Abstract
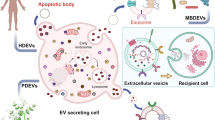
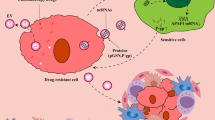
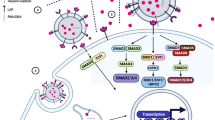
Intercellular communication sets the pace for transformed cells to survive and to thrive. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), such as exosomes, microvesicles and large oncosomes, are involved in this process shuttling reciprocal signals and other molecules between transformed and stromal cells, including fibroblasts, endothelial and immune cells. As a result, these cells are adapted or recruited to a constantly evolving cancer microenvironment. Moreover, EVs take part in the response to anticancer therapeutics not least by promoting drug resistance throughout the targeted tumor. Finally, circulating EVs can also transport important molecules to remote destinations in order to prime metastatic niches in an otherwise healthy tissue. Although the understanding of EV biology remains a major challenge in the field, their characteristics create new opportunities for advances in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abels ER, Breakefield XO . Introduction to extracellular vesicles: biogenesis, RNA cargo selection, content, release, and uptake. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2016; 36: 301–312.
Colombo M, Raposo G, Thery C . Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2014; 30: 255–289.
Khan S, Jutzy JM, Valenzuela MM, Turay D, Aspe JR, Ashok A et al. Plasma-derived exosomal survivin, a plausible biomarker for early detection of prostate cancer. PLoS One 2012; 7: e46737.
Melo SA, Luecke LB, Kahlert C, Fernandez AF, Gammon ST, Kaye J et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015; 523: 177–182.
Ogata-Kawata H, Izumiya M, Kurioka D, Honma Y, Yamada Y, Furuta K et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PLoS One 2014; 9: e92921.
Cazzoli R, Buttitta F, Di Nicola M, Malatesta S, Marchetti A, Rom WN et al. microRNAs derived from circulating exosomes as noninvasive biomarkers for screening and diagnosing lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2013; 8: 1156–1162.
Wang T, Gilkes DM, Takano N, Xiang L, Luo W, Bishop CJ et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors and RAB22A mediate formation of microvesicles that stimulate breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: E3234–E3242.
Parolini I, Federici C, Raggi C, Lugini L, Palleschi S, De Milito A et al. Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 34211–34222.
Yu X, Harris SL, Levine AJ . The regulation of exosome secretion: a novel function of the p53 protein. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 4795–4801.
Amorim M, Fernandes G, Oliveira P, Martins-de-Souza D, Dias-Neto E, Nunes D . The overexpression of a single oncogene (ERBB2/HER2) alters the proteomic landscape of extracellular vesicles. Proteomics 2014; 14: 1472–1479.
Ji H, Erfani N, Tauro BJ, Kapp EA, Zhu HJ, Moritz RL et al. Difference gel electrophoresis analysis of Ras-transformed fibroblast cell-derived exosomes. Electrophoresis 2008; 29: 2660–2671.
Clark DJ, Fondrie WE, Yang A, Mao L . Triple SILAC quantitative proteomic analysis reveals differential abundance of cell signaling proteins between normal and lung cancer-derived exosomes. J Proteomics 2016; 133: 161–169.
Ekstrom EJ, Bergenfelz C, von Bulow V, Serifler F, Carlemalm E, Jonsson G et al. WNT5A induces release of exosomes containing pro-angiogenic and immunosuppressive factors from malignant melanoma cells. Mol Cancer 2014; 13: 88.
Meckes Jr DG, Gunawardena HP, Dekroon RM, Heaton PR, Edwards RH, Ozgur S et al. Modulation of B-cell exosome proteins by gamma herpesvirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: E2925–E2933.
Halestrap AP . The monocarboxylate transporter family—structure and functional characterization. IUBMB Life 2012; 64: 1–9.
Halestrap AP, Wilson MC . The monocarboxylate transporter family—role and regulation. IUBMB Life 2012; 64: 109–119.
Le Floch R, Chiche J, Marchiq I, Naiken T, Ilc K, Murray CM et al. CD147 subunit of lactate/H+ symporters MCT1 and hypoxia-inducible MCT4 is critical for energetics and growth of glycolytic tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 16663–16668.
Webb BA, Chimenti M, Jacobson MP, Barber DL . Dysregulated pH: a perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2011; 11: 671–677.
Porporato PE, Payen VL, Baselet B, Sonveaux P . Metabolic changes associated with tumor metastasis, part 2: mitochondria, lipid and amino acid metabolism. Cell Mol Life Sci 2016; 73: 1349–1363.
Ronquist KG, Sanchez C, Dubois L, Chioureas D, Fonseca P, Larsson A et al. Energy-requiring uptake of prostasomes and PC3 cell-derived exosomes into non-malignant and malignant cells. J Extracell Vesicles 2016; 5: 29877.
Zhao H, Yang L, Baddour J, Achreja A, Bernard V, Moss T et al. Tumor microenvironment derived exosomes pleiotropically modulate cancer cell metabolism. Elife 2016; 5.
Kerr EM, Gaude E, Turrell FK, Frezza C, Martins CP . Mutant Kras copy number defines metabolic reprogramming and therapeutic susceptibilities. Nature 2016; 531: 110–113.
Liou GY, Doppler H, DelGiorno KE, Zhang L, Leitges M, Crawford HC et al. Mutant KRas-induced mitochondrial oxidative stress in acinar cells upregulates EGFR signaling to drive formation of pancreatic precancerous lesions. Cell Rep 2016; 14: 2325–2336.
Belmont PJ, Jiang P, McKee TD, Xie T, Isaacson J, Baryla NE et al. Resistance to dual blockade of the kinases PI3K and mTOR in KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer models results in combined sensitivity to inhibition of the receptor tyrosine kinase EGFR. Sci Signal 2014. 7ra107.
Mazzeo C, Calvo V, Alonso R, Merida I, Izquierdo M . Protein kinase D1/2 is involved in the maturation of multivesicular bodies and secretion of exosomes in T and B lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ 2016; 23: 99–109.
Minciacchi VR, You S, Spinelli C, Morley S, Zandian M, Aspuria PJ et al. Large oncosomes contain distinct protein cargo and represent a separate functional class of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 11327–11341.
Plebanek MP, Mutharasan RK, Volpert O, Matov A, Gatlin JC, Thaxton CS . Nanoparticle targeting and cholesterol flux through scavenger receptor type B-1 inhibits cellular exosome uptake. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 15724.
Aga M, Bentz GL, Raffa S, Torrisi MR, Kondo S, Wakisaka N et al. Exosomal HIF1alpha supports invasive potential of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-associated LMP1-positive exosomes. Oncogene 2014; 33: 4613–4622.
Kalluri R, Zeisberg M . Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 392–401.
Cho JA, Park H, Lim EH, Lee KW . Exosomes from breast cancer cells can convert adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblast-like cells. Int J Oncol 2012; 40: 130–138.
Chowdhury R, Webber JP, Gurney M, Mason MD, Tabi Z, Clayton A . Cancer exosomes trigger mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into pro-angiogenic and pro-invasive myofibroblasts. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 715–731.
Morello M, Minciacchi VR, de Candia P, Yang J, Posadas E, Kim H et al. Large oncosomes mediate intercellular transfer of functional microRNA. Cell Cycle 2013; 12: 3526–3536.
Franzen CA, Blackwell RH, Todorovic V, Greco KA, Foreman KE, Flanigan RC et al. Urothelial cells undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition after exposure to muscle invasive bladder cancer exosomes. Oncogenesis 2015; 4: e163.
Paggetti J, Haderk F, Seiffert M, Janji B, Distler U, Ammerlaan W et al. Exosomes released by chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce the transition of stromal cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Blood 2015; 126: 1106–1117.
Luga V, Zhang L, Viloria-Petit AM, Ogunjimi AA, Inanlou MR, Chiu E et al. Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell 2012; 151: 1542–1556.
Au Yeung CL, Co NN, Tsuruga T, Yeung TL, Kwan SY, Leung CS et al. Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat Commun 2016; 7: 11150.
Frydrychowicz M, Kolecka-Bednarczyk A, Madejczyk M, Yasar S, Dworacki G . Exosomes—structure, biogenesis and biological role in non-small-cell lung cancer. Scand J Immunol 2015; 81: 2–10.
Park JE, Tan HS, Datta A, Lai RC, Zhang H, Meng W et al. Hypoxic tumor cell modulates its microenvironment to enhance angiogenic and metastatic potential by secretion of proteins and exosomes. Mol Cell Proteomics 2010; 9: 1085–1099.
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 1470–1476.
Taverna S, Flugy A, Saieva L, Kohn EC, Santoro A, Meraviglia S et al. Role of exosomes released by chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in angiogenesis. Int J Cancer 2012; 130: 2033–2043.
Hood JL, Pan H, Lanza GM, Wickline SA, Consortium for Translational Research in Advanced Imaging and Nanomedicine (C-TRAIN).. Paracrine induction of endothelium by tumor exosomes. Lab Invest 2009; 89: 1317–1328.
Millimaggi D, Mari M, D'Ascenzo S, Carosa E, Jannini EA, Zucker S et al. Tumor vesicle-associated CD147 modulates the angiogenic capability of endothelial cells. Neoplasia 2007; 9: 349–357.
Gopal SK, Greening DW, Hanssen EG, Zhu HJ, Simpson RJ, Mathias RA . Oncogenic epithelial cell-derived exosomes containing Rac1 and PAK2 induce angiogenesis in recipient endothelial cells. Oncotarget 2016, e-pub ahead of print 22 February 2016 doi:10.18632/oncotarget.7573.
Grange C, Tapparo M, Collino F, Vitillo L, Damasco C, Deregibus MC et al. Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 5346–5356.
Kucharzewska P, Christianson HC, Welch JE, Svensson KJ, Fredlund E, Ringner M et al. Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 7312–7317.
Vader P, Breakefield XO, Wood MJ . Extracellular vesicles: emerging targets for cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med 2014; 20: 385–393.
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Kerbel RS, Allison AC, Rak J . Endothelial expression of autocrine VEGF upon the uptake of tumor-derived microvesicles containing oncogenic EGFR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 3794–3799.
Huber V, Fais S, Iero M, Lugini L, Canese P, Squarcina P et al. Human colorectal cancer cells induce T-cell death through release of proapoptotic microvesicles: role in immune escape. Gastroenterology 2005; 128: 1796–1804.
Fasanaro P, D'Alessandra Y, Di Stefano V, Melchionna R, Romani S, Pompilio G et al. MicroRNA-210 modulates endothelial cell response to hypoxia and inhibits the receptor tyrosine kinase ligand Ephrin-A3. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 15878–15883.
Kosaka N . Decoding the secret of cancer by means of extracellular vesicles. J Clin Med 2016; 5.
Zhang Y, Liu D, Chen X, Li J, Li L, Bian Z et al. Secreted monocytic miR-150 enhances targeted endothelial cell migration. Mol Cell 2010; 39: 133–144.
Fan GC . Hypoxic exosomes promote angiogenesis. Blood 2014; 124: 3669–3670.
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Hagiwara K, Yoshioka Y, Takeshita F, Ochiya T . Neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2)-dependent exosomal transfer of angiogenic microRNAs regulate cancer cell metastasis. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 10849–10859.
Tadokoro H, Umezu T, Ohyashiki K, Hirano T, Ohyashiki JH . Exosomes derived from hypoxic leukemia cells enhance tube formation in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 34343–34351.
Zhuang G, Wu X, Jiang Z, Kasman I, Yao J, Guan Y et al. Tumour-secreted miR-9 promotes endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis by activating the JAK-STAT pathway. EMBO J 2012; 31: 3513–3523.
Umezu T, Tadokoro H, Azuma K, Yoshizawa S, Ohyashiki K, Ohyashiki JH . Exosomal miR-135b shed from hypoxic multiple myeloma cells enhances angiogenesis by targeting factor-inhibiting HIF-1. Blood 2014; 124: 3748–3757.
van Balkom BW, de Jong OG, Smits M, Brummelman J, den Ouden K, de Bree PM et al. Endothelial cells require miR-214 to secrete exosomes that suppress senescence and induce angiogenesis in human and mouse endothelial cells. Blood 2013; 121: 3997–4006; S3991-3915.
Bovy N, Blomme B, Freres P, Dederen S, Nivelles O, Lion M et al. Endothelial exosomes contribute to the antitumor response during breast cancer neoadjuvant chemotherapy via microRNA transfer. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 10253–10266.
Sun L, Wang HX, Zhu XJ, Wu PH, Chen WQ, Zou P et al. Serum deprivation elevates the levels of microvesicles with different size distributions and selectively enriched proteins in human myeloma cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2014; 35: 381–393.
King HW, Michael MZ, Gleadle JM . Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2012; 12: 421.
Raimondo S, Corrado C, Raimondi L, De Leo G, Alessandro R . Role of extracellular vesicles in hematological malignancies. Biomed Res Int 2015; 2015: 821613.
Salomon C, Ryan J, Sobrevia L, Kobayashi M, Ashman K, Mitchell M et al. Exosomal signaling during hypoxia mediates microvascular endothelial cell migration and vasculogenesis. PLoS One 2013; 8: e68451.
Zitvogel L, Regnault A, Lozier A, Wolfers J, Flament C, Tenza D et al. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med 1998; 4: 594–600.
Montecalvo A, Larregina AT, Shufesky WJ, Stolz DB, Sullivan ML, Karlsson JM et al. Mechanism of transfer of functional microRNAs between mouse dendritic cells via exosomes. Blood 2012; 119: 756–766.
Mittelbrunn M, Gutierrez-Vazquez C, Villarroya-Beltri C, Gonzalez S, Sanchez-Cabo F, Gonzalez MA et al. Unidirectional transfer of microRNA-loaded exosomes from T cells to antigen-presenting cells. Nat Commun 2011; 2: 282.
Okoye IS, Coomes SM, Pelly VS, Czieso S, Papayannopoulos V, Tolmachova T et al. MicroRNA-containing T-regulatory-cell-derived exosomes suppress pathogenic T helper 1 cells. Immunity 2014; 41: 89–103.
Andreola G, Rivoltini L, Castelli C, Huber V, Perego P, Deho P et al. Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis by tumor cell secretion of FasL-bearing microvesicles. J Exp Med 2002; 195: 1303–1316.
Lv LH, Wan YL, Lin Y, Zhang W, Yang M, Li GL et al. Anticancer drugs cause release of exosomes with heat shock proteins from human hepatocellular carcinoma cells that elicit effective natural killer cell antitumor responses in vitro. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 15874–15885.
Liu C, Yu S, Zinn K, Wang J, Zhang L, Jia Y et al. Murine mammary carcinoma exosomes promote tumor growth by suppression of NK cell function. J Immunol 2006; 176: 1375–1385.
Cai Z, Yang F, Yu L, Yu Z, Jiang L, Wang Q et al. Activated T cell exosomes promote tumor invasion via Fas signaling pathway. J Immunol 2012; 188: 5954–5961.
Costa-Silva B, Aiello NM, Ocean AJ, Singh S, Zhang H, Thakur BK et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat Cell Biol 2015; 17: 816–826.
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF, de Tribolet N, Weller M et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 997–1003.
Shao H, Chung J, Lee K, Balaj L, Min C, Carter BS et al. Chip-based analysis of exosomal mRNA mediating drug resistance in glioblastoma. Nat Commun 2015; 6: 6999.
Chen Y, Wang L, Zhu Y, Chen Z, Qi X, Jin L et al. Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)-containing circulating microvesicles contribute to chemoresistance in breast cancer. Oncol Lett 2015; 10: 3742–3748.
Ma X, Chen Z, Hua D, He D, Wang L, Zhang P et al. Essential role for TrpC5-containing extracellular vesicles in breast cancer with chemotherapeutic resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 6389–6394.
O'Brien K, Rani S, Corcoran C, Wallace R, Hughes L, Friel AM et al. Exosomes from triple-negative breast cancer cells can transfer phenotypic traits representing their cells of origin to secondary cells. Eur J Cancer 2013; 49: 1845–1859.
Chen WX, Liu XM, Lv MM, Chen L, Zhao JH, Zhong SL et al. Exosomes from drug-resistant breast cancer cells transmit chemoresistance by a horizontal transfer of microRNAs. PLoS One 2014; 9: e95240.
Putz U, Howitt J, Doan A, Goh CP, Low LH, Silke J et al. The tumor suppressor PTEN is exported in exosomes and has phosphatase activity in recipient cells. Sci Signal 2012; 5: ra70.
Ragusa M, Statello L, Maugeri M, Barbagallo C, Passanisi R, Alhamdani MS et al. Highly skewed distribution of miRNAs and proteins between colorectal cancer cells and their exosomes following Cetuximab treatment: biomolecular, genetic and translational implications. Oncoscience 2014; 1: 132–157.
Hannafon BN, Carpenter KJ, Berry WL, Janknecht R, Dooley WC, Ding WQ . Exosome-mediated microRNA signaling from breast cancer cells is altered by the anti-angiogenesis agent docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Mol Cancer 2015; 14: 133.
Ohno S, Takanashi M, Sudo K, Ueda S, Ishikawa A, Matsuyama N et al. Systemically injected exosomes targeted to EGFR deliver antitumor microRNA to breast cancer cells. Mol Ther 2013; 21: 185–191.
Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C, Lakhal S, Wood MJ . Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol 2011; 29: 341–345.
Tkach M, Thery C . Communication by extracellular vesicles: where we are and where we need to go. Cell 2016; 164: 1226–1232.
Budnik V, Ruiz-Canada C, Wendler F . Extracellular vesicles round off communication in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 2016; 17: 160–172.
Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, Rajendran L, Wenzel D, Wieland F et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 2008; 319: 1244–1247.
Hurley JH . ESCRTs are everywhere. EMBO J 2015; 34: 2398–2407.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Action Against Cancer and NIHR grant #NIHR-RP-011-053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wendler, F., Favicchio, R., Simon, T. et al. Extracellular vesicles swarm the cancer microenvironment: from tumor–stroma communication to drug intervention. Oncogene 36, 877–884 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.253
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.253
This article is cited by
-
Radiogenomic analysis of cellular tumor-stroma heterogeneity as a prognostic predictor in breast cancer
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
Extracellular vesicles remodel tumor environment for cancer immunotherapy
Molecular Cancer (2023)
-
The potential applications of microparticles in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of lung cancer
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
The critical role of STAT3 in biogenesis of tumor-derived exosomes with potency of inducing cancer cachexia in vitro and in vivo
Oncogene (2022)
-
Tumor-produced and aging-associated oncometabolite methylmalonic acid promotes cancer-associated fibroblast activation to drive metastatic progression
Nature Communications (2022)