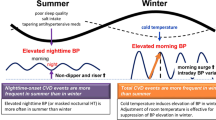
Abstract
The clinical and experimental data on seasonal variation in blood pressure is mainly from office and home blood pressure (BP) monitoring studies. There are few studies from temperate climates on seasonal changes with ambulatory blood pressure (ABP) monitoring and none from India. This is a prospective, observational study among healthy adults. ABP was measured in four different seasons in 28 subjects. Mean arterial pressure (MAP), ambulatory systolic blood pressure (SBP), and ambulatory diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were significantly higher in winter compared to summer season. 24-hour MAP was lowest in summer while highest MAP was recorded in winter (97.04 ± 8.30 and 103.89 ± 8.54, respectively). The mean difference was −6.86 mm Hg (95% CI: −10.74 to −2.97, p = 0.001). This difference was mainly due to increase in day time MAP. There was no difference in 24 h systolic and diastolic blood pressure between summer and winter. There was significant difference between summer and winter in the SBP (day time) [125.61 ± 11.44 and 131.93 ± 9.46, mean difference −6.32 (95% CI: −10.69 to −1.95, p = 0.005)] and DBP (day time) [79.57 ± 9.95 and 87.07 ± 9.9, mean difference −7.50 (95% CI: −12.49 to −2.51, p = 0.003)]. The night time systolic and diastolic BP was similar during winter and summer. Thus, BP increases significantly during winter compared to summer season. This change is primarily in the day time systolic, diastolic and mean blood pressures. Larger studies are required to further validate our findings.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goyal A, Aslam N, Kaur S, Soni RK, Midha V, Chaudhary A, et al. Factors affecting seasonal changes in blood pressure in North India: a population based four-seasons study. Indian Heart J. 2018;70:360–7.
Keatinge WR, Coleshaw SR, Cotter F, Mattock M, Murphy M, Chelliah R. Increases in platelet and red cell counts, blood viscosity, and arterial pressure during mild surface cooling: factors in mortality from coronary and cerebral thrombosis in winter. Br Med J. 1984;289:1405–8.
Sharma BK, Sagar S, Sood GK, Varma, Kalra S, Seasonal OP. variations of arterial blood pressure in normotensive and essential hypertensives. Indian Heart J. 1990;42:66–72.
Aubinière-Robb L, Jeemon P, Hastie CE, Patel RK, McCallum L, Morrison D, et al. Blood pressure response to patterns of weather fluctuations and effect on mortality. Hypertension. 2013;62:190–6.
Su D, Du H, Zhang X, Qian Y, Chen L, Chen Y, et al. Season and outdoor temperature in relation to detection and control of hypertension in a large rural Chinese population. Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43:1835–45.
Lewington S, Li L, Sherliker P, Guo Y, Millwood I, Bian Z, et al. Seasonal variation in blood pressure and its relationship with outdoor temperature in 10 diverse regions of China: the China KadoorieBiobank. J Hypertens. 2012;30:1383–91.
Madsen C, Nafstad P. Associations between environmental exposure and blood pressure among participants in the Oslo Health Study (HUBRO). Eur J Epidemiol. 2006;21:485–91.
Barnett AG, Sans S, Salomaa V, Kuulasmaa K, Dobson AJ. WHO MONICA Project The effect of temperature on systolic blood pressure. Blood Press Monit. 2007;12:195–203.
Jenner DA, English DR, Vandongen R, Beilin LJ, Armstrong BK, Dunbar D, et al. Environmental temperature and blood pressure in 9-year-old Australian children. J Hypertens. 1987;5:683–6.
Sega R, Cesana G, Bombelli M, Grassi G, Stella ML, Zanchetti A, et al. Seasonal variations in home and ambulatory blood pressure in the PAMELA population. Pressione Arteriose Monitorate E Loro Associazioni. J Hypertens. 1998;16:1585–92.
Modesti PA. Season, temperature and blood pressure: a complex interaction. Eur J Intern Med. 2013;24:604–7.
Cuspidi C, Ochoa JE, Parati G. Seasonal variations in blood pressure: a complex phenomenon. J Hypertens. 2012;30:1315–20.
Banegas JR, Ruilope LM, Sierra ADL, Vinyoles E, Gorostidi M, JJDL Cruz, et al. Relationship between clinic and ambulatory blood-pressure measurements and mortality. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1509–20.
Brennan PJ, Greenberg G, Miall WE, Thompson SG. Seasonal variation in arterial blood pressure. Br. Med. J.1982;285:919–23.
Alperovitch A, Lacombe JM, Hanon O, Dartigues JF, Ritchie K, Ducimetière P, et al. Relationship between blood pressure and outdoor temperature in a large sample of elderly individuals: the Three-City study. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:75–80.
Modesti PA, Morabito M, Bertolozzi I, Massetti L, Panci G, Lumachi C, et al. Weather-related changes in 24-h blood pressure profile: effects of age and implications for hypertension management. Hypertension. 2006;47:155–61.
O’Brien E, Parati G, Stergiou G, Asmar R, Beilin L, Bilo G, et al. European society of hypertension position paper on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. J Hypertens. 2013;31:1731–68.
Sheth T, Nair C, Muller J, Yusuf S. Increased winter mortality from acute myocardial infarction and stroke: the effect of age. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999;33:1916–9.
Ockene IS, Chiriboga DE, Stanek EJ 3rd, Harmatz MG, Nicolosi R, Saperia G, et al. Seasonal variation in serum cholesterol levels: treatment implications and possible mechanisms. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:863–70.
Fedecostante M, Barbatelli P, Guerra F, Espinosa E, Dessì-Fulgheri P, Sarzani R. Summer does not always mean lower: seasonality of 24 h, daytime, and night-time blood pressure. J Hypertens. 2012;30:1392–8.
Minami J, Kawano Y, Ishimitsu T, Espinosa E, Dessì-Fulgheri P, Sarzani R. Seasonal variations in office, home and 24 h ambulatory blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 1996;14:1421–5.
Winnicki M, Canali C, Accurso V, Dorigatti F, Giovinazzo P, Palatini P, et al. Relation of 24-h ambulatory blood pressure and short-term blood pressure variability to seasonal changes in environmental temperature in stage I hypertensive subjects. Results of the Harvest Trial. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1996;18:995–1012.
Sun Z, Cade R, Morales C. Role of central angiotensin II receptors in coldinduced hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2002;15:85–92.
Sun Z, Cade R, Zhang Z, Alouidor J, Van H. Angiotensinogen gene knockout delays and attenuates cold-induced hypertension. Hypertension. 2003;41:322–7.
Psaltopoulou T, Orfanos P, Naska A, Lenas D, Trichopoulos A. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in a general population sample of 26 913 adults in the Greek EPIC study. Int. J. Epidemiol.2004;33:1345–52.
Funding
Institutional Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, A., Narang, K., Ahluwalia, G. et al. Seasonal variation in 24 h blood pressure profile in healthy adults- A prospective observational study. J Hum Hypertens 33, 626–633 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-019-0173-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-019-0173-3
This article is cited by
-
Gender-specific effect of outdoor temperature and seasonal variation on blood pressure components: a cross-sectional study on Iranian adults from 2015 to 2018
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
-
Indian guidelines on hypertension-IV (2019)
Journal of Human Hypertension (2020)
-
Spotlight on hypertension in the Indian subcontinent
Journal of Human Hypertension (2019)