Abstract
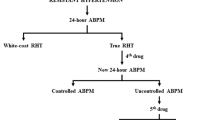
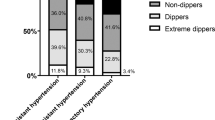
Data regarding the prognosis of resistant hypertension (RHTN) with respect to its severity is limited. We investigated the cardiovascular risk of severe RHTN in a prospective observational study. A cohort of 1700 hypertensive patient with treated uncontrolled HTN was followed for a mean period of 3.6 ± 1.8 years. At baseline, standard clinical and laboratory workup was performed, including testing for secondary causes of RHT where applicable. Three groups were identified depending on presence of RHTN (office-based uncontrolled HTN under at least three drugs including a diuretic) and levels of office systolic blood pressure (BP): 1187 patients (70%) without RHTN, 313 (18%) with not-severe RHTN (systolic BP < 160 mmHg) and 200 (12%) with severe RHTN (systolic BP ≥ 160 mmHg). Endpoint of interest was cardiovascular morbidity set as the composite of coronary heart disease and stroke. During follow-up, incidence rates of cardiovascular events per 1000 person-years were 7.1 cases in the non-RHTN group, 12.4 cases in the not-severe RHTN group and 18 cases in the severe RHTN group. Unadjusted analysis showed that compared to uncontrolled patients without RHTN, patients with not-severe RHTN exhibited a similar risk but patients with severe RHTN had a significantly higher risk, by 2.5 times (CI: 1.28–4.73, p = 0.007). Even after multivariate adjustment for established risk factors including BP levels and isolated systolic HTN, severe RHTN remained as an independent predictor of the cardiovascular outcome (OR: 2.30, CI: 1.00–5.29, p = 0.05). In conclusion, among treated yet uncontrolled hypertensive patients, severe RHTN exhibits a significantly higher cardiovascular risk indicating the need for prompt management.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turner JR, Lee J. American Society of Hypertension Scientific Statements Addressing Resistant Hypertension. J ClinHypertens. 2016;18:175–8.
Doumas M, Tsioufis C, Faselis C, Lazaridis A, Grassos H, Papademetriou V. Non-interventional management of resistant hypertension. World J Cardiol. 2014;6:1080–90.
Daugherty SL, Powers JD, Magid DJ, Tavel HM, Masoudi FA, Margolis KL, et al. Incidence and prognosis of resistant hypertension in hypertensive patients. Circulation. 2012;125:1635–42.
Tsioufis C, Kasiakogias A, Kordalis A, Dimitriadis K, Thomopoulos C, Tsiachris D, et al. Dynamic resistant hypertension patterns as predictors of cardiovascular morbidity: a 4-year prospective study. J Hypertens. 2014;32:415–22.
Kumbhani DJ, Steg PG, Cannon CP, Eagle KA, Smith SC Jr, Crowley K, et al. REACH Registry Investigators. Resistant hypertension: a frequent and ominous finding among hypertensive patients with atherothrombosis. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:1204–14.
Thomas G, Xie D, Chen HY, Anderson AH, Appel LJ, Bodana S, et al. CRIC Study Investigators. Prevalence and prognostic significance of apparent treatment resistant hypertension in chronic kidney disease: Report from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study. Hypertension. 2016;67:387–96.
Persu A, Jin Y, Baelen M, Vink E, Verloop WL, Schmidt B, et al. European Network Coordinating research on REnal Denervation Consortium. Eligibility for renal denervation: experience at 11 European expert centers. Hypertension. 2014;63:1319–25.
Tsioufis CP, Papademetriou V, Dimitriadis KS, Kasiakogias A, Tsiachris D, Worthley MI, et al. Catheter-based renal denervation for resistant hypertension: twenty-four month results of the EnligHTN I first-in-human study using a multi-electrode ablation system. Int J Cardiol. 2015;201:345–50.
Schmieder RE, Redon J, Grassi G, Kjeldsen SE, Mancia G, Narkiewicz K, et al. European Society of Hypertension. Updated ESH position paper on interventional therapy of resistant hypertension. EuroIntervention. 2013;9(Suppl R):R58–66.
Isles CG, Walker LM, Beevers GD, Brown I, Cameron HL, Clarke J, et al. Mortality in patients of the Glasgow Blood Pressure Clinic. J Hypertens. 1986;4:141–56.
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G. et al. ESH-ESC task force on the management of arterial hypertension. 2007 ESH-ESC practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: ESH-ESC task force on the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens. 2007;25:1751–62.
Thomopoulos C, Kasiakogias A, Dimitriadis K, Tsioufis C. Sleep apnea a cause or risk factor for secondary hypertension? J ClinHypertens. 2012;14:405–6.
Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, et al. Chamber Quantification Writing Group; American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee; European Association of Echocardiography. Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am SocEchocardiogr. 2005;18:1440–63.
National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: evaluation, classification and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39:S1–266.
Smith SM, Gong Y, Handberg E, Messerli FH, Bakris GL, Ahmed A, Bavry AA, et al. Predictors and outcomes of resistant hypertension among patients with coronary artery disease and hypertension. J Hypertens. 2014;32:635–43.
de la Sierra A, Segura J, Banegas JR, Gorostidi M, de la Cruz JJ, Armario P, et al. Clinical features of 8295 patients with resistant hypertension classified on the basis of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Hypertension. 2011;57:898–902.
Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN, Brzezinski WA, Ferdinand KC. Uncontrolled and apparent treatment resistant hypertension in the United States, 1988 to 2008. Circulation. 2011;124:1046–58.
Böhm M, Mahfoud F, Ukena C, Hoppe UC, Narkiewicz K, Negoita M, et al. GSR Investigators. First report of the Global SYMPLICITY Registry on the effect of renal artery denervation in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Hypertension. 2015;65:766–74.
Bhatt DL, Kandzari DE, O’Neill WW, D’Agostino R, Flack JM, Katzen BT, et al. SYMPLICITY HTN-3 Investigators. A controlled trial of renal denervation for resistant hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1393–401.
Sim JJ, Bhandari SK, Shi J, Reynolds K, Calhoun DA, Kalantar-Zadeh K, et al. Comparative risk of renal, cardiovascular, and mortality outcomes in controlled, uncontrolled resistant, and nonresistant hypertension. Kidney Int. 2015;88:622–32.
Kannel WB. Historic perspectives on the relative contributions of diastolic and systolic blood pressure elevation to cardiovascular risk profile. Am Heart J. 1999;138:205–10.
Bangalore S, Fayyad R, Laskey R, Demicco DA, Deedwania P, Kostis JB, et al. Treating to New Targets Steering Committee and Investigators. Prevalence, predictors, and outcomes in treatment-resistant hypertension in patients with coronary disease. Am J Med. 2014;127:71–81. e1
Irvin MR, Booth JN 3rd, Shimbo D, Lackland DT, Oparil S, Howard G, et al. Apparent treatment-resistant hypertension and risk for stroke, coronary heart disease, and all-cause mortality. J Am SocHypertens. 2014;8:405–13.
Oliveras A, Armario P, Clarà A, Sans-Atxer L, Vázquez S, Pascual J, et al. Spironolactone versus sympathetic renal denervation to treat true resistant hypertension: results from the DENERVHTA study—a randomized controlled trial. J Hypertens. 2016;34:1863–71.
Bobrie G, Frank M, Azizi M, Peyrard S, Boutouyrie P, Chatellier G, et al. Sequential nephron blockade versus sequential renin-angiotensin system blockade in resistant hypertension: a prospective, randomized, open blinded endpoint study. J Hypertens. 2012;30:1656–64.
Ott C, Lobo MD, Sobotka PA, Mahfoud F, Stanton A, Cockcroft J, et al. Effect of arteriovenous anastomosis on blood pressure reduction in patients with isolated systolic hypertension compared with combined hypertension. J Am Heart Assoc 2016;5:e004234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasiakogias, A., Tsioufis, C., Dimitriadis, K. et al. Cardiovascular morbidity of severe resistant hypertension among treated uncontrolled hypertensives: a 4-year follow-up study. J Hum Hypertens 32, 487–493 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0065-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0065-y
This article is cited by
-
Renal Artery Denervation for Hypertension
Current Treatment Options in Cardiovascular Medicine (2019)