diagnosis. AV was supported by the 2019 grant of the Histio UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pegoraro, F., Papo, M., Maniscalco, V. et al. Erdheim–Chester disease: a rapidly evolving disease model. Leukemia 34, 2840–2857 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-020-0944-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-020-0944-4
This article is cited by
-
Erdheim-Chester disease with bilateral orbital masses and multi-systemic symptoms: two case reports
World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2023)
-
Rare presentation of multiple thromboses in Erdheim–Chester disease: a case-based review
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Beyond Giant Cell Arteritis and Takayasu’s Arteritis: Secondary Large Vessel Vasculitis and Vasculitis Mimickers
Current Rheumatology Reports (2020)