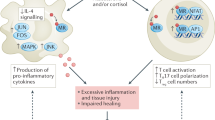
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and cardiovascular disease (CVD) share major risk factors and mechanistic pathways for progression. Furthermore, either decreased glomerular filtration rate or increased albuminuria are major risk factors for cardiovascular events. Evidence from previous renal outcome trials in patients with proteinuric CKD showed that angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin-II receptor blockers (ARBs) effectively slow CKD progression, establishing these agents as fundamental CKD pharmacologic treatments. However, in all these trials and subsequent meta-analyses, ACEIs and ARBs did not significantly reduce cardiovascular events or mortality, indicating a high residual risk for CVD progression in individuals with CKD. In contrast to the above, several outcome trials with old and novel mineralocorticoid receptor-antagonists (MRAs) clearly suggest that these agents, apart from nephroprotection, offer important cardioprotection in this population. This article is an overview of previous and recent evidence on the effects of MRAs on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CKD attempting to highlight a pathway able to improve both cardiovascular and renal prognosis in this population.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298:2038–47.
GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2020;395:709–33.
Jager KJ, Kovesdy C, Langham R, Rosenberg M, Jha V, Zoccali C. A single number for advocacy and communication-worldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases. Kidney Int. 2019;96:1048–50.
Johansen KL, Chertow GM, Foley RN, Gilbertson DT, Herzog CA, Ishani A, et al. US renal data system 2020 annual data report: epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021;77:A7–A8.
Vanholder R, Massy Z, Argiles A, Spasovski G, Verbeke F, Lameire N, et al. Chronic kidney disease as cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20:1048–56.
Stenvinkel P, Carrero JJ, Axelsson J, Lindholm B, Heimbürger O, Massy Z. Emerging biomarkers for evaluating cardiovascular risk in the chronic kidney disease patient: how do new pieces fit into the uremic puzzle? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:505–21.
Ruiz-Hurtado G, Sarafidis P, Fernández-Alfonso MS, Waeber B, Ruilope LM. Global cardiovascular protection in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016;13:603–8.
Cheung AK, Rahman M, Reboussin DM, Craven TE, Greene T, Kimmel PL, et al. Effects of Intensive BP Control in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:2812–23.
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013;3:1–150.
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2018;36:1953–2041.
Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JG, Coats AJ, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016;18:891–975.
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–9.
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:851–60.
Agodoa LY, Appel L, Bakris GL, Beck G, Bourgoignie J, Briggs JP, et al. Effect of ramipril vs amlodipine on renal outcomes in hypertensive nephrosclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2001;285:2719–28.
Sarafidis PA, Stafylas PC, Kanaki AI, Lasaridis AN. Effects of renin-angiotensin system blockers on renal outcomes and all-cause mortality in patients with diabetic nephropathy: an updated meta-analysis. Am J Hypertens. 2008;21:922–9.
Sharma P, Blackburn RC, Parke CL, McCullough K, Marks A, Black C. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for adults with early (stage 1 to 3) non-diabetic chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;CD007751.
Zhao H-J, Li Y, Liu S-M, Sun X-G, Li M, Hao Y, et al. Effect of calcium channels blockers and inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system on renal outcomes and mortality in patients suffering from chronic kidney disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren Fail. 2016;38:849–56.
Lin Y-C, Lin J-W, Wu M-S, Chen K-C, Peng C-C, Kang Y-N. Effects of calcium channel blockers comparing to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with hypertension and chronic kidney disease stage 3 to 5 and dialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0188975.
Sarafidis PA, Alexandrou ME, Ruilope LM. A review of chemical therapies for treating diabetic hypertension. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017;18:909–23.
Parving HH, Brenner BM, McMurray JJ, de Zeeuw D, Haffner SM, Solomon SD, et al. Cardiorenal end points in a trial of aliskiren for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:2204–13.
Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, Brophy M, Conner TA, Duckworth W, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1892–903.
Sarafidis PA, Ruilope LM. Aggressive blood pressure reduction and renin-angiotensin system blockade in chronic kidney disease: time for re-evaluation? Kidney Int. 2014;85:536–46.
Rossignol P, Frimat L, Zannad F. The safety of mineralocorticoid antagonists in maintenance hemodialysis patients: two steps forward. Kidney Int. 2019;95:747–9.
Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Anker SD, Pitt B, Ruilope LM, Rossing P, et al. Effect of finerenone on chronic kidney disease outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2219–29.
Filippatos G, Anker SD, Agarwal R, Pitt B, Ruilope LM, Rossing P, et al. Finerenone and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. Circulation. 2021;143:540–52.
Sarafidis PA, Memmos E, Alexandrou M-E, Papagianni A. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists for nephroprotection: current evidence and future perspectives. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24:5528–36.
Agarwal R, Kolkhof P, Bakris G, Bauersachs J, Haller H, Wada T, et al. Steroidal and non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in cardiorenal medicine. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:152–61.
Gomez-Sanchez E, Gomez-Sanchez CE. The multifaceted mineralocorticoid receptor. Compr Physiol. 2014;4:965–94.
Seckl JR, Walker BR. Minireview: 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1- a tissue-specific amplifier of glucocorticoid action. Endocrinology. 2001;142:1371–6.
Barrera-Chimal J, Girerd S, Jaisser F. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and kidney diseases: pathophysiological basis. Kidney Int. 2019;96:302–19.
Young MJ, Kanki M, Fuller PJ, Yang J. Identifying new cellular mechanisms of mineralocorticoid receptor activation in the heart. J Hum Hypertens. 2021;35:124–30.
Yang J, Chang C, Safi R, Morgan J, McDonnell DP, Fuller PJ, et al. Identification of ligand-selective peptide antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor using phage display. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25:32–43.
Viengchareun S, Le Menuet D, Martinerie L, Munier M, Pascual-Le Tallec L, Lombès M. The mineralocorticoid receptor: insights into its molecular and (patho)physiological biology. Nucl Recept Signal. 2007;5:e012.
Connell JMC, Davies E. The new biology of aldosterone. J Endocrinol. 2005;186:1–20.
Hermidorff MM, de Assis LVM, Isoldi MC. Genomic and rapid effects of aldosterone: what we know and do not know thus far. Heart Fail Rev. 2017;22:65–89.
Funder JW. The nongenomic actions of aldosterone. Endocr Rev. 2005;26:313–21.
Gilbert KC, Brown NJ. Aldosterone and inflammation. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2010;17:199–204.
Zhu X, Manning RD, Lu D, Gomez-Sanchez CE, Fu Y, Juncos LA, et al. Aldosterone stimulates superoxide production in macula densa cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2011;301:F529–535.
Nagase M, Fujita T. Aldosterone and glomerular podocyte injury. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2008;12:233–42.
Brown NJ. Contribution of aldosterone to cardiovascular and renal inflammation and fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013;9:459–69.
Lavall D, Selzer C, Schuster P, Lenski M, Adam O, Schäfers H-J, et al. The mineralocorticoid receptor promotes fibrotic remodeling in atrial fibrillation. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:6656–68.
Nagase M, Ayuzawa N, Kawarazaki W, Ishizawa K, Ueda K, Yoshida S, et al. Oxidative stress causes mineralocorticoid receptor activation in rat cardiomyocytes: role of small GTPase Rac1. Hypertension. 2012;59:500–6.
Köhler E, Bertschin S, Woodtli T, Resink T, Erne P. Does aldosterone-induced cardiac fibrosis involve direct effects on cardiac fibroblasts? J Vasc Res. 1996;33:315–26.
Chai W, Garrelds IM, de Vries R, Batenburg WW, van Kats JP, Danser AHJ. Nongenomic effects of aldosterone in the human heart: interaction with angiotensin II. Hypertension. 2005;46:701–6.
Terada Y, Kobayashi T, Kuwana H, Tanaka H, Inoshita S, Kuwahara M, et al. Aldosterone stimulates proliferation of mesangial cells by activating mitogen-activated protein kinase 1/2, Cyclin D1, and Cyclin A. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:2296–305.
Shibata S, Nagase M, Yoshida S, Kawachi H, Fujita T. Podocyte as the target for aldosterone: roles of oxidative stress and Sgk1. Hypertension. 2007;49:355–64.
Calò LA, Zaghetto F, Pagnin E, Davis PA, De Mozzi P, Sartorato P, et al. Effect of aldosterone and glycyrrhetinic acid on the protein expression of PAI-1 and p22(phox) in human mononuclear leukocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:1973–6.
Rocha R, Rudolph AE, Frierdich GE, Nachowiak DA, Kekec BK, Blomme EAG, et al. Aldosterone induces a vascular inflammatory phenotype in the rat heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;283:H1802–1810.
Greene EL, Kren S, Hostetter TH. Role of aldosterone in the remnant kidney model in the rat. J Clin Investig. 1996;98:1063–8.
Sun Y, Zhang J, Lu L, Chen SS, Quinn MT, Weber KT. Aldosterone-induced inflammation in the rat heart: role of oxidative stress. Am J Pathol. 2002;161:1773–81.
Rocha R, Stier CT, Kifor I, Ochoa-Maya MR, Rennke HG, Williams GH, et al. Aldosterone: a mediator of myocardial necrosis and renal arteriopathy. Endocrinology. 2000;141:3871–8.
Briet M, Schiffrin EL. Vascular actions of aldosterone. J Vasc Res. 2013;50:89–99.
Iwashima F, Yoshimoto T, Minami I, Sakurada M, Hirono Y, Hirata Y. Aldosterone induces superoxide generation via Rac1 activation in endothelial cells. Endocrinology. 2008;149:1009–14.
Bomback AS, Klemmer PJ. The incidence and implications of aldosterone breakthrough. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2007;3:486–92.
Sarafidis PA, Ruilope LM. Cardiorenal disease development under chronic renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system suppression. J Renin angiotensin aldosterone Syst. 2012;13:217–9.
Shrestha A, Che R-C, Zhang A-H. Role of aldosterone in renal fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1165:325–46.
Stavropoulos K, Imprialos K, Papademetriou V, Faselis C, Tsioufis K, Dimitriadis K, et al. Primary aldosteronism: novel insights. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2020;16:19–23.
Epstein M, Williams GH, Weinberger M, Lewin A, Krause S, Mukherjee R, et al. Selective aldosterone blockade with eplerenone reduces albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1:940–51.
Mehdi UF, Adams-Huet B, Raskin P, Vega GL, Toto RD. Addition of angiotensin receptor blockade or mineralocorticoid antagonism to maximal angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:2641–50.
Alexandrou M-E, Papagianni A, Tsapas A, Loutradis C, Boutou A, Piperidou A, et al. Effects of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in proteinuric kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Hypertens. 2019;37:2307–24.
Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Chan JC, Cooper ME, Gansevoort RT, Haller H, et al. Effect of finerenone on albuminuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;314:884–94.
Wan N, Rahman A, Nishiyama A. Esaxerenone, a novel nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor blocker (MRB) in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. J Hum Hypertens. 2021;35:148–56.
Fuller PJ, Yang J, Young MJ. 30 YEARS OF THE MINERALOCORTICOID RECEPTOR: Coregulators as mediators of mineralocorticoid receptor signalling diversity. J Endocrinol. 2017;234:T23–T34.
Kolkhof P, Delbeck M, Kretschmer A, Steinke W, Hartmann E, Bärfacker L, et al. Finerenone, a novel selective nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist protects from rat cardiorenal injury. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014;64:69–78.
Grune J, Beyhoff N, Smeir E, Chudek R, Blumrich A, Ban Z, et al. Selective mineralocorticoid receptor cofactor modulation as molecular basis for finerenone’s antifibrotic activity. Hypertension. 2018;71:599–608.
Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme WJ, Cody R, Castaigne A, Perez A, et al. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. N. Engl J Med. 1999;341:709–17.
Pitt B, Remme W, Zannad F, Neaton J, Martinez F, Roniker B, et al. Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1309–21.
Zannad F, McMurray JJV, Krum H, van Veldhuisen DJ, Swedberg K, Shi H, et al. Eplerenone in patients with systolic heart failure and mild symptoms. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:11–21.
Ferreira JP, Abreu P, McMurray JJV, van Veldhuisen DJ, Swedberg K, Pocock SJ, et al. Renal function stratified dose comparisons of eplerenone versus placebo in the EMPHASIS-HF trial. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21:345–51.
Matsumoto Y, Mori Y, Kageyama S, Arihara K, Sugiyama T, Ohmura H, et al. Spironolactone reduces cardiovascular and cerebrovascular morbidity and mortality in hemodialysis patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:528–36.
Lin C, Zhang Q, Zhang H, Lin A. Long-term effects of low-dose spironolactone on chronic dialysis patients: a randomized placebo-controlled study. J Clin Hypertens. 2016;18:121–8.
Sarafidis PA, Persu A, Agarwal R, Burnier M, de Leeuw P, Ferro C, et al. Hypertension in dialysis patients: a consensus document by the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine (EURECA-m) working group of the European Renal Association - European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) and the Hypertension and the Kidney working group of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). J Hypertens. 2017;35:657–76.
Georgianos PI, Sarafidis PA, Liakopoulos V, Balaskas EV, Zebekakis PE. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism for cardiovascular protection in end-stage renal disease: new data but the controversy continues. J Clin Hypertens. 2016;18:197–9.
University Hospital, Brest. ALdosterone Antagonist Chronic HEModialysis Interventional Survival Trial (ALCHEMIST), Phase III b. 2020 https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01848639. Accessed 11 Feb 2021.
Population Health Research Institute. Aldosterone bloCkade for Health Improvement EValuation in End-stage Renal Disease. 2020 https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03020303. Accessed 11 Feb 2021.
Bianchi S, Bigazzi R, Campese VM. Long-term effects of spironolactone on proteinuria and kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2006;70:2116–23.
Ando K, Ohtsu H, Uchida S, Kaname S, Arakawa Y, Fujita T. Anti-albuminuric effect of the aldosterone blocker eplerenone in non-diabetic hypertensive patients with albuminuria: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:944–53.
Lindhardt M, Persson F, Oxlund C, Jacobsen IA, Zurbig P, Mischak H, et al. Predicting albuminuria response to spironolactone treatment with urinary proteomics in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018;33:296–303.
Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Anker SD, Pitt B, Ruilope LM, Nowack C, et al. Design and baseline characteristics of the finerenone in reducing kidney failure and disease progression in diabetic kidney disease trial. Am J Nephrol. 2019;50:333–44.
Research Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. FDA approves drug to reduce risk of serious kidney and heart complications in adults with chronic kidney disease associated with type 2 diabetes. FDA. 2021.https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-approves-drug-reduce-risk-serious-kidney-and-heart-complications-adults-chronic-kidney-disease. Accessed 15 July 2021.
Pitt B, Filippatos G, Agarwal R, Anker SD, Bakris GL, Rossing P, et al. Cardiovascular events with finerenone in kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2110956. Online ahead of print.
Packer M, Butler J, Zannad F, Filippatos G, Ferreira JP, Pocock SJ, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on worsening heart failure events in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: EMPEROR-preserved trial. Circulation. 2021;144:1284–94.
Kasiakogias A, Rosei EA, Camafort M, Ehret G, Faconti L, Ferreira JP, et al. Hypertension and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: position paper by the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2021;39:1522–45.
Bonsu KO, Arunmanakul P, Chaiyakunapruk N. Pharmacological treatments for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction-a systematic review and indirect comparison. Heart Fail Rev. 2018;23:147–56.
A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, Parallel-group, Placebo-controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone on Morbidity and Mortality in Participants With Heart Failure (NYHA II-IV) and Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction ≥ 40% (LVEF ≥ 40%). 2021. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04435626. Accessed 20 Sep 2021.
Takahashi M, Ubukata O, Homma T, Asoh Y, Honzumi M, Hayashi N, et al. Crystal structure of the mineralocorticoid receptor ligand-binding domain in complex with a potent and selective nonsteroidal blocker, esaxerenone (CS-3150). FEBS Lett. 2020;594:1615–23.
Ito S, Itoh H, Rakugi H, Okuda Y, Yoshimura M, Yamakawa S. Double-blind randomized phase 3 study comparing esaxerenone (CS-3150) and eplerenone in patients with essential. Hypertension. 2020;75:51–58.
Ito S, Shikata K, Nangaku M, Okuda Y, Sawanobori T. Efficacy and safety of esaxerenone (CS-3150) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with microalbuminuria: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;14:1161–72.
Ito S, Kashihara N, Shikata K, Nangaku M, Wada T, Okuda Y, et al. Esaxerenone (CS-3150) in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria (ESAX-DN): phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;15:1715–27.
Palmer BF. A physiologic-based approach to the evaluation of a patient with hyperkalemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;56:387–93.
Juurlink DN, Mamdani MM, Lee DS, Kopp A, Austin PC, Laupacis A, et al. Rates of hyperkalemia after publication of the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:543–51.
Moura-Neto JA, Ronco C. The RALES legacy and finerenone use on CKD patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021;16:1432–4.
Heerspink HJL, Stefánsson BV, Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou F-F, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1436–46.
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl J Med. 2019;380:2295–306.
Sarafidis P, Ortiz A, Ferro CJ, Halimi J-M, Kreutz R, Mallamaci F, et al. Sodium_glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for patients with diabetic and nondiabetic chronic kidney disease: a new era has already begun. J Hypertens. 2021;39:1090–7.
McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1995–2008.
McMurray JJV, Packer M, Desai AS, Gong J, Lefkowitz MP, Rizkala AR, et al. Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:993–1004.
Vaduganathan M, Claggett BL, Jhund PS, Cunningham JW, Pedro Ferreira J, Zannad F, et al. Estimating lifetime benefits of comprehensive disease-modifying pharmacological therapies in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a comparative analysis of three randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 2020;396:121–8.
Sarafidis P, Ferro CJ, Morales E, Ortiz A, Malyszko J, Hojs R, et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists for nephroprotection and cardioprotection in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. A consensus statement by the EURECA-m and the DIABESITY working groups of the ERA-EDTA. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019;34:208–30.
Sarafidis P, Papadopoulos CE, Kamperidis V, Giannakoulas G, Doumas M. Cardiovascular protection with sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in chronic kidney disease: a milestone achieved. Hypertension. 2021;77:1442–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to this study, which was conceived by PS and MK, and drafted by all authors (MA, MT, MK, and PS).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
PS is an advisor/speaker to Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Elpen Pharmaceuticals, Genesis Pharma, Menarini, Innovis Pharma, Sanofi, Winmedica and has received research support for an Investigator-Initiated Study from Astra Zeneca. MA, MPT, and MK have no competing interests in relation to the work described.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexandrou, ME., Theodorakopoulou, M.P., Kanbay, M. et al. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists for cardioprotection in chronic kidney disease: a step into the future. J Hum Hypertens 36, 695–704 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-021-00641-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-021-00641-1