Abstract
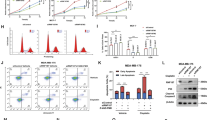
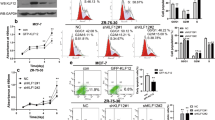
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4, GKLF) is a zinc-finger transcription factor involved in a large variety of cellular processes, including apoptosis, cell cycle progression, as well as stem cell renewal. KLF4 is critical for cell fate decision and has an ambivalent role in tumorigenesis. Emerging data keep reminding us that KLF4 dysregulation either facilitates or impedes tumor progression, making it important to clarify the regulating network of KLF4. Like most transcription factors, KLF4 has a rather short half-life within the cell and its turnover must be carefully orchestrated by ubiquitination and ubiquitin–proteasome system. To better understand the mechanism of KLF4 ubiquitination, we performed a genome-wide screen of E3 ligase small interfering RNA library based on western blot and identified SCF-FBXO32 to be a new E3 ligase, which is responsible for KLF4 ubiquitination and degradation. The F-box domain is critical for FBXO32-dependent KLF4 ubiquitination and degradation. Furthermore, we demonstrated that FBXO32 physically interacts with the N-terminus (1–60 aa) of KLF4 via its C-terminus (228–355 aa) and directly targets KLF4 for ubiquitination and degradation. We also found out that p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway may be implicated in FBXO32-mediated ubiquitination of KLF4, as p38 kinase inhibitor coincidently abrogates endogenous KLF4 ubiquitination and degradation, as well as FBXO32-dependent exogenous KLF4 ubiquitination and degradation. Finally, FBXO32 inhibits colony formation in vitro and primary tumor initiation and growth in vivo through targeting KLF4 into degradation. Our findings thus further elucidate the tumor-suppressive function of FBXO32 in breast cancer. These results expand our understanding of the posttranslational modification of KLF4 and of its role in breast cancer development and provide a potential target for diagnosis and therapeutic treatment of breast cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garrett-Sinha LA, Eberspaecher H, Seldin MF, de Crombrugghe B . A gene for a novel zinc-finger protein expressed in differentiated epithelial cells and transiently in certain mesenchymal cells. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 31384–31390.
Rowland BD, Peeper DS . KLF4, p21 and context-dependent opposing forces in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 11–23.
Ghaleb AM, Katz JP, Kaestner KH, Du JX, Yang VW . Kruppel-like factor 4 exhibits antiapoptotic activity following gamma-radiation-induced DNA damage. Oncogene 2007; 26: 2365–2373.
McConnell BB, Yang VW . Mammalian Kruppel-like factors in health and diseases. Physiol Rev 2010; 90: 1337–1381.
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S . Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006; 126: 663–676.
Shields JM, Christy RJ, Yang VW . Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expressed during growth arrest. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 20009–20017.
Zhang W, Geiman DE, Shields JM, Dang DT, Mahatan CS, Kaestner KH et al. The gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor (Kruppel-like factor 4) mediates the transactivating effect of p53 on the p21WAF1/Cip1 promoter. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 18391–18398.
Yoon HS, Ghaleb AM, Nandan MO, Hisamuddin IM, Dalton WB, Yang VW . Kruppel-like factor 4 prevents centrosome amplification following gamma-irradiation-induced DNA damage. Oncogene 2005; 24: 4017–4025.
Shie JL, Chen ZY, Fu M, Pestell RG, Tseng CC . Gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor represses cyclin D1 promoter activity through Sp1 motif. Nucleic Acids Res 2000; 28: 2969–2976.
Yoon HS, Yang VW . Requirement of Kruppel-like factor 4 in preventing entry into mitosis following DNA damage. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 5035–5041.
Rowland BD, Bernards R, Peeper DS . The KLF4 tumour suppressor is a transcriptional repressor of p53 that acts as a context-dependent oncogene. Nat Cell Biol 2005; 7: 1074–1082.
Zhou Q, Hong Y, Zhan Q, Shen Y, Liu Z . Role for Kruppel-like factor 4 in determining the outcome of p53 response to DNA damage. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 8284–8292.
Zhao W, Hisamuddin IM, Nandan MO, Babbin BA, Lamb NE, Yang VW . Identification of Kruppel-like factor 4 as a potential tumor suppressor gene in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2004; 23: 395–402.
Wei D, Kanai M, Huang S, Xie K . Emerging role of KLF4 in human gastrointestinal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2006; 27: 23–31.
Wang N, Liu ZH, Ding F, Wang XQ, Zhou CN, Wu M . Down-regulation of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expression in esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8: 966–970.
Tetreault MP, Yang Y, Travis J, Yu QC, Klein-Szanto A, Tobias JW et al. Esophageal squamous cell dysplasia and delayed differentiation with deletion of kruppel-like factor 4 in murine esophagus. Gastroenterology 2010; 139: e179.
Ohnishi S, Ohnami S, Laub F, Aoki K, Suzuki K, Kanai Y et al. Downregulation and growth inhibitory effect of epithelial-type Kruppel-like transcription factor KLF4, but not KLF5, in bladder cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 308: 251–256.
Hu W, Hofstetter WL, Li H, Zhou Y, He Y, Pataer A et al. Putative tumor-suppressive function of Kruppel-like factor 4 in primary lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 5688–5695.
Wei D, Wang L, Yan Y, Jia Z, Gagea M, Li Z et al. KLF4 is essential for induction of cellular identity change and acinar-to-ductal reprogramming during early pancreatic carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell 2016; 29: 324–338.
Foster KW, Frost AR, McKie-Bell P, Lin CY, Engler JA, Grizzle WE et al. Increase of GKLF messenger RNA and protein expression during progression of breast cancer. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 6488–6495.
Yu F, Li J, Chen H, Fu J, Ray S, Huang S et al. Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is required for maintenance of breast cancer stem cells and for cell migration and invasion. Oncogene 2011; 30: 2161–2172.
Hu D, Wan Y . Regulation of Kruppel-like factor 4 by the anaphase promoting complex pathway is involved in TGF-beta signaling. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 6890–6901.
Kim MO, Kim SH, Cho YY, Nadas J, Jeong CH, Yao K et al. ERK1 and ERK2 regulate embryonic stem cell self-renewal through phosphorylation of Klf4. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2012; 19: 283–290.
Gamper AM, Qiao X, Kim J, Zhang L, DeSimone MC, Rathmell WK et al. Regulation of KLF4 turnover reveals an unexpected tissue-specific role of pVHL in tumorigenesis. Mol Cell 2012; 45: 233–243.
Hu D, Zhou Z, Davidson NE, Huang Y, Wan Y . Novel insight into KLF4 proteolytic regulation in estrogen receptor signaling and breast carcinogenesis. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 13584–13597.
Gomes MD, Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Navon A, Goldberg AL . Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly expressed during muscle atrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 14440–14445.
Kipreos ET, Pagano M . The F-box protein family. Genome Biol 2000; 1: REVIEWS3002.1–REVIEWS3002.7.
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK, Nunez L, Clarke BA et al. Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 2001; 294: 1704–1708.
Skaar JR, Pagan JK, Pagano M . SnapShot: F box proteins I. Cell 2009; 137: 1160–1160 e1161.
Jogo M, Shiraishi S, Tamura TA . Identification of MAFbx as a myogenin-engaged F-box protein in SCF ubiquitin ligase. FEBS Lett 2009; 583: 2715–2719.
Chou JL, Su HY, Chen LY, Liao YP, Hartman-Frey C, Lai YH et al. Promoter hypermethylation of FBXO32, a novel TGF-beta/SMAD4 target gene and tumor suppressor, is associated with poor prognosis in human ovarian cancer. Lab Invest 2010; 90: 414–425.
Guo W, Zhang M, Guo Y, Shen S, Guo X, Dong Z . FBXO32, a new TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway target gene, is epigenetically inactivated in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. Neoplasma 2015; 62: 646–657.
Mei Z, Zhang D, Hu B, Wang J, Shen X, Xiao W . FBXO32 targets c-Myc for proteasomal degradation and inhibits c-Myc activity. J Biol Chem 2015; 290: 16202–16214.
Chen ZY, Wang X, Zhou Y, Offner G, Tseng CC . Destabilization of Kruppel-like factor 4 protein in response to serum stimulation involves the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 10394–10400.
Sarikas A, Hartmann T, Pan ZQ . The cullin protein family. Genome Biol 2011; 12: 220.
Cardozo T, Pagano M . The SCF ubiquitin ligase: insights into a molecular machine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5: 739–751.
Tan J, Yang X, Zhuang L, Jiang X, Chen W, Lee PL et al. Pharmacologic disruption of polycomb-repressive complex 2-mediated gene repression selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 1050–1063.
Wu Z, Lee ST, Qiao Y, Li Z, Lee PL, Lee YJ et al. Polycomb protein EZH2 regulates cancer cell fate decision in response to DNA damage. Cell Death Differ 2011; 18: 1771–1779.
Foster KW, Liu Z, Nail CD, Li X, Fitzgerald TJ, Bailey SK et al. Induction of KLF4 in basal keratinocytes blocks the proliferation-differentiation switch and initiates squamous epithelial dysplasia. Oncogene 2005; 24: 1491–1500.
Shie JL, Chen ZY, O'Brien MJ, Pestell RG, Lee ME, Tseng CC . Role of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor in colonic cell growth and differentiation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000; 279: G806–G814.
Zheng H, Shen M, Zha YL, Li W, Wei Y, Blanco MA et al. PKD1 phosphorylation-dependent degradation of SNAIL by SCF-FBXO11 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cancer Cell 2014; 26: 358–373.
Tian X, Dai S, Sun J, Jin G, Jiang S, Meng F et al. F-box protein FBXO22 mediates polyubiquitination and degradation of KLF4 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 22767–22775.
Li YP, Chen Y, John J, Moylan J, Jin B, Mann DL et al. TNF-alpha acts via p38 MAPK to stimulate expression of the ubiquitin ligase atrogin1/MAFbx in skeletal muscle. FASEB J 2005; 19: 362–370.
Derbre F, Ferrando B, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Sanchis-Gomar F, Martinez-Bello VE, Olaso-Gonzalez G et al. Inhibition of xanthine oxidase by allopurinol prevents skeletal muscle atrophy: role of p38 MAPKinase and E3 ubiquitin ligases. PloS One 2012; 7: e46668.
Wagner EF, Nebreda AR . Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 537–549.
Dolado I, Swat A, Ajenjo N, De Vita G, Cuadrado A, Nebreda AR . p38alpha MAP kinase as a sensor of reactive oxygen species in tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2007; 11: 191–205.
Hui L, Bakiri L, Mairhorfer A, Schweifer N, Haslinger C, Kenner L et al. p38alpha suppresses normal and cancer cell proliferation by antagonizing the JNK-c-Jun pathway. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 741–749.
Ventura JJ, Tenbaum S, Perdiguero E, Huth M, Guerra C, Barbacid M et al. p38alpha MAP kinase is essential in lung stem and progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 750–758.
Santner SJ, Dawson PJ, Tait L, Soule HD, Eliason J, Mohamed AN et al. Malignant MCF10CA1 cell lines derived from premalignant human breast epithelial MCF10AT cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2001; 65: 101–110.
Luo A, Yu X, Li G, Ma G, Chen H, Ding F et al. Differentiation-associated genes regulated by c-Jun and decreased in the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PloS One 2014; 9: e96610.
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81130043 and 81420108025) and grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology (2016YFC1302100 and 2013CB911004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Liu, Y., Zhu, R. et al. FBXO32 suppresses breast cancer tumorigenesis through targeting KLF4 to proteasomal degradation. Oncogene 36, 3312–3321 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.479
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.479
This article is cited by
-
FBXO32-mediated degradation of PTEN promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression
Cell Death & Disease (2024)
-
USP39 stabilizes β-catenin by deubiquitination and suppressing E3 ligase TRIM26 pre-mRNA maturation to promote HCC progression
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
LINC00629 protects osteosarcoma cell from ER stress-induced apoptosis and facilitates tumour progression by elevating KLF4 stability
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2022)
-
DUB3/KLF4 combats tumor growth and chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
FBXO32 targets PHPT1 for ubiquitination to regulate the growth of EGFR mutant lung cancer
Cellular Oncology (2022)