Abstract
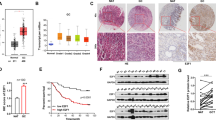
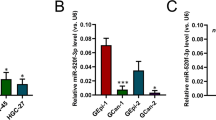
RNA-sequencing-based microRNA (miRNA) expression signatures have revealed that miR-148a-5p (the passenger strand of the miR-148a-duplex) is downregulated in various kinds of cancer tissues. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database showed that low expression of miR-148a-5p was predictive of a lower survival rate (p = 0.041) in patients with gastric cancer (GC). Downregulation of miR-148a-5p was confirmed in GC clinical specimens, and its ectopic expression attenuated GC cell proliferation. Our search for miRNA target genes identified a total of 18 oncogenic targets of miR-148a-5p in GC cells. Among these targets, high expression levels of six genes (THBS2, P4HA3, SERPINH1, CDH11, BCAT1, and KCNG3) were closely associated with a poor prognosis (10-year survival rates) in GC patients (p < 0.05) according to TCGA database analyses. Furthermore, we focused on SERPINH1 as a chaperone protein involved in collagen folding in humans. Aberrant expression of SERPINH1 (mRNA and protein levels) was confirmed in GC clinical specimens. Knockdown assays of SERPINH1 using siRNAs resulted in inhibition of the aggressive phenotype of GC cells. Exploring the molecular networks controlled by miRNAs (including miRNA passenger strands) will broaden our understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of GC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Smyth EC, Verheij M, Allum W, Cunningham D, Cervantes A, Arnold D, et al. Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:v38–49.
Van Cutsem E, Sagaert X, Topal B, Haustermans K, Prenen H. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:2654–64.
Fontana E, Smyth EC. Novel targets in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer: a perspective review. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2016;8:113–25.
Pellino A, Riello E, Nappo F, Brignola S, Murgioni S, Djaballah SA, et al. Targeted therapies in metastatic gastric cancer: current knowledge and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25:5773–88.
Verma R, Sharma PC. Next generation sequencing-based emerging trends in molecular biology of gastric cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2018;8:207–25.
Hudler P. Challenges of deciphering gastric cancer heterogeneity. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:10510–27.
Anfossi S, Babayan A, Pantel K, Calin GA. Clinical utility of circulating non-coding RNAs—an update. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:541–63.
Ha M, Kim VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:509–24.
Gebert LFR, MacRae IJ. Regulation of microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:21–37.
Lin S, Gregory RI. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15:321–33.
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:203–22.
Koshizuka K, Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, Arai T, Okato A, et al. Deep sequencing-based microRNA expression signatures in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: dual strands of pre-miR-150 as antitumor miRNAs. Oncotarget. 2017;8:30288–304.
Goto Y, Kurozumi A, Arai T, Nohata N, Kojima S, Okato A, et al. Impact of novel miR-145-3p regulatory networks on survival in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2017;117:409–20.
Yonemori K, Seki N, Idichi T, Kurahara H, Osako Y, Koshizuka K, et al. The microRNA expression signature of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by RNA sequencing: anti-tumour functions of the microRNA-216 cluster. Oncotarget. 2017;8:70097–115.
Toda H, Kurozumi S, Kijima Y, Idichi T, Shinden Y, Yamada Y, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of triple-negative breast cancer based on microRNA expression signatures: antitumor miR-204-5p targets AP1S3. J Hum Genet. 2018;63:1197–210.
Toda H, Seki N, Kurozumi S, Shinden Y, Yamada Y, Nohata N, et al. RNA-sequence-based microRNA expression signature in breast cancer: tumor-suppressive miR-101-5p regulates molecular pathogenesis. Mol Oncol. 2019;14:426–46.
Osako Y, Seki N, Koshizuka K, Okato A, Idichi T, Arai T, et al. Regulation of SPOCK1 by dual strands of pre-miR-150 inhibit cancer cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Hum Genet. 2017;62:935–44.
Sugawara S, Yamada Y, Arai T, Okato A, Idichi T, Kato M, et al. Dual strands of the miR-223 duplex (miR-223-5p and miR-223-3p) inhibit cancer cell aggressiveness: targeted genes are involved in bladder cancer pathogenesis. J Hum Genet. 2018;63:657–68.
Misono S, Seki N, Mizuno K, Yamada Y, Uchida A, Arai T, et al. Dual strands of the miR-145 duplex (miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p) regulate oncogenes in lung adenocarcinoma pathogenesis. J Hum Genet. 2018;63:1015–28.
Fukuhisa H, Seki N, Idichi T, Kurahara H, Yamada Y, Toda H, et al. Gene regulation by antitumor miR-130b-5p in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: the clinical significance of oncogenic EPS8. J Hum Genet. 2019;64:521–34.
Lei Z, Tan IB, Das K, Deng N, Zouridis H, Pattison S, et al. Identification of molecular subtypes of gastric cancer with different responses to PI3-kinase inhibitors and 5-fluorouracil. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:554–65.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature. 2014;513:202–9.
Benita Y, Cao Z, Giallourakis C, Li C, Gardet A, Xavier RJ. Gene enrichment profiles reveal T-cell development, differentiation, and lineage-specific transcription factors including ZBTB25 as a novel NF-AT repressor. Blood. 2010;115:5376–84.
Ooi CH, Ivanova T, Wu J, Lee M, Tan IB, Tao J, et al. Oncogenic pathway combinations predict clinical prognosis in gastric cancer. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000676.
Cristescu R, Lee J, Nebozhyn M, Kim KM, Ting JC, Wong SS, et al. Molecular analysis of gastric cancer identifies subtypes associated with distinct clinical outcomes. Nat Med. 2015;21:449–56.
Arienti C, Pignatta S, Tesei A. Epidermal growth factor receptor family and its role in gastric cancer. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1308.
Selim JH, Shaheen S, Sheu WC, Hsueh CT. Targeted and novel therapy in advanced gastric cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2019;8:25.
Alessandrini L, Manchi M, De Re V, Dolcetti R, Canzonieri V. Proposed molecular and miRNA classification of gastric cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:E1683.
Necula L, Matei L, Dragu D, Neagu AI, Mambet C, Nedeianu S, et al. Recent advances in gastric cancer early diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25:2029–44.
Komatsu S, Otsuji E. Essential updates 2017/2018: recent topics in the treatment and research of gastric cancer in Japan. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2019;3:581–91.
Stojanovic J, Tognetto A, Tiziano DF, Leoncini E, Posteraro B, Pastorino R, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles as diagnostic biomarkers of gastric cancer: a systematic literature review. Biomarkers. 2019;24:110–9.
Idichi T, Seki N, Kurahara H, Fukuhisa H, Toda H, Shimonosono M, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: impact of passenger strand of pre-miR-148a on gene regulation. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:2013–26.
Duan F, Liu W, Fu X, Feng Y, Dai L, Cui S, et al. Evaluating the prognostic value of miR-148/152 family in cancers: based on a systemic review of observational studies. Oncotarget. 2017;8:77999–8010.
Li Y, Deng X, Zeng X, Peng X. The role of mir-148a in cancer. J Cancer. 2016;7:1233–41.
Xia J, Guo X, Yan J, Deng K. The role of miR-148a in gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140:1451–6.
Chen Y, Song YX, Wang ZN. The microRNA-148/152 family: multi-faceted players. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:43.
Nakamura Y, Tanaka F, Nagahara H, Ieta K, Haraguchi N, Mimori K, et al. Opa interacting protein 5 (OIP5) is a novel cancer-testis specific gene in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:885–92.
Chun HK, Chung KS, Kim HC, Kang JE, Kang MA, Kim JT, et al. OIP5 is a highly expressed potential therapeutic target for colorectal and gastric cancers. BMB Rep. 2010;43:349–54.
Kim TW, Lee SJ, Park YJ, Park SY, Oh BM, Park YS, et al. Opa-interacting protein 5 modulates docetaxel-induced cell death via regulation of mitophagy in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2017;39:1010428317733985.
Xu Y, Yu W, Yang T, Zhang M, Liang C, Cai X, et al. Overexpression of BCAT1 is a prognostic marker in gastric cancer. Hum Pathol. 2018;75:41–6.
Duarte BDP, Bonatto D. The heat shock protein 47 as a potential biomarker and a therapeutic agent in cancer research. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018;144:2319–28.
Ito S, Nagata K. Biology of Hsp47 (Serpin H1), a collagen-specific molecular chaperone. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;62:142–51.
Kamikawaji K, Seki N, Watanabe M, Mataki H, Kumamoto T, Takagi K, et al. Regulation of LOXL2 and SERPINH1 by antitumor microRNA-29a in lung cancer with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Hum Genet. 2016;61:985–93.
Yamada Y, Sugawara S, Arai T, Kojima S, Kato M, Okato A, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of renal cell carcinoma: impact of the anti-tumor miR-29 family on gene regulation. Int J Urol. 2018;25:953–65.
Gong J, Li J, Wang Y, Liu C, Jia H, Jiang C, et al. Characterization of microRNA-29 family expression and investigation of their mechanistic roles in gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:497–506.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by KAKENHI grants (grant nos. 17H04285, 18K08626, 18K09338, 18K16322, 19K09200, 19K09077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawagoe, K., Wada, M., Idichi, T. et al. Regulation of aberrantly expressed SERPINH1 by antitumor miR-148a-5p inhibits cancer cell aggressiveness in gastric cancer. J Hum Genet 65, 647–656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-020-0746-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-020-0746-6
This article is cited by
-
H19 may regulate the immune cell infiltration in carcinogenesis of gastric cancer through miR-378a-5p/SERPINH1 signaling
World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2022)
-
STAT3 regulates SRGN and promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the FoxO1-miR-148a-5p-CREB1 axis
Laboratory Investigation (2022)
-
Identification of long non-coding RNAs and RNA binding proteins in breast cancer subtypes
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
A novel strategy to identify candidate diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for gastric cancer
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
Current perspectives on the dysregulated microRNAs in gastric cancer
Molecular Biology Reports (2020)