Abstract
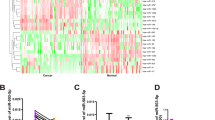
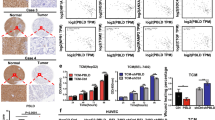
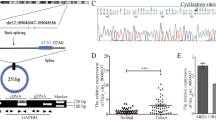
Mindin, a secreted, highly conserved extracellular matrix (ECM) protein, exerts a broad spectrum of effects on the innate immune system. However, its function in colorectal cancer (CRC) progression is not well established, and its upstream regulation mechanisms remain unclear. Contrary to previous reports, this study used two different enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits to show that the serum level of mindin was significantly decreased in CRC patients and that this decreased level is more significantly associated with the early stages of the disease. To explore the regulation of mindin, we used a bioinformatics approach to predict potential transcription factors and determined that early growth response factor (Egr)-1 directly regulates mindin expression at the transcriptional level using dual luciferase, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) DNA and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) methods. Egr-1 regulates mindin mRNA and protein expression in CRC cells, and the protein expression of both Egr-1 and mindin was significantly decreased in tumor lesions of patients compared with adjacent control tissues. Mindin is essential for Egr-1-mediated inhibition of endothelial cell tube formation, and mindin inhibits endotheliocyte proliferation, migration and angiogenic sprouts in vitro. Overexpression of mindin suppressed xenograft tumor growth by blocking angiogenesis instead of directly suppressing CRC cell proliferation. Mechanically, mindin inhibits the hypoxia-induced HIF-1a and VEGFA protein expression in CRC cells and the phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 in endothelial cells. The results suggest that the serum level of mindin can be used as a novel biomarker for early detection of CRC and that the Egr-1/mindin axis is a potential therapeutic target for the inhibition of angiogenesis in CRC development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fontao L, Stutzmann J, Gendry P, Launay JF . Regulation of the type II hemidesmosomal plaque assembly in intestinal epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res 1999; 250: 298–312.
Geiger B, Bershadsky A, Pankov R, Yamada KM . Transmembrane crosstalk between the extracellular matrix—cytoskeleton crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 793–805.
Quante M, Varga J, Wang TC, Greten FR . The gastrointestinal tumor microenvironment. Gastroenterology 2013; 145: 63–78.
Adams JC, Tucker RP . The thrombospondin type 1 repeat (TSR) superfamily: diverse proteins with related roles in neuronal development. Dev Dyn 2000; 218: 280–299.
He YW, Li H, Zhang J, Hsu CL, Lin E, Zhang N et al. The extracellular matrix protein mindin is a pattern-recognition molecule for microbial pathogens. Nat Immunol 2004; 5: 88–97.
Tan K, Lawler J . The structure of the Ca(2)+-binding, glycosylated F-spondin domain of F-spondin - a C2-domain variant in an extracellular matrix protein. BMC Struct Biol 2011; 11: 22.
Jia W, Li H, He YW . The extracellular matrix protein mindin serves as an integrin ligand and is critical for inflammatory cell recruitment. Blood 2005; 106: 3854–3859.
Jia W, Li H, He YW . Pattern recognition molecule mindin promotes intranasal clearance of influenza viruses. J Immunol 2008; 180: 6255–6261.
Guleng B, Lian YM, Ren JL . Mindin is upregulated during colitis and may activate NF-kappaB in a TLR-9 mediated manner. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16: 1070–1075.
Murakoshi M, Tanimoto M, Gohda T, Hagiwara S, Takagi M, Horikoshi S et al. Mindin: a novel marker for podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2011; 26: 2153–2160.
Zhu LH, Wang A, Luo P, Wang X, Jiang DS, Deng W et al. Mindin/Spondin 2 inhibits hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and obesity via interaction with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha in mice. J Hepatol 2014; 60: 1046–1054.
Qian X, Li C, Pang B, Xue M, Wang J, Zhou J . Spondin-2 (SPON2), a more prostate-cancer-specific diagnostic biomarker. PLoS One 2012; 7: e37225.
Simon I, Liu Y, Krall KL, Urban N, Wolfert RL, Kim NW et al. Evaluation of the novel serum markers B7-H4, Spondin 2, and DcR3 for diagnosis and early detection of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 2007; 106: 112–118.
Liao CH, Yeh SC, Huang YH, Chen RN, Tsai MM, Chen WJ et al. Positive regulation of spondin 2 by thyroid hormone is associated with cell migration and invasion. Endocrine-related Cancer 2010; 17: 99–111.
Schmid F, Wang Q, Huska MR, Andrade-Navarro MA, Lemm M, Fichtner I et al. SPON2, a newly identified target gene of MACC1, drives colorectal cancer metastasis in mice and is prognostic for colorectal cancer patient survival. Oncogene 2016; 35: 5942–5952.
Zhu LH, Huang L, Zhang X, Zhang P, Zhang SM, Guan H et al. Mindin regulates vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype and prevents neointima formation. Clin Sci 2015; 129: 129–145.
Liu Y, Fu L, Chen DG, Deeb SS . Identification of novel retinal target genes of thyroid hormone in the human WERI cells by expression microarray analysis. Vis Res 2007; 47: 2314–2326.
Romanuik TL, Ueda T, Le N, Haile S, Yong TM, Thomson T et al. Novel biomarkers for prostate cancer including noncoding transcripts. Am J Pathol 2009; 175: 2264–2276.
Bergers G, Hanahan D, Coussens LM . Angiogenesis and apoptosis are cellular parameters of neoplastic progression in transgenic mouse models of tumorigenesis. Int J Dev Biol 1998; 42: 995–1002.
Gashler A, Sukhatme VP . Early growth response protein 1 (Egr-1): prototype of a zinc-finger family of transcription factors. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 1995; 50: 191–224.
Liu M, Wang X, Peng Y, Shen S, Li G . Egr-1 regulates the transcription of NGX6 gene through a Sp1/Egr-1 overlapping site in the promoter. BMC Mol Biol 2014; 15: 14.
Shin SY, Kim JH, Baker A, Lim Y, Lee YH . Transcription factor Egr-1 is essential for maximal matrix metalloproteinase-9 transcription by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mol Cancer Res 2010; 8: 507–519.
Scharnhorst V, Menke AL, Attema J, Haneveld JK, Riteco N, van Steenbrugge GJ et al. EGR-1 enhances tumor growth and modulates the effect of the Wilms' tumor 1 gene products on tumorigenicity. Oncogene 2000; 19: 791–800.
Wirth M, Stojanovic N, Christian J, Paul MC, Stauber RH, Schmid RM et al. MYC and EGR1 synergize to trigger tumor cell death by controlling NOXA and BIM transcription upon treatment with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42: 10433–10447.
Ferraro B, Bepler G, Sharma S, Cantor A, Haura EB . EGR1 predicts PTEN and survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 1921–1926.
Liu J, Liu YG, Huang R, Yao C, Li S, Yang W et al. Concurrent down-regulation of Egr-1 and gelsolin in the majority of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2007; 4: 377–385.
Sobolewski C, Sanduja S, Blanco FF, Hu L, Dixon DA . Histone deacetylase inhibitors activate tristetraprolin expression through induction of early growth response protein 1 (EGR1) in colorectal cancer cells. Biomolecules 2015; 5: 2035–2055.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin 2007; 57: 43–66.
Folkman J, Beckner K . Angiogenesis imaging. Acad Radiol 2000; 7: 783–785.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000; 100: 57–70.
Bouck N, Stellmach V, Hsu SC . How tumors become angiogenic. Adv Cancer Res 1996; 69: 135–174.
Folkman J . Addressing tumor blood vessels. Nat Biotechnol 1997; 15: 510.
Munkley J, Elliott DJ . Hallmarks of glycosylation in cancer. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 35478–35489.
Hanahan D, Folkman J . Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 1996; 86: 353–364.
Zhang Q, Wang XQ, Wang J, Cui SJ, Lou XM, Yan B et al. Upregulation of spondin-2 predicts poor survival of colorectal carcinoma patients. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 15095–15110.
Fournier ML, Paulson A, Pavelka N, Mosley AL, Gaudenz K, Bradford WD et al. Delayed correlation of mRNA and protein expression in rapamycin-treated cells and a role for Ggc1 in cellular sensitivity to rapamycin. Mol Cell Proteomics 2010; 9: 271–284.
Feinstein Y, Klar A . The neuronal class 2 TSR proteins F-spondin and Mindin: a small family with divergent biological activities. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2004; 36: 975–980.
Parry R, Schneider D, Hudson D, Parkes D, Xuan JA, Newton A et al. Identification of a novel prostate tumor target, mindin/RG-1, for antibody-based radiotherapy of prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 8397–8405.
Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S, He J . Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2011. Chin J Cancer Res 2015; 27: 2–12.
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zeng H, Xia C, Zuo T et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2013. Cancer Lett 2017; 401: 63–71.
Zhang M, Zhao QC, Liu YP, Yang L, Zhu HM, Chhetri JK . Prognostic analysis and comparison of colon cancer in Han and Hui patients. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20: 5082–5086.
Jing F, Mao Y, Zhang Z, Li Y, Cai S, Li Q et al. The association of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 polymorphisms and lifestyle habits with colorectal cancer risk in a Chinese population. Tumour Biol 2014; 35: 9233–9240.
Qin M, Ma LQ, Tan J, Chen YR, Zhu LR, Lin R et al. Risk factors for colorectal neoplasms based on colonoscopy and pathological diagnoses of Chinese citizens: a multicenter, case-control study. Int J Colorectal Dis 2015; 30: 353–361.
Villani F, Busia A, Villani M, Vismara C, Viviani S, Bonfante V . Serum cytokine in response to chemo-radiotherapy for Hodgkin's disease. Tumori 2008; 94: 803–808.
Pusztai L, Mendoza TR, Reuben JM, Martinez MM, Willey JS, Lara J et al. Changes in plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines in response to paclitaxel chemotherapy. Cytokine 2004; 25: 94–102.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F . Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008; 454: 436–444.
Khachigian LM, Lindner V, Williams AJ, Collins T . Egr-1-induced endothelial gene expression: a common theme in vascular injury. Science 1996; 271: 1427–1431.
Muthukkumar S, Nair P, Sells SF, Maddiwar NG, Jacob RJ, Rangnekar VM . Role of EGR-1 in thapsigargin-inducible apoptosis in the melanoma cell line A375-C6. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15: 6262–6272.
Nguyen HQ, Hoffman-Liebermann B, Liebermann DA . The zinc finger transcription factor Egr-1 is essential for and restricts differentiation along the macrophage lineage. Cell 1993; 72: 197–209.
Santiago FS, Atkins DG, Khachigian LM . Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and regrowth after mechanical injury in vitro are Egr-1/NGFI-A-dependent. Am J Pathol 1999; 155: 897–905.
Duclot F, Kabbaj M . The role of early growth response 1 (EGR1) in brain plasticity and neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Behav Neurosci 2017; 11: 35.
Baron V, Adamson ED, Calogero A, Ragona G, Mercola D . The transcription factor Egr1 is a direct regulator of multiple tumor suppressors including TGFbeta1, PTEN, p53, and fibronectin. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 115–124.
Li D, Ilnytskyy Y, Kovalchuk A, Khachigian LM, Bronson RT, Wang B et al. Crucial role for early growth response-1 in the transcriptional regulation of miR-20b in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2013; 4: 1373–1387.
Zwang Y, Oren M, Yarden Y . Consistency test of the cell cycle: roles for p53 and EGR1. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 1051–1054.
Cai H, Liu X, Zheng J, Xue Y, Ma J, Li Z et al. Long non-coding RNA taurine upregulated 1 enhances tumor-induced angiogenesis through inhibiting microRNA-299 in human glioblastoma. Oncogene 2017; 36: 318–331.
Nie L, Wang S, Wang X, Rong P, Ma Y, Liu G et al. In vivo volumetric photoacoustic molecular angiography and therapeutic monitoring with targeted plasmonic nanostars. Small 2014; 10: 1441.
Acknowledgements
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81570496, 81370505, 81370591 and 91229201) and 973 programs (2015CB553800) in China supported this study.
Author contributions
Bayasi Guleng and Jian-Lin Ren designed the experiments; Li-fen Wang, Yuan-sheng Liu, Ping Li, Bing Yang, Xiao-Shen Cheng, Chuan-Xing Xiao, Jing-Jing Liu and Shao Li performed the experiments; Guleng B and Li-fen Wang wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LF., Liu, YS., Yang, B. et al. The extracellular matrix protein mindin attenuates colon cancer progression by blocking angiogenesis via Egr-1-mediated regulation. Oncogene 37, 601–615 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.359
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.359
This article is cited by
-
Friend or foe, the role of EGR-1 in cancer
Medical Oncology (2020)
-
FUS/circ_002136/miR-138-5p/SOX13 feedback loop regulates angiogenesis in Glioma
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
Independent prognostic genes and mechanism investigation for colon cancer
Biological Research (2018)
-
Egr-1 increases angiogenesis in cartilage via binding Netrin-1 receptor DCC promoter
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018)
-
CCL19 suppresses angiogenesis through promoting miR-206 and inhibiting Met/ERK/Elk-1/HIF-1α/VEGF-A pathway in colorectal cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2018)