Abstract
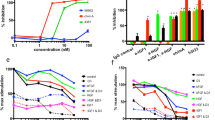
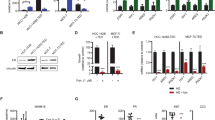
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system is a well-studied growth regulatory pathway implicated in breast cancer biology. Clinical trials testing monoclonal antibodies directed against the type I IGF receptor (IGF1R) in combination with estrogen receptor-α (ER) targeting have been completed, but failed to show benefits in patients with endocrine-resistant tumors compared to ER targeting alone. We have previously shown that the closely related insulin receptor (InsR) is expressed in tamoxifen-resistant (TamR) breast cancer cells. Here we examined if inhibition of InsR affected TamR breast cancer cells. InsR function was inhibited by three different mechanisms: InsR short hairpin RNA, a small InsR-blocking peptide, S961 and an InsR monoclonal antibody (mAb). Suppression of InsR function by these methods in TamR cells successfully blocked insulin-mediated signaling, monolayer proliferation, cell cycle progression and anchorage-independent growth. This strategy was not effective in parental cells likely because of the presence of IGFR /InsR hybrid receptors. Downregulation of IGF1R in conjunction with InsR inhibition was more effective in blocking IGF- and insulin-mediated signaling and growth in parental cells compared with single-receptor targeting alone. Our findings show TamR cells were stimulated by InsR and were not sensitive to IGF1R inhibition, whereas in tamoxifen-sensitive parental cancer cells, the presence of both receptors, especially hybrid receptors, allowed cross-reactivity of ligand-mediated activation and growth. To suppress the IGF system, targeting of both IGF1R and InsR is optimal in endocrine-sensitive and -resistant breast cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nadji M, Gomez-Fernandez C, Ganjei-Azar P, Morales AR . Immunohistochemistry of estrogen and progesterone receptors reconsidered: experience with 5,993 breast cancers. Am J Clin Pathol 2005; 123: 21–27.
Macaskill EJ, Renshaw L, Dixon JM . Neoadjuvant use of hormonal therapy in elderly patients with early or locally advanced hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncologist 2006; 11: 1081–1088.
Paridaens RJ, Dirix LY, Beex LV, Nooij M, Cameron DA, Cufer T et al. Phase III study comparing exemestane with tamoxifen as first-line hormonal treatment of metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women: the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Breast Cancer Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 4883–4890.
Ring A, Dowsett M . Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance. Endocr Relat Cancer 2004; 11: 643–658.
Giuliano M, Schifp R, Osborne CK, Trivedi MV . Biological mechanisms and clinical implications of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Breast 2011; 20: S42–S49.
Baselga J, Campone M, Piccart M, Burris HA, Rugo HS, Sahmoud T et al. Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor–positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2011; 366: 520–529.
Garber K . The cancer drug that almost wasn't. Science 2014; 345: 865–867.
Fagan DH, Yee D . Crosstalk between IGF1R and estrogen receptor signaling in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2008; 13: 423–429.
Arpino G, De Angelis C, Giuliano M, Giordano A, Falato C, De Laurentiis M et al. Molecular mechanism and clinical implications of endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer. Oncology 2009; 77: 23–37.
Lee AV, Weng CN, Jackson JG, Yee D . Activation of estrogen receptor-mediated gene transcription by IGF-I in human breast cancer cells. J Endocrinol 1997; 152: 39–47.
Becker MA, Ibrahim YH, Cui X, Lee AV, Yee D . The IGF pathway regulates ERalpha through a S6K1-dependent mechanism in breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 2011; 25: 516–528.
Yee D . Insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibitors: baby or the bathwater? J Natl Cancer Inst 2012; 104: 975–981.
Fagan DH, Uselman RR, Sachdev D, Yee D . Acquired resistance to tamoxifen is associated with loss of the type i insulin-like growth factor receptor: implications for breast cancer treatment. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 3372–3380.
Drury SC, Detre S, Leary A, Salter J, Reis-Filho J, Barbashina V et al. Changes in breast cancer biomarkers in the IGF1R/PI3K pathway in recurrent breast cancer after tamoxifen treatment. Endocr Relat Cancer 2011; 18: 565–577.
Arnedos M, Drury S, Afentakis M, A'Hern R, Hills M, Salter J et al. Biomarker changes associated with the development of resistance to aromatase inhibitors (AIs) in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Ann Oncol 2014; 25: 605–610.
Chen HX, Sharon E . IGF-1R as an anti-cancer target—trials and tribulations. Chin J Cancer 2013; 32: 242–252.
Ullrich A, Gray A, Tam AW, Yang-Feng T, Tsubokawa M, Collins C et al. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. Embo J 1986; 5: 2503–2512.
Fulzele K, DiGirolamo DJ, Liu Z, Xu J, Messina JL, Clemens TL . Disruption of the insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor in osteoblasts enhances insulin signaling and action. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 25649–25658.
Zhang H, Pelzer AM, Kiang DT, Yee D . Down-regulation of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor increases sensitivity of breast cancer cells to insulin. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 391–397.
Shah SP, Morin RD, Khattra J, Prentice L, Pugh T, Burleigh A et al. Mutational evolution in a lobular breast tumour profiled at single nucleotide resolution. Nature 2009; 461: 809–813.
Milazzo G, Giorgino F, Damante G, Sung C, Stampfer MR, Vigneri R et al. Insulin receptor expression and function in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 3924–3930.
Zhang H, Fagan DH, Zeng X, Freeman KT, Sachdev D, Yee D . Inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by insulin receptor downregulation. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2517–2527.
Belfiore A, Malaguarnera R . Insulin receptor and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 2011; 18: R125–R147.
Papa V, Pezzino V, Costantino A, Belfiore A, Giuffrida D, Frittitta L et al. Elevated insulin receptor content in human breast cancer. J Clin Invest 1990; 86: 1503–1510.
Puzanov I, Lindsay CR, Goff L, Sosman J, Gilbert J, Berlin J et al. A phase I study of continuous oral dosing of OSI-906, a dual inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin receptors, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21: 701–711.
Jones RL, Kim ES, Nava-Parada P, Alam S, Johnson FM, Stephens AW et al. Phase I study of intermittent oral dosing of the insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin receptors inhibitor OSI-906 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21: 693–700.
Knudsen L, Hansen BF, Jensen P, Pedersen TA, Vestergaard K, Schaffer L et al. Agonism and antagonism at the insulin receptor. PLoS One 2012; 7: e51972.
Soos MA, Siddle K, Baron MD, Heward JM, Luzio JP, Bellatin J et al. Monoclonal antibodies reacting with multiple epitopes on the human insulin receptor. Biochem J 1986; 235: 199–208.
O'Brien RM, Soos MA, Siddle K . Monoclonal antibodies to the insulin receptor stimulate the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity by cross-linking receptor molecules. EMBO J 1987; 6: 4003–4010.
Zhang H, Sachdev D, Wang C, Hubel A, Gaillard-Kelly M, Yee D . Detection and downregulation of type I IGF receptor expression by antibody-conjugated quantum dots in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009; 114: 277–285.
Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA et al. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. CA Cancer J Clin 2010; 60: 207–221.
Josefson D . High insulin levels linked to deaths from breast cancer. BMJ 2000; 320: 1496.
Rose DP, Haffner SM, Baillargeon J . Adiposity, the metabolic syndrome, and breast cancer in African-American and white American women. Endocr Rev 2007; 28: 763–777.
Weinstein D, Sarfstein R, Laron Z, Werner H . Insulin receptor compensates for IGF1R inhibition and directly induces mitogenic activity in prostate cancer cells. Endocr Connect 2014; 3: 24–35.
Ulanet DB, Ludwig DL, Kahn CR, Hanahan D . Insulin receptor functionally enhances multistage tumor progression and conveys intrinsic resistance to IGF-1R targeted therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 10791–10798.
Frasca F, Pandini G, Scalia P, Sciacca L, Mineo R, Costantino A et al. Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized, high-affinity insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 3278–3288.
Moller DE, Yokota A, Caro JF, Flier JS . Tissue-specific expression of two alternatively spliced insulin receptor mRNAs in man. Mol Endocrinol 1989; 3: 1263–1269.
Jones HE, Gee JMW, Barrow D, Tonge D, Holloway B, Nicholson RI . Inhibition of insulin receptor isoform-A signalling restores sensitivity to gefitinib in previously de novo resistant colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer 2006; 95: 172–180.
Jiang L, Zhu W, Streicher K, Morehouse C, Brohawn P, Ge X et al. Increased IR-A/IR-B ratio in non-small cell lung cancers associates with lower epithelial-mesenchymal transition signature and longer survival in squamous cell lung carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014; 14: 131.
Harrington SC, Weroha SJ, Reynolds C, Suman VJ, Lingle WL, Haluska P . Quantifying insulin receptor isoform expression in FFPE breast tumors. Growth Horm IGF Res 2012; 22: 108–115.
Kalli KR, Falowo OI, Bale LK, Zschunke MA, Roche PC, Conover CA . Functional insulin receptors on human epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells: implications for IGF-II mitogenic signaling. Endocrinology 2002; 143: 3259–3267.
Belfiore A, Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L, Vigneri R . Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr Rev 2009; 30: 586–623.
Rostoker R, Abelson S, Bitton-Worms K, Genkin I, Ben-Shmuel S, Dakwar M et al. Highly specific role of the insulin receptor in breast cancer progression. Endocr Relat Cancer 2015; 22: 145–157.
Dowling RJO, Niraula S, Stambolic V, Goodwin PJ . Metformin in cancer: translational challenges. J Mol Endocrinol 2012; 48: R31–R43.
Jaques G, Kiefer P, Rotsch M, Hennig C, Goke R, Richter G et al. Production of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins by small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Exp Cell Res 1989; 184: 396–406.
Thompson MD, Grubbs CJ, Bode AM, Reid JM, McGovern R, Bernard PS et al. Lack of effect of metformin on mammary carcinogenesis in nondiabetic rat and mouse models. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2015; 8: 231–239.
Ramos RR, Swanson AJ, Bass J . Calreticulin and Hsp90 stabilize the human insulin receptor and promote its mobility in the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 10470–10475.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the assistance of the University Flow Cytometry Resource at the University of Minnesota; Novo Nordisk for supplying S961 peptides. Funding was provided by NIH/NCI 2P30-CA077598 (JYC, KL and DY), NIH/NCI P50CA116201 (DY), and Komen for the Cure SAC110039 (DY).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, J., LaPara, K. & Yee, D. Disruption of insulin receptor function inhibits proliferation in endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells. Oncogene 35, 4235–4243 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.488
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.488
This article is cited by
-
Metformin counteracts stimulatory effects induced by insulin in primary breast cancer cells
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
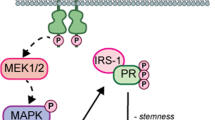
Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) mediates progesterone receptor-driven stemness and endocrine resistance in oestrogen receptor+ breast cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2021)
-
DDAB cationic lipid-mPEG, PCL copolymer hybrid nano-carrier synthesis and application for delivery of siRNA targeting IGF-1R into breast cancer cells
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2021)
-
Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Pathway Targeting in Cancer: Role of the IGF Axis and Opportunities for Future Combination Studies
Targeted Oncology (2017)