Abstract
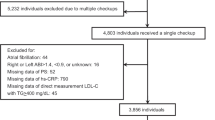
We aimed to explore the impact of blood pressure (BP) levels on atherosclerosis in a rural Chinese population with a low-education level, low income, high incidence of stroke, and high prevalence of hypertension. B-mode ultrasonography was used to measure carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) in adults aged ≥ 45 years with no history of stroke or cardiovascular disease. A total of 5403 eligible subjects were included in this study. The mean CIMT was 0.57 mm overall, 0.58 mm for men and 0.56 mm for women. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) and hypertension were significantly associated with increased CIMT. CIMT increased by 0.42 μm for every 1 mm Hg-increase in SBP (P < 0.001). The mean CIMT in participants with a history of hypertension was 17.42 μm greater than that in participants with no history of hypertension (P < 0.001). Diastolic blood pressure (DBP) was a protective factor, as CIMT decreased by 0.44 μm with every 1 mm Hg-increase in DBP (P = 0.011).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2009;119:480–6.
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129:e28–292.
Brook RD, Bard RL, Patel S, Rubenfire M, Clarke NS, Kazerooni EA, et al. A negative carotid plaque area test is superior to other noninvasive atherosclerosis studies for reducing the likelihood of having underlying significant coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:656–62.
Prabhakaran S, Rundek T, Ramas R, Elkind MS, Paik MC, Boden-Albala B, et al. Carotid plaque surface irregularity predicts ischemic stroke: the northern Manhattan study. Stroke. 2006;37:2696–701.
Polak JF, Pencina MJ, Pencina KM, O’Donnell CJ, Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB Sr, et al. Carotid-wall intima-media thickness and cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:213–21.
Lakka TA, Salonen R, Kaplan GA, Salonen JT. Blood pressure and the progression of carotid atherosclerosis in middle-aged men. Hypertension. 1999;34:51–6.
Su TC, Lee YT, Chou S, Hwang WT, Chen CF, Wang JD, et al. Twenty-four-hour ambulatory blood pressure and duration of hypertension as major determinants for intima-media thickness and atherosclerosis of carotid arteries. Atherosclerosis. 2006;184:151–6.
Ferreira JP,Girerd N,Bozec E,Machu JL,Boivin JM,London GM, et al. Intima-media thickness is linearly and continuously associated with systolic blood pressure in a population-based cohort (STANISLAS cohort study). J Am Heart Assoc. 2016;5:e003529
Cheng G, Fan F, Zhang Y, Qi L, Jia J, Liu Y, et al. Different associations between blood pressure indices and carotid artery damages in a community-based population of China. J Hum Hypertens. 2016;30:750–4.
Wang HM, Chen TC, Jiang SQ, Liu YJ, Tian JW. Association of conventional risk factors for cardiovascular disease with IMT in middle-aged and elderly Chinese. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;30:759–68.
Wang J, Ning X, Yang L, Lu H, Tu J, Jin W, et al. Trends of hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment and control in rural areas of northern China during 1991-2011. J Hum Hypertens. 2014;28:25–31.
Ong KL, Cheung BM, Man YB, Lau CP, Lam KS. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among United States adults 1999–2004. Hypertension. 2007;49:69–75.
Wang J, An Z, Li B, Yang L, Tu J, Gu H, et al. Increasing stroke incidence and prevalence of risk factors in a low-income Chinese population. Neurology. 2015;84:374–81.
Zhan C, Shi M, Yang Y, Pang H, Fei S, Bai L, et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Carotid Plaque Among Middle-aged and Elderly Adults in Rural Tianjin, China. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23870.
National Health and Family Planning Commission of the people’s Republic of China (editors). China Health and Family Planning Statistics Yearbook 2014. China Union Medical University Press: Beijing, China; 2015.
Tattersall MC, Gassett A, Korcarz CE, Gepner AD, Kaufman JD, Liu KJ, et al. Predictors of carotid thickness and plaque progression during a decade: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Stroke. 2014;45:3257–62.
Zhou BF. Effect of body mass index on all-cause mortality and incidence of cardiovascular diseases–report for meta-analysis of prospective studies open optimal cut-off points of body mass index in Chinese adults. Biomed Environ Sci1. 2002;5:245–52.
Yang D, Iyer S, Gardener H, Della-Morte D, Crisby M, Dong C, et al. Cigarette smoking and carotid plaque echodensity in the Northern Manhattan Study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;40:136–43.
Wang JG, Staessen JA, Li Y, Van Bortel LM, Nawrot T, Fagard R, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness and antihypertensive treatment: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2006;37:1933–40.
Su TC, Chien KL, Jeng JS, Chen MF, Hsu HC, Torng PL, et al. Age- and gender-associated determinants of carotid intima-media thickness: a community-based study. J Atheroslerosis Thromb. 2012;9:872–80.
Vicenzini E, Ricciardi MC, Puccinelli F, Altieri M, Vanacore N, Di Piero V, et al. Common carotid artery intima-media thickness determinants in a population study. J Ultrasound Med. 2007;26:427–32.
Inaba Y, Chen JA, Bergmann SR. Carotid plaque, compared with carotid intima-media thickness, more accurately predicts coronary artery disease events: a meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis. 2012;220:128–33.
Zureik M, Touboul PJ, Bonithon-Kopp C, Courbon D, Berr C, Leroux C, et al. Cross-sectional and 4-year longitudinal associations between brachial pulse pressure and common carotid intima-media thickness in a general population the EVA study. Stroke. 1999;30:550–5.
Kozàkovà M, Palombo C, Morizzo C, Nolan JJ, Konrad T, Dekker JM, et al. Gender-specific differences in carotid intima-media thickness and its progression over three years: a multicenter European study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23:151–8.
Howard G, Sharrett AR, Heiss G, Evans GW, Chambless LE, Riley WA, et al. Carotid artery intimal-medial thickness distribution in general populations as evaluated by B-mode ultrasound. Stroke. 1993;24:1297–304.
Rosvall M, Ostergren PO, Hedblad B, Isacsson SO, Janzon L, Berglund G. Occupational status, educational level, and the prevalence of carotid atherosclerosis in a general population sample of middle-aged Swedish men and women: results from the Malmo Diet and Cancer Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;152:334–46.
Johnson HM, Douglas PS, Srinivasan SR, Bond MG, Tang R, Li S, et al. Predictors of carotid intima-media thickness progression in young adults the Bogalusa Heart Study. Stroke. 2007;38:900–5.
Chen W, Yun M, Fernandez C, Li S, Sun D, Lai CC, et al. Secondhand smoke exposure is associated with increased carotid artery intima-media thickness: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Atherosclerosis. 2015;240:374–9.
Kotsis VT, Stabouli SV, Papamichael CM, Zakopoulos NA. Impact of obesity in intima media thickness of carotid arteries. Obesity. 2006;14:1708–15.
Dalmas E, Kahn JF, Giral P, Abdennour M, Bouillot JL, Fellahi S, et al. Intima-media thickness in severe obesity. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:3793–802.
Bots ML, Groenewegen KA, Anderson TJ, Britton AR, Dekker JM, Engström G, et al. Common carotid intima-media thickness measurements do not improve cardiovascular risk prediction in individuals with elevated blood pressure: the USE-IMT Collaboration. Hypertension. 2014;63:1173–81.
Lorenz MW, Polak JF, Kavousi M, Mathiesen EB, Völzke H, Tuomainen TP, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness progression to predictcardiovascular events in the general population (the PROG-IMT ollaborative project): a meta-analysis of individual participant data. Lancet. 2012;379:2053–62.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported partly by Tianjin Medical University General Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, L., Shi, M., Wu, Y. et al. Correlation between hypertension and common carotid artery intima-media thickness in rural China: a population-based study. J Hum Hypertens 32, 548–554 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0074-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0074-x
This article is cited by
-
Association of carotid atherosclerotic plaque and intima-media thickness with the monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio among low-income residents of rural China: a population-based cross-sectional study
BMC Public Health (2023)
-
Vascular, cardiac and renal target organ damage associated to arterial hypertension: which noninvasive tools for detection?
Journal of Human Hypertension (2020)