Abstract
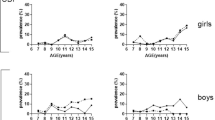
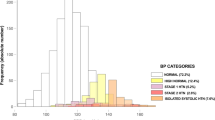
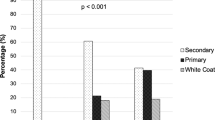
This cross-sectional study examined the prevalence, stages, subtypes of hypertension, and the associated risk factors in adolescent school children in Western India. We screened 2,644 adolescents, from 10 different private and government schools in urban and rural areas for hypertension, as defined by the 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines. The association of stages and subtypes with age, gender, body mass index, type of school, and place of residence was analysed. 197 children (7.5%) had hypertension; 170 (6.4%) had stage I, 27 (1%) had stage II and 76 (2.9%) had elevated blood pressure (EBP). The risk of EBP was higher in children > 15 years of age (p = 0.006). Compared with normal-weight children, obese, and overweight children had a higher risk of hypertension [odds ratio (OR) 9 (5.84, 13.88) and 3.77 (2.59, 5.48) respectively], whereas underweight children had a lower risk [OR 0.39 (0.16, 0.98)]. Normal-weight hypertension was seen in 5.2% and was higher in children from government schools (9.4%). Systolic-diastolic hypertension (SDH) was the most common subtype, seen in 136 (5.1%). SDH was more common in girls, in rural children, and in those with stage II hypertension. Isolated diastolic hypertension, seen in 51 (1.9%), was more common in boys, in urban children, and in those with EBP.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kollias A, Dafni M, Poulidakis E, Ntineri A, Stergiou GS. Out-of-office blood pressure and target organ damage in children and adolescents: A systematic reviewand meta-analysis. J Hypertens. 2014;32:2315–31.
Chen X, Wang Y. Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Circulation 2008;117:3171–80.
Urbina EM, Khoury PR, Mccoy C, Daniels SR, Kimball TR, Dolan LM. Cardiac and vascular consequences of pre-hypertension in youth. J Clin Hypertens. 2011;13:332–42.
Yang L, Magnussen CG, Yang L, Bovet P, Xi B. Elevated blood pressure in childhood or adolescence and cardiovascular outcomes in adulthood: A systematic review. Hypertension 2020;75:948–55.
World Health Organisation. Global Health risks. Mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks. 2009. Available from: https://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GlobalHealthRisks_report_full.pdf [Accessed 6 July 2021].
Juhola J, Magnussen CG, Berenson GS, Venn A, Burns TL, Sabin MA, et al. Combined effects of child and adult elevated blood pressure on subclinical atherosclerosis: The international childhood cardiovascular cohort consortium. Circulation 2013;128:217–24.
Koskinen J, Juonala M, Dwyer T, Venn A, Petkeviciene J, Čeponienė I, et al. Utility of different blood pressure measurement components in childhood to predict adult carotid intima-media thickness: The i3C consortium study. Hypertension 2019;73:335–41.
Franklin SS, Pio JR, Wong ND, Larson MG, Leip EP, Vasan RS, et al. Predictors of new-onset diastolic and systolic hypertension: The framingham heart study. Circulation 2005;111:1121–7.
Sorof JM, Poffenbarger T, Franco K, Bernard L, Portman RJ. Isolated systolic hypertension,obesity, and hyperkinetic hemodynamic states in children. J Pediatr. 2002;140:660–6.
Daniel RA, Haldar P, Prasad M, Kant S, Krishnan A, Gupta SK, et al. Prevalence of hypertension among adolescents (10-19 years) in India: A systematic review and meta-analysis of crosssectional studies. PLoS One. 2020;15(10):e0239929.
Center for Health Statistics N. Anthropometry Procedures Manual. 2009. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes_09_10/BodyMeasures_09.pdf [Accessed 10 July 2021].
Khadilkar VV, Khadilkar AV, Borade AB, Chiplonkar SA. Body mass index cut-offs for screening for childhood overweight and obesity in Indian children. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:29–34.
Khadilkar V, Yadav S, Agrawal KK, Tamboli S, Banerjee M, Cherian A, et al. Revised IAP growth charts for height, weight and body mass index for 5- to 18-year-old Indian children. Indian Pediatr. 2015;52:47–55.
Shah AS, Dolan LM, D’Agostino RB, Standiford D, Davis C, Testaverde L, et al. Comparison of mercury and aneroid blood pressure measurements in youth. Pediatrics 2012;129:e1205–10.
Canzanello VJ, Jensen PL, Schwartz GL. Are aneroid sphygmomanometers accurate in hospital and clinic settings? Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:729–31.
Flynn JT, Kaelber DC, Baker-Smith CM, Blowey D, Carroll AE, Daniels SR, et al. Clinical practice guideline for screening and management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2017;140:e20171904.
Patil RR, Garg BS. Prevalence of hypertension and variation in blood pressure among school children in rural area of Wardha. Indian J Public Health. 2014;58:78–83.
Song P, Zhang Y, Yu J, Zha M, Zhu Y, Rahimi K, et al. Global prevalence of hypertension in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatrics. 2019;173:1154–63.
Jose AP, Awasthi A, Kondal D, Kapoor M, Roy A, Prabhakaran D. Impact of repeated blood pressure measurement on blood pressure categorization in a population-based study from India. J Hum Hypertens. 2019;33:594–601.
Falkstedt D, Koupil I, Hemmingsson T. Blood pressure in late adolescence and early incidence of coronary heart disease and stroke in the Swedish 1969 conscription cohort. J Hypertens. 2008;26:1313–20.
Sorof J, Daniels S. Obesity hypertension in children: A problem of epidemic proportions. Hypertension 2002;40:441–7.
Zhao Y, Wang L, Xue B, Wang Y. Associations between general and central obesity and hypertension among children: The childhood obesity study in China mega-cities. Sci Rep. 2017;7:1–7.
Dong Y, Song Y, Zou Z, Ma J, Dong B, Prochaska JJ. Updates to pediatric hypertension guidelines: Influence on classification of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. J Hypertens. 2019;37:297–306.
Cheung EL, Bell CS, Samuel JP, Poffenbarger T, Redwine KMN, Samuels JA. Race and obesity in adolescent hypertension. Pediatrics 2017;139:e20161433.
Goel M, Pal P, Agrawal A, Ashok C. Relationship of body mass index and other life style factors with hypertension in adolescents. Ann Pediatr Cardiol. 2016;9:29–34.
Kaczmarek M, Stawińska-Witoszyńska B, Krzyżaniak A, Krzywińska-Wiewiorowska M, Siwińska A. Who is at higher risk of hypertension? Socioeconomic status differences in blood pressure among Polish adolescents: A population-based ADOPOLNOR study. Eur J Pediatr. 2015;174:1461–73.
Ewald DR, Bond SH, Haldeman LA. Hypertension in low-income adolescents. Glob Pediatr Heal. 2017;4:2333794×17741819.
Singh Thangjam R, Indrajit Singh A, Cindy L, Rameshchandra T. The profile of blood pressure (BP) and the prevalence of hypertension in school going children aged 5-15 years of Manipur, a North-Eastern hilly Indian state. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017;4:2151–7.
Genovesi S, Antolini L, Gallieni M, Aiello A, Mandal SKB, Doneda A, et al. High prevalence of hypertension in normal and underweight Indian children. J Hypertens. 2011;29:217–21.
Kumar J, Deshmukh PR, Garg BS. Prevalence and correlates of sustained hypertension in adolescents of rural wardha, central India. Indian J Pediatr. 2012;79:1206–12.
Vispute S, Shaikh N, Mandlik R, Gondhalekar K, Patwardhan V, Khadilkar A. Are rural Indian children and adolescents ages 9–18 years at risk of hypertension? A multicenter study. Curr Dev Nutr. 2021;5:192.
Tripathy JP, Thakur JS, Jeet G, Chawla S, Jain S, Prasad R. Urban rural differences in diet, physical activity and obesity in India: are we witnessing the great Indian equalisation? Results from a cross-sectional STEPS survey. BMC Public Health. 2016;16:816.
Thakur J, Jeet G, Nangia R, Singh D, Grover S, Lyngdoh T, et al. Non-communicable diseases risk factors and their determinants: A cross-sectional state-wide STEPS survey, Haryana, North India. PLoS One. 2019;4:e0208872.
Falkner B. Maternal and gestational influences on childhood blood pressure. Pediatr Nephrol. 2020;35:1409–18.
Sorof JM, Alexandrov AV, Cardwell G, Portman RJ. Carotid artery intimal-medial thickness and left ventricular hypertrophy in children with elevated blood pressure. Pediatrics 2003;111:61–6.
Raj M, Sundaram KR, Paul M, Deepa AS, Kumar RK. Obesity in Indian children: time trends and relationship with hypertension. Natl Med J India. 2007;20:288–93.
Yang Y, Dong B, Wang S, Dong Y, Zou Z, Fu L, et al. Prevalence of high blood pressure subtypes and its associations with BMI in Chinese children: A national cross-sectional survey. BMC Public Health. 2017;17:598.
McEvoy JW, Daya N, Rahman F, Hoogeveen RC, Blumenthal RS, Shah AM, et al. Association of isolated diastolic hypertension as defined by the 2017 ACC/AHA blood pressure guideline with incident cardiovascular outcomes. JAMA. 2020;323:329–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
USA: concept, study design, protocol, data acquisition, data analysis, review of literature, ethics clearance for Mumbai schools, and writing the final draft of the article. HAP: protocol, ethics clearance for Mumbai schools, data analysis and literature review, training of medical officers in procedures [height, weight, and blood pressure]. RGP: data acquisition, data analysis, data formatting, tables, and revisions. VBM: study design, protocol, implementation, and data acquisition, literature review, drafting of article JS: ethics clearance for Pune schools, data acquisition, literature review. training of medical officers in procedures [height, weight, and blood pressure] drafting of article JSS: ethics clearance for Pune schools, data acquisition, literature review, training of medical officers in procedures [height, weight, and blood pressure], drafting of the article. PSC: data acquisition, data analysis, literature review VSK: data acquisition, data analysis, literature review, drafting of article PS: study design, protocol, data acquisition, data analysis, drafting of the article, and responding to reviewers’ comments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, U.S., Patil, H.A., Prakash, R.G. et al. Prevalence and subtypes of hypertension in normal-weight and obese Indian adolescents: a cross-sectional study. J Hum Hypertens 36, 1003–1010 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-021-00605-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-021-00605-5