Abstract
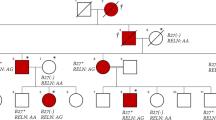
Behçet disease (BD) is an immune-mediated disease. The cause of BD remains unknown, but the existence of multiple pathological pathways is suspected, including different genetic factors. Polymorphisms in ERAP1 gene have been associated with an increased risk of BD. However, while current BD-associated ERAP1 variants are suggested to contribute to disease by altering the activity of the encoded protein, there is no knowledge of variants that alter the expression level of ERAP1, despite previous associations between ERAP1 expression and BD. Here, we used whole-exome sequencing of a patient with a Behçet-like MHC-I-opathy to identify that the patient, unlike its healthy parents, was homozygous for a rare 1-bp deletion, rs140416843, in the promoter region of ERAP1. rs140416843 has not previously been associated with disease, but is linked to ERAP1 haplotype Hap10 which is associated with BD. The expression of ERAP1 by both RT-qPCR and RNA sequencing showed that ERAP1 mRNA expression correlated with the zygosity for the identified deletion and was decreased in comparison to a healthy cohort. In conclusion, we diagnosed the patient as having BD, and hypothesize that rs140416843-mediated changes in ERAP1 expression play a causative role in BD and that this risk factor is contributing to the association between Hap10 and BD. This is the first report to identify a variant that may cause BD by altering the expression of ERAP1, and our findings suggest that downregulation of ERAP1 expression can serve as a diagnostic marker for BD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this manuscript will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation, to any qualified researcher. The distribution of the human genetic data is personally identifiable and can only be shared upon approval from Danish authorities.
References
Rock KL, Reits E, Neefjes J. Present yourself! by MHC Class I and MHC Class II molecules. Trends Immunol. 2016;37:724–37.
Goto Y, Ogawa K, Hattori A, Tsujimoto M. Secretion of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 is involved in the activation of macrophages induced by lipopolysaccharide and interferon-γ. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:21906–14.
Cui X, Hawari F, Alsaaty S, Lawrence M, Combs CA, Geng W, et al. Identification of ARTS-1 as a novel TNFR1-binding protein that promotes TNFR1 ectodomain shedding. J Clin Invest. 2002;110:515–26.
Cui X, Rouhani FN, Hawari F, Levine SJ. An aminopeptidase, ARTS-1, is required for interleukin-6 receptor shedding. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:28677–85.
Tsujimoto M, Hattori A. The oxytocinase subfamily of M1 aminopeptidases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins Proteom. 2005;1751:9–18.
Ombrello MJ, Kastner DL, Remmers EF. Endoplasmic reticulum-associated amino-peptidase 1 and rheumatic disease: genetics. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27:349–56.
Reeves E, Edwards CJ, Elliott T, James E. Naturally occurring ERAP1 haplotypes encode functionally distinct alleles with fine substrate specificity. J Immunol. 2013;191:35–43.
Tran TM, Colbert RA. Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 and rheumatic disease: functional variation. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27:357–63.
Martin-Esteban A, Guasp P, Barnea E, Admon A, Lopez de Castro JA. Functional interaction of the ankylosing spondylitis-associated endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 2 with the HLA-B*27 peptidome in human cells. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:2466–75.
Barnea E, Melamed Kadosh D, Haimovich Y, Satumtira N, Dorris ML, Nguyen MT, et al. The human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-B27 peptidome in Vivo, in spondyloarthritis-susceptible HLA-B27 transgenic rats and the effect of erap1 deletion. Mol Cell Proteom MCP. 2017;16:642–62.
McGonagle D, Aydin SZ, Gul A, Mahr A, Direskeneli H. ‘MHC-I-opathy'[mdash]unified concept for spondyloarthritis and Behcet disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11:731–40.
Castro-Santos P, Moro-Garcia MA, Marcos-Fernandez R, Alonso-Arias R, Diaz-Pena R. ERAP1 and HLA-C interaction in inflammatory bowel disease in the Spanish population. Innate Immun. 2017;23:476–81.
Farah S, Al-Shubaili A, Montaser A, Hussein JM, Malaviya AN, Mukhtar M, et al. Behçet’s syndrome: a report of 41 patients with emphasis on neurological manifestations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998;64:382–4.
Patel P, Steinschneider M, Boneparth A, Lantos G. Neuro-Behcet disease presenting with acute psychosis in an adolescent. J Child Neurol. 2014;29:NP86–91.
Siva A, Saip S. The spectrum of nervous system involvement in Behçet’s syndrome and its differential diagnosis. J Neurol. 2009;256:513.
Grigg EL, Kane S, Katz S. Mimicry and deception in inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal behcet disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2012;8:103–12.
Wallace GR. HLA-B*51 the primary risk in Behçet disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:8706–7.
Yu H, Zheng M, Zhang L, Li H, Zhu Y, Cheng L, et al. Identification of susceptibility SNPs in IL10 and IL23R-IL12RB2 for Behçet's disease in Han Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:621–7.
Sousa I, Shahram F, Francisco D, Davatchi F, Abdollahi BS, Ghaderibarmi F, et al. Brief report: association of CCR1, KLRC4, IL12A-AS1, STAT4, and ERAP1 With Behcet's disease in Iranians. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:2742–8.
Zhang L, Yu H, Zheng M, Li H, Liu Y, Kijlstra A, et al. Association of ERAP1 gene polymorphisms with Behcet's disease in han Chinese. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56:6029–35.
Kirino Y, Bertsias G, Ishigatsubo Y, Mizuki N, Tugal-Tutkun I, Seyahi E, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies new susceptibility loci for Behcet's disease and epistasis between HLA-B [ast] 51 and ERAP1. Nat Genet. 2013;45:202–7.
Guasp P, Barnea E, Gonzalez-Escribano MF, Jimenez-Reinoso A, Regueiro JR, Admon A, et al. The Behcet's disease-associated variant of the aminopeptidase ERAP1 shapes a low-affinity HLA-B*51 peptidome by differential subpeptidome processing. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:9680–9.
Chen L, Fischer R, Peng Y, Reeves E, McHugh K, Ternette N, et al. Critical role of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 in determining the length and sequence of peptides bound and presented by HLA-B27. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:284–94.
Hammer GE, Gonzalez F, James E, Nolla H, Shastri N. In the absence of aminopeptidase ERAAP, MHC class I molecules present many unstable and highly immunogenic peptides. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:101–8.
Szolek A, Schubert B, Mohr C, Sturm M, Feldhahn M, Kohlbacher O. OptiType: precision HLA typing from next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:3310–6.
Machiela MJ, Chanock SJ. LDlink: a web-based application for exploring population-specific haplotype structure and linking correlated alleles of possible functional variants. Bioinformatics. 2015;31:3555–7.
Costantino F, Talpin A, Evnouchidou I, Kadi A, Leboime A, Said‐Nahal R, et al. ERAP1 gene expression is influenced by nonsynonymous polymorphisms associated with predisposition to spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:1525–34.
Hattori A, Matsumoto K, Mizutani S, Tsujimoto M. Genomic organization of the human adipocyte-derived leucine aminopeptidase gene and its relationship to the placental leucine aminopeptidase/oxytocinase gene. J Biochem. 2001;130:235–41.
Shifera AS, Hardin JA. Factors modulating expression of Renilla luciferase from control plasmids used in luciferase reporter gene assays. Anal Biochem. 2010;396:167–72.
Marinho KCT, Caputo BV, Noro-Filho GA, Giovani EM. Behçet's syndrome: literature review and clinical case report. Rev Española Cirugía Oral Maxilofac. 2016;38:105–10.
Kalra S, Silman A, Akman-Demir G, Bohlega S, Borhani-Haghighi A, Constantinescu CS, et al. Diagnosis and management of Neuro-Behcet's disease: international consensus recommendations. J Neurol. 2014;261:1662–76.
The Genomes Project Consortium. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature. 2015;526:68.
Takeuchi M, Ombrello MJ, Kirino Y, Erer B, Tugal-Tutkun I, Seyahi E, et al. A single endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase-1 protein allotype is a strong risk factor for Behcet's disease in HLA-B*51 carriers. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:2208–11.
Cortes A, Pulit SL, Leo PJ, Pointon JJ, Robinson PC, Weisman MH, et al. Major histocompatibility complex associations of ankylosing spondylitis are complex and involve further epistasis with ERAP1. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7146.
Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis C, the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet. 2010;42:985.
Ombrello MJ, Kirino Y, de Bakker PIW, Gül A, Kastner DL, Remmers EF. Behçet disease-associated MHC class I residues implicate antigen binding and regulation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111:8867–72.
Evans DM, Spencer CCA, Pointon JJ, Su Z, Harvey D, Kochan G, et al. Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis implicates peptide handling in the mechanism for HLA-B27 in disease susceptibility. Nat Genet. 2011;43:761–7.
Reeves E, James E. The role of polymorphic ERAP1 in autoinflammatory disease. Biosci Rep. 2018;38:BSR20171503.
Khan MA. Polymorphism of HLA-B27: 105 subtypes currently known. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013;15:362.
Garcia-Medel N, Sanz-Bravo A, Van Nguyen D, Galocha B, Gomez-Molina P, Martin-Esteban A, et al. Functional interaction of the ankylosing spondylitis-associated endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 polymorphism and HLA-B27 in vivo. Mol Cell Proteom: MCP. 2012;11:1416–29.
Guasp P, Alvarez-Navarro C, Gomez-Molina P, Martin-Esteban A, Marcilla M, Barnea E, et al. The peptidome of Behcet's disease-associated HLA-B*51:01 includes two subpeptidomes differentially shaped by endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:505–15.
Martín-Esteban A, Sanz-Bravo A, Guasp P, Barnea E, Admon A, López de Castro JA. Separate effects of the ankylosing spondylitis associated ERAP1 and ERAP2 aminopeptidases determine the influence of their combined phenotype on the HLA-B*27 peptidome. J Autoimmun. 2017;79:28–38.
Lopez de Castro JA, Alvarez-Navarro C, Brito A, Guasp P, Martin-Esteban A, Sanz-Bravo A. Molecular and pathogenic effects of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases ERAP1 and ERAP2 in MHC-I-associated inflammatory disorders: towards a unifying view. Mol Immunol. 2016;77:193–204.
Al-Okaily F, Al-Rashidi S, Al-Balawi M, Mustafa M, Arfin M, Al-Asmari A. Genetic association of HLA-A*26, -A*31, and -B*51 with Behcet’s disease in Saudi patients. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;9:167–73.
Radouane A, Oudghiri M, Chakib A, Naya A, Belhouari A, El Malki A, et al. HLA-B*27 allele associated to Behcet's disease and to anterior uveitis in Moroccan patients. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2011;69:419–24.
Gul A, Uyar FA, Inan M, Ocal L, Barrett JH, Aral O, et al. A weak association of HLA-B*2702 with Behcet/'s disease. Genes Immun. 2002;3:368–72.
Ahn J, Park Y. Human leukocyte antigen b27 and b51 double-positive behçet uveitis. Arch Ophthalmol. 2007;125:1375–80.
Mizuki N. HLA-C genotyping of patients with Behcet's disease in the Japanese population. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996;42:494–502.
Pirim I, Atasoy M, Ikbal M, Erdem T, Aliagaoglu C. HLA class I and class II genotyping in patients with Behcet's disease: a regional study of eastern part of Turkey. Tissue Antigens. 2004;64:293–7.
Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM, Oksvold P, Kampf C, Djureinovic D, Odeberg J, et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteom. 2014;13:397–406.
Consortium GT. The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat Genet. 2013;45:580–5.
Fruci D, Ferracuti S, Limongi MZ, Cunsolo V, Giorda E, Fraioli R. et al. Expression of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases in EBV-B cell lines from healthy donors and in leukemia/lymphoma, carcinoma, and melanoma cell lines. J Immunol. 2006;176:4869.
Hughes T, Coit P, Adler A, Yilmaz V, Aksu K, Duzgun N, et al. Identification of multiple independent susceptibility loci in the HLA region in Behcet's disease. Nat Genet. 2013;45:319–24.
Harvey D, Pointon JJ, Evans DM, Karaderi T, Farrar C, Appleton LH, et al. Investigating the genetic association between ERAP1 and ankylosing spondylitis. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:4204–12.
Adcock IM, Ito K, Barnes PJ. Glucocorticoids: effects on gene transcription. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2004;1:247–54.
Hayashi R, Wada H, Ito K, Adcock IM. Effects of glucocorticoids on gene transcription. Eur J Pharm. 2004;500:51–62.
Yousaf N, Low WY, Onipinla A, Mein C, Caulfield M, Munroe PB, et al. Differences between disease-associated endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) isoforms in cellular expression, interactions with tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNF-R1) and regulation by cytokines. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015;180:289–304.
Hanson AL, Cuddihy T, Haynes K, Loo D, Morton CJ, Oppermann U, et al. Genetic variants in ERAP1 and ERAP2 associated with immune-mediated diseases influence protein expression and isoform profile. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;70:255–65.
Conde-Jaldón M, Montes-Cano MA, García-Lozano JR, Ortiz-Fernández L, Ortego-Centeno N, González-León R, et al. Epistatic interaction of ERAP1 and HLA-B in Behçet disease: a replication study in the Spanish population. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e102100.
International Team for the Revision of the International Criteria for Behçet's D, Davatchi F, Assaad-Khalil S, Calamia KT, Crook JE, Sadeghi-Abdollahi B, et al. The international criteria for Behçet's disease (ICBD): a collaborative study of 27 countries on the sensitivity and specificity of the new criteria. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:338–47.
Acknowledgements
We thank Angels Mateu Regue for technical assistance with the luciferase reporter assays.
Funding
This work was supported by the Danish National Research Foundation (grant number 126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JDL, FCN, and RLM conceived the study. CD, JDL, FCN, and RLM designed the experiments. CD and RLM performed the experiments. JDL, JS, HU, and PA contributed materials and provided clinical information. CD and RLM analyzed the data. CD and RLM drafted the manuscript. All authors revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dimopoulou, C., Lundgren, J.D., Sundal, J. et al. Variant in ERAP1 promoter region is associated with low expression in a patient with a Behçet-like MHC-I-opathy. J Hum Genet 65, 325–335 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-019-0709-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-019-0709-y
This article is cited by
-
Down-regulation of ERAP1 mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer
BMC Cancer (2023)