Abstract
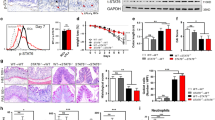
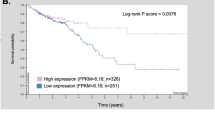
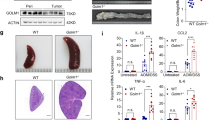
The hyperactivated Wnt/β-catenin signaling acts as a switch to induce epithelial to mesenchymal transition and promote colorectal cancer. However, due to its essential role in gut homeostasis, therapeutic targeting of this pathway has proven challenging. Additionally, IL-6/Stat-3 signaling, activated by microbial translocation through the dysregulated mucosal barrier in colon adenomas, facilitates the adenoma to adenocarcinomas transition. However, inter-dependence between these signaling pathways and key mucosal barrier components in regulating colon tumorigenesis and cancer progression remains unclear. In current study, we have discovered, using a comprehensive investigative regimen, a novel and tissue-specific role of claudin-3, a tight junction integral protein, in inhibiting colon cancer progression by serving as the common rheostat of Stat-3 and Wnt-signaling activation. Loss of claudin-3 also predicted poor patient survival. These findings however contrasted an upregulated claudin-3 expression in other cancer types and implicated role of the epigenetic regulation. Claudin-3−/− mice revealed dedifferentiated and leaky colonic epithelium, and developed invasive adenocarcinoma when subjected to colon cancer. Wnt-signaling hyperactivation, albeit in GSK-3β independent manner, differentiated colon cancer in claudin-3−/− mice versus WT-mice. Claudin-3 loss also upregulated the gp130/IL6/Stat3 signaling in colonic epithelium potentially assisted by infiltrating immune components. Genetic and pharmacological studies confirmed that claudin-3 loss induces Wnt/β-catenin activation, which is further exacerbated by Stat-3-activation and help promote colon cancer. Overall, these novel findings identify claudin-3 as a therapeutic target for inhibiting overactivation of Wnt-signaling to prevent CRC malignancy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grivennikov SI, Wang K, Mucida D, Stewart CA, Schnabl B, Jauch D et al. Adenoma-linked barrier defects and microbial products drive IL-23/IL-17-mediated tumour growth. Nature 2012; 491: 254–258.
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S et al. IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell 2009; 15: 103–113.
Soler AP, Miller RD, Laughlin KV, Carp NZ, Klurfeld DM, Mullin JM . Increased tight junctional permeability is associated with the development of colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 1999; 20: 1425–1431.
Mullin JM, McGinn MT . Epidermal growth factor-induced mitogenesis in kidney epithelial cells (LLC-PK1). Cancer Res 1988; 48: 4886–4891.
Mullin JM, McGinn MT . Effects of diacylglycerols on LLC-PK1 renal epithelia: similarity to phorbol ester tumor promoters. J Cell Physiol 1988; 134: 357–366.
Singh AB, Dhawan P . Claudins and cancer: fall of the soldiers entrusted to protect the gate and keep the barrier intact. Semin cell dev biol 2015; 42: 58–65.
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, Barker N, Clevers H, Vogelstein B et al. Activation of beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in beta-catenin or APC. Science 1997; 275: 1787–1790.
Anastas JN, Moon RT . WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2013; 13: 11–26.
Holmes JL, Van Itallie CM, Rasmussen JE, Anderson JM . Claudin profiling in the mouse during postnatal intestinal development and along the gastrointestinal tract reveals complex expression patterns. Gene Expr Patterns 2006; 6: 581–588.
de Souza WF, Fortunato-Miranda N, Robbs BK, de Araujo WM, de-Freitas-Junior JC, Bastos LG et al. Claudin-3 overexpression increases the malignant potential of colorectal cancer cells: roles of ERK1/2 and PI3K-Akt as modulators of EGFR signaling. PLoS One 2013; 8: e74994.
Long H, Crean CD, Lee WH, Cummings OW, Gabig TG . Expression of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin receptors claudin-3 and claudin-4 in prostate cancer epithelium. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 7878–7881.
Royer C, Lu X . Epithelial cell polarity: a major gatekeeper against cancer? Cell Death Differ 2011; 18: 1470–1477.
Cereijido M, Contreras RG, Shoshani L, Flores-Benitez D, Larre I . Tight junction and polarity interaction in the transporting epithelial phenotype. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008; 1778: 770–793.
Matsumoto H, Erickson RH, Gum JR, Yoshioka M, Gum E, Kim YS . Biosynthesis of alkaline phosphatase during differentiation of the human colon cancer cell line Caco-2. Gastroenterology 1990; 98 (5 Pt 1): 1199–1207.
Dzierzewicz Z, Orchel A, Weglarz L, Latocha M, Wilczok T . Changes in the cellular behaviour of human colonic cell line Caco-2 in response to butyrate treatment. Acta Biochim Pol 2002; 49: 211–220.
Deschenes C, Vezina A, Beaulieu JF, Rivard N . Role of p27(Kip1) in human intestinal cell differentiation. Gastroenterology 2001; 120: 423–438.
Kedinger M, Simon-Assmann P, Bouziges F, Arnold C, Alexandre E, Haffen K . Smooth muscle actin expression during rat gut development and induction in fetal skin fibroblastic cells associated with intestinal embryonic epithelium. Differentiation 1990; 43: 87–97.
Rajput A, Dominguez San Martin I, Rose R, Beko A, Levea C, Sharratt E et al. Characterization of HCT116 human colon cancer cells in an orthotopic model. J surg res 2008; 147: 276–281.
Dhawan P, Singh AB, Deane NG, No Y, Shiou SR, Schmidt C et al. Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1765–1776.
Vucic EA, Brown CJ, Lam WL . Epigenetics of cancer progression. Pharmacogenomics 2008; 9: 215–234.
Honda H, Pazin MJ, D'Souza T, Ji H, Morin PJ . Regulation of the CLDN3 gene in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer biol ther 2007; 6: 1733–1742.
Moser AR, Luongo C, Gould KA, McNeley MK, Shoemaker AR, Dove WF . ApcMin: a mouse model for intestinal and mammary tumorigenesis. Eur j cancer 1995; 31A: 1061–1064.
Thaker AI, Shaker A, Rao MS, Ciorba MA . Modeling colitis-associated cancer with azoxymethane (AOM) and dextran sulfate sodium (DSS). J vis exp 2012; e-pub ahead of print 11 September 2012; doi:10.3791/4100.
Dhawan P, Ahmad R, Chaturvedi R, Smith JJ, Midha R, Mittal MK et al. Claudin-2 expression increases tumorigenicity of colon cancer cells: role of epidermal growth factor receptor activation. Oncogene 2011; 30: 3234–3247.
Bhat AA, Pope JL, Smith JJ, Ahmad R, Chen X, Washington MK et al. Claudin-7 expression induces mesenchymal to epithelial transformation (MET) to inhibit colon tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2015; 34: 4570–4580.
Dube PE, Yan F, Punit S, Girish N, McElroy SJ, Washington MK et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibits colitis-associated cancer in mice. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 2780–2792.
Ngan CY, Yamamoto H, Seshimo I, Tsujino T, Man-i M, Ikeda JI et al. Quantitative evaluation of vimentin expression in tumour stroma of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2007; 96: 986–992.
Nagaraja GM, Othman M, Fox BP, Alsaber R, Pellegrino CM, Zeng Y et al. Gene expression signatures and biomarkers of noninvasive and invasive breast cancer cells: comprehensive profiles by representational difference analysis, microarrays and proteomics. Oncogene 2006; 25: 2328–2338.
Jiang L, Yang YD, Fu L, Xu W, Liu D, Liang Q et al. CLDN3 inhibits cancer aggressiveness via Wnt-EMT signaling and is a potential prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2014; 5: 7663–7676.
Hinoi T, Yamamoto H, Kishida M, Takada S, Kishida S, Kikuchi A . Complex formation of adenomatous polyposis coli gene product and axin facilitates glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta-dependent phosphorylation of beta-catenin and down-regulates beta-catenin. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 34399–34406.
Giles RH, van Es JH, Clevers H . Caught up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 2003; 1653: 1–24.
Pramanik KC, Fofaria NM, Gupta P, Ranjan A, Kim S-H, Srivastava SK . Inhibition of β-Catenin signaling suppresses pancreatic tumor growth by disrupting nuclear β-Catenin/TCF-1 complex: Critical role of STAT-3. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 11561–11574.
Wu J, Keng VW, Patmore DM, Kendall JJ, Patel AV, Jousma E et al. Insertional mutagenesis identifies a STAT3/Arid1b/beta-catenin pathway driving neurofibroma initiation. Cell Rep 2016; 14: 1979–1990.
Tenbaum SP, Ordonez-Moran P, Puig I, Chicote I, Arques O, Landolfi S et al. beta-catenin confers resistance to PI3K and AKT inhibitors and subverts FOXO3a to promote metastasis in colon cancer. Nat Med 2012; 18: 892–901.
Gavert N, Ben-Ze'ev A . beta-Catenin signaling in biological control and cancer. J Cell Biochem 2007; 102: 820–828.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R . STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 798–809.
Pramanik KC, Fofaria NM, Gupta P, Ranjan A, Kim SH, Srivastava SK . Inhibition of beta-catenin signaling suppresses pancreatic tumor growth by disrupting nuclear beta-catenin/TCF-1 complex: critical role of STAT-3. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 11561–11574.
Heinzelmann-Schwarz VA, Gardiner-Garden M, Henshall SM, Scurry J, Scolyer RA, Davies MJ et al. Overexpression of the cell adhesion molecules DDR1, Claudin 3, and Ep-CAM in metaplastic ovarian epithelium and ovarian cancer. Clin cancer res 2004; 10: 4427–4436.
Bartholow TL, Chandran UR, Becich MJ, Parwani AV . Immunohistochemical profiles of claudin-3 in primary and metastatic prostatic adenocarcinoma. Diagn pathol 2011; 6: 12.
de Araujo WM, Vidal FC, de Souza WF, de Freitas JC Jr, de Souza W, Morgado-Diaz JA . PI3K/Akt and GSK-3beta prevents in a differential fashion the malignant phenotype of colorectal cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2010; 136: 1773–1782.
Kwon MJ, Kim SS, Choi YL, Jung HS, Balch C, Kim SH et al. Derepression of CLDN3 and CLDN4 during ovarian tumorigenesis is associated with loss of repressive histone modifications. Carcinogenesis 2010; 31: 974–983.
Yaqinuddin A, Qureshi SA, Qazi R, Farooq S, Abbas F . DNMT1 silencing affects locus specific DNA methylation and increases prostate cancer derived PC3 cell invasiveness. J Urol 2009; 182: 756–761.
Singh AB, Dhawan P . Claudins and cancer: fall of the soldiers entrusted to protect the gate and keep the barrier intact. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2015; 42: 58–65.
Patel RM, Myers LS, Kurundkar AR, Maheshwari A, Nusrat A, Lin PW . Probiotic bacteria induce maturation of intestinal claudin 3 expression and barrier function. Am J Pathol 2012; 180: 626–635.
Ramalingam A, Wang X, Gabello M, Valenzano MC, Soler AP, Ko A et al. Dietary methionine restriction improves colon tight junction barrier function and alters claudin expression pattern. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2010; 299: C1028–C1035.
Gibson DL, Ma C, Rosenberger CM, Bergstrom KS, Valdez Y, Huang JT et al. Toll-like receptor 2 plays a critical role in maintaining mucosal integrity during Citrobacter rodentium-induced colitis. Cell Microbiol 2008; 10: 388–403.
Clark JA, Doelle SM, Halpern MD, Saunders TA, Holubec H, Dvorak K et al. Intestinal barrier failure during experimental necrotizing enterocolitis: protective effect of EGF treatment. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2006; 291: G938–G949.
Turgeon N, Blais M, Gagne JM, Tardif V, Boudreau F, Perreault N et al. HDAC1 and HDAC2 restrain the intestinal inflammatory response by regulating intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. PLoS One 2013; 8: e73785.
Lee J, Kim JC, Lee SE, Quinley C, Kim H, Herdman S et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) protein suppresses adenoma-to-carcinoma transition in Apcmin/+ mice via regulation of Snail-1 (SNAI) protein stability. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 18182–18189.
Henttinen T, Levy DE, Silvennoinen O, Hurme M . Activation of the signal transducer and transcription (STAT) signaling pathway in a primary T cell response. Critical role for IL-6. J Immunol 1995; 155: 4582–4587.
Mullin JM . Epithelial barriers, compartmentation, and cancer. Sci STKE 2004; 2004: pe2.
Ray S, Ju X, Sun H, Finnerty CC, Herndon DN, Brasier AR . The IL-6 trans-signaling-STAT3 pathway mediates ECM and cellular proliferation in fibroblasts from hypertrophic scar. J Invest Dermatol 2013; 133: 1212–1220.
Tadlaoui Hbibi A, Laguillier C, Souissi I, Lesage D, Le Coquil S, Cao A et al. Efficient killing of SW480 colon carcinoma cells by a signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 hairpin decoy oligodeoxynucleotide—interference with interferon-gamma-STAT1-mediated killing. FEBS J 2009; 276: 2505–2515.
Ahmad R, Chaturvedi R, Olivares-Villagomez D, Habib T, Asim M, Shivesh P et al. Targeted colonic claudin-2 expression renders resistance to epithelial injury, induces immune suppression, and protects from colitis. Mucosal Immunol 2014; 7: 1340–1353.
Kooij G, Kopplin K, Blasig R, Stuiver M, Koning N, Goverse G et al. Disturbed function of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier aggravates neuro-inflammation. Acta Neuropathol 2014; 128: 267–277.
Krishnan M, Singh AB, Smith JJ, Sharma A, Chen X, Eschrich S et al. HDAC inhibitors regulate claudin-1 expression in colon cancer cells through modulation of mRNA stability. Oncogene 2010; 29: 305–312.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by BX002086 (PD), DK088902 and BX002761 (ABS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, R., Kumar, B., Chen, Z. et al. Loss of claudin-3 expression induces IL6/gp130/Stat3 signaling to promote colon cancer malignancy by hyperactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncogene 36, 6592–6604 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.259
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.259
This article is cited by
-
Activated fibroblasts modify keratinocyte stem niche through TET1 and IL-6 to promote their rapid transformation in a mouse model of prenatal arsenic exposure
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Intestinal dysbiosis exacerbates the pathogenesis of psoriasis-like phenotype through changes in fatty acid metabolism
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Preliminary study on the mechanism of POFUT1 in colorectal cancer
Medical Oncology (2023)
-
Downregulation of SLC9A8 Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer Cells via the IL6-JAK1/STAT3 Signaling Pathway
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2023)
-
Exploring the complex role of gut microbiome in the development of precision medicine strategies for targeting microbial imbalance-induced colon cancer
Folia Microbiologica (2023)