Abstract
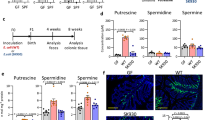
Saccharomyces boulardii is a yeast widely used in humans for the prevention and treatment of infectious enteritis and Clostridium difficile-associated enterocolopathies. After oral administration to human volunteers or growing rats, S. boulardii enhances markedly the expression of intestinal enzymes as well as the production of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor by mechanisms that remain unknown. We have analyzed the role of the yeast polyamines as potential mediators in the intestinal trophic response. In weanling rats (d 20 to d 30), a daily dose of 100 mg of lyophilized S. boulardii produced significant (p < 0.025) increases in sucrase (157%) and maltase (47%) activities. This dose corresponded to a total oral load of 678 nmol of polyamines per day (spermidine: 376 ± 32, sper-mine: 293 ± 26, putrescine: 9.5 ± 1.4 nmol/100 mg). Sper-mine, given orally to growing rats at doses nearly equivalent (500 nmol) to the load of polyamines provided by the yeast (678 nmol), reproduced similar enzymatic changes, including a 2.5-fold induction of sucrase, and enhanced maltase activity (+24%). Spermidine and spermine concentrations measured in the jejunal mucosa of treated rats were increased over matched controls by 21.4% (p < 0.005) and 21.9%, respectively (p < 0.002). After being centrifuged and filtered to discard residual yeast cells, 2-mL samples of jejunal and ileal fluid collected from 5. boulardii-treated rats by intestinal flushing contained higher levels of spermidine (48 and 60%) and spermine (150 and 316%) than did control rats. our data indicate that lyophilized S. boulardii exerts trophic effects on the small intestine that are likely mediated by the endoluminal release of spermine and spermidine.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buts, JP., Keyser, N. & Raedemaeker, L. Saccharomyces boulardii Enhances Rat Intestinal Enzyme Expression by Endoluminal Release of Polyamines. Pediatr Res 36, 522–527 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199410000-00019
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199410000-00019
This article is cited by
-
Pretreatment with probiotics ameliorate gut health and necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens, a substitute to antibiotics
AMB Express (2020)
-
Short-term feeding of probiotics and synbiotics modulates caecal microbiota during Salmonella Typhimurium infection but does not reduce shedding and invasion in chickens
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2020)
-
Clostridium difficile, the Difficult “Kloster” Fuelled by Antibiotics
Current Microbiology (2019)
-
Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 — die medizinische Hefe verbessert die Funktion intestinaler Enzyme
MMW - Fortschritte der Medizin (2019)
-
Complete genome sequence and comparative genomics of the probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii
Scientific Reports (2017)