Abstract
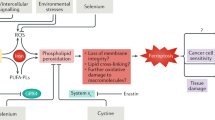
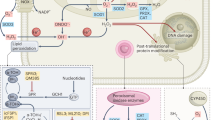
Mixed lineage kinase 3 (MLK3) functions in migration and/or invasion of several human cancers; however, the role of MLK3 in colorectal cancer (CRC) invasion is unknown. MLK3 is a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase kinase (MAP3K) which activates MAPK pathways through either kinase-dependent or -independent mechanisms. Human colorectal tumors display increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) or oxidative stress. ROS, such as H2O2, are important for carcinogenesis and activate MAPK signaling pathways. In human colorectal carcinoma (HCT116) cells treated with H2O2, extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) were activated and MLK3 exhibited reduced electrophoretic mobility (shift) in sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE), which was eliminated by phosphatase treatment. Pretreatment with the ROS scavenger N-acetyl-L-cysteine, the ERK1/2 inhibitor UO126, or ERK1/2 siRNA knockdown blocked the H2O2-induced shift of MLK3, while MLK3 inhibition with Cep1347 did not. In co-immunoprecipitation experiments performed on H2O2-treated HCT116 cells, endogenous MLK3 associated with endogenous ERK1/2 and B-Raf. Active ERK1 phosphorylated kinase dead FLAG-MLK3 in vitro, whereas ERK1 phosphorylation of kinase dead FLAG-MLK3-S705A-S758A was reduced. Both MLK3 siRNA knockdown and FLAG-MLK3-S705A-S758A expression decreased ERK1/2 activation in H2O2-treated cells. Prolonged H2O2 treatment activated ERK1/2 and promoted invasion of colon cancer cells, which was attenuated by MLK3 siRNA knockdown. Furthermore, S705A-S758A-FLAG-MLK3 demonstrated decreased oxidative-stress induced colon cancer cell invasion, but increased interaction with GST-B-Raf as compared with wild-type-FLAG-MLK3 in H2O2-treated cells. These results suggest oxidative stress stimulates an ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation of MLK3 on Ser705 and Ser758, which promotes MLK3-dependent B-Raf and ERK1/2 activation; this positive feedback loop enhances the invasion of colon cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ing YL, Leung IW, Heng HH, Tsui LC, Lassam NJ . MLK-3: identification of a widely-expressed protein kinase bearing an SH3 domain and a leucine zipper-basic region domain. Oncogene 1994; 9: 1745–1750.
Gallo KA, Mark MR, Scadden DT, Wang Z, Gu Q, Godowski PJ . Identification and characterization of SPRK, a novel src-homology 3 domain-containing proline-rich kinase with serine/threonine kinase activity. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 15092–15100.
Gallo KA, Johnson GL . Mixed-lineage kinase control of JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002; 3: 663–672.
Bock BC, Vacratsis PO, Qamirani E, Gallo KA . Cdc42-induced activation of the mixed-lineage kinase SPRK in vivo. Requirement of the Cdc42/Rac interactive binding motif and changes in phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 14231–14241.
Teramoto H, Coso OA, Miyata H, Igishi T, Miki T, Gutkind JS . Signaling from the small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 to the c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase pathway. A role for mixed lineage kinase 3/protein-tyrosine kinase 1, a novel member of the mixed lineage kinase family. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 27225–27228.
Leung IW, Lassam N . Dimerization via tandem leucine zippers is essential for the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase, MLK-3. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 32408–32415.
Du Y, Bock BC, Schachter KA, Chao M, Gallo KA . Cdc42 induces activation loop phosphorylation and membrane targeting of mixed lineage kinase 3. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 42984–42993.
Leung IW, Lassam N . The kinase activation loop is the key to mixed lineage kinase-3 activation via both autophosphorylation and hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 1961–1967.
Rana A, Gallo K, Godowski P, Hirai S, Ohno S, Zon L et al. The mixed lineage kinase SPRK phosphorylates and activates the stress-activated protein kinase activator, SEK-1. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 19025–19028.
Whitmarsh AJ, Cavanagh J, Tournier C, Yasuda J, Davis RJ . A mammalian scaffold complex that selectively mediates MAP kinase activation. Science 1998; 281: 1671–1674.
Tibbles LA, Ing YL, Kiefer F, Chan J, Iscove N, Woodgett JR et al. MLK-3 activates the SAPK/JNK and p38/RK pathways via SEK1 and MKK3/6. EMBO J 1996; 15: 7026–7035.
Marusiak AA, Edwards ZC, Hugo W, Trotter EW, Girotti MR, Stephenson NL et al. Mixed lineage kinases activate MEK independently of RAF to mediate resistance to RAF inhibitors. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 3901.
Chadee DN, Kyriakis JM . MLK3 is required for mitogen activation of B-Raf, ERK and cell proliferation. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 770–776.
Chadee DN, Xu D, Hung G, Andalibi A, Lim DJ, Luo Z et al. Mixed-lineage kinase 3 regulates B-Raf through maintenance of the B-Raf/Raf-1 complex and inhibition by the NF2 tumor suppressor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 4463–4468.
Swenson-Fields KI, Sandquist JC, Rossol-Allison J, Blat IC, Wennerberg K, Burridge K et al. MLK3 limits activated Galphaq signaling to Rho by binding to p63RhoGEF. Mol Cell 2008; 32: 43–56.
Chien ST, Lin SS, Wang CK, Lee YB, Chen KS, Fong Y et al. Acacetin inhibits the invasion and migration of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells by suppressing the p38alpha MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 2011; 350: 135–148.
Mishra P, Senthivinayagam S, Rangasamy V, Sondarva G, Rana B . Mixed lineage kinase-3/JNK1 axis promotes migration of human gastric cancer cells following gastrin stimulation. Mol Endocrinol 2010; 24: 598–607.
Chen J, Miller EM, Gallo KA . MLK3 is critical for breast cancer cell migration and promotes a malignant phenotype in mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene 2010; 29: 4399–4411.
Chen J, Gallo KA . MLK3 regulates paxillin phosphorylation in chemokine-mediated breast cancer cell migration and invasion to drive metastasis. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 4130–4140.
Cronan MR, Nakamura K, Johnson NL, Granger DA, Cuevas BD, Wang JG et al. Defining MAP3 kinases required for MDA-MB-231 cell tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene 2012; 31: 3889–3900.
Rattanasinchai C, Llewellyn BJ, Conrad SE, Gallo KA . MLK3 regulates FRA-1 and MMPs to drive invasion and transendothelial migration in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2017; 6: e345.
Zhan Y, Abi Saab WF, Modi N, Stewart AM, Liu J, Chadee DN . Mixed lineage kinase 3 is required for matrix metalloproteinase expression and invasion in ovarian cancer cells. Exp Cell Res 2012; 318: 1641–1648.
Zhang J, Lu L, Xiong Y, Qin W, Zhang Y, Qian Y et al. MLK3 promotes melanoma proliferation and invasion and is a target of microRNA-125b. Clin Exp Dermatol 2014; 39: 376–384.
Misek SA, Chen J, Schroeder L, Rattanasinchai C, Sample A, Sarkaria JN et al. EGFR signals through a DOCK180-MLK3 axis to drive glioblastoma cell invasion. Mol Cancer Res 2017.
Lan T, Ma W, Hong Z, Wu L, Chen X, Yuan Y . Long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 12 (SNHG12) promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis by targeting miR-199a/b-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2017; 36: 11.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2015. CA: Cancer J Clin 2015; 65: 5–29.
Perse M . Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer: cause or consequence? BioMed Res Int 2013; 2013: 725710.
Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang DG, Pae HO . Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: how can ros activate MAPK pathways? J Signal Transduct 2011; 2011: 792639.
Velho S, Oliveira C, Paredes J, Sousa S, Leite M, Matos P et al. Mixed lineage kinase 3 gene mutations in mismatch repair deficient gastrointestinal tumours. Hum Mol Genet 2010; 19: 697–706.
Liu H, Nishitoh H, Ichijo H, Kyriakis JM . Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 requires prior dissociation of the ASK1 inhibitor thioredoxin. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 2198–2208.
Schachter KA, Du Y, Lin A, Gallo KA . Dynamic positive feedback phosphorylation of mixed lineage kinase 3 by JNK reversibly regulates its distribution to Triton-soluble domains. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 19134–19144.
Maroney AC, Finn JP, Connors TJ, Durkin JT, Angeles T, Gessner G et al. Cep-1347 (KT7515), a semisynthetic inhibitor of the mixed lineage kinase family. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 25302–25308.
Gonzalez FA, Raden DL, Davis RJ . Identification of substrate recognition determinants for human ERK1 and ERK2 protein kinases. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 22159–22163.
Vacratsis PO, Phinney BS, Gage DA, Gallo KA . Identification of in vivo phosphorylation sites of MLK3 by mass spectrometry and phosphopeptide mapping. Biochemistry 2002; 41: 5613–5624.
Wlochowitz D, Haubrock M, Arackal J, Bleckmann A, Wolff A, Beissbarth T et al. Computational identification of key regulators in two different colorectal cancer cell lines. Front Genet 2016; 7: 42.
Lee HS, Hwang CY, Shin SY, Kwon KS, Cho KH . MLK3 is part of a feedback mechanism that regulates different cellular responses to reactive oxygen species. Sci Signal 2014; 7: ra52.
Xu Z, Kukekov NV, Greene LA . Regulation of apoptotic c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling by a stabilization-based feed-forward loop. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 9949–9959.
Wang C, Tao Y, Wang Y, Xu Z . Regulation of the protein stability of POSH and MLK family. Protein Cell 2010; 1: 871–878.
Xu Z, Kukekov NV, Greene LA . POSH acts as a scaffold for a multiprotein complex that mediates JNK activation in apoptosis. EMBO J 2003; 22: 252–261.
Blessing NA, Brockman AL, Chadee DN . The E3 ligase CHIP mediates ubiquitination and degradation of mixed-lineage kinase 3. Mol Cell Biol 2014; 34: 3132–3143.
Boulton TG, Gregory JS, Cobb MH . Purification and properties of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, an insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. Biochemistry 1991; 30: 278–286.
Partridge J, Flaherty P . An in vitro FluoroBlok tumor invasion assay. J Vis Exp 2009; 29: 1475.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants R15 CA199164 and R15 GM102831 (to DNC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schroyer, A., Stimes, N., Abi Saab, W. et al. MLK3 phosphorylation by ERK1/2 is required for oxidative stress-induced invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Oncogene 37, 1031–1040 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.396
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.396
This article is cited by
-
ROS production by mitochondria: function or dysfunction?
Oncogene (2024)
-
Disrupting PIAS3-mediated SUMOylation of MLK3 ameliorates poststroke neuronal damage and deficits in cognitive and sensorimotor behaviors
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2024)
-
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging biomaterials for anti-inflammatory diseases: from mechanism to therapy
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
MLK3 localizes mainly to the cytoplasm and promotes oxidative stress injury via a positive feedback loop
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2023)
-
NETISCE: a network-based tool for cell fate reprogramming
npj Systems Biology and Applications (2022)