Abstract
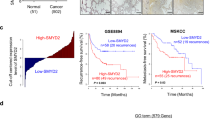
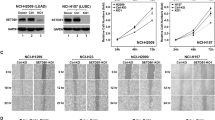
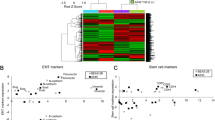
Malignant tumors are exemplified by excessive proliferation and aggressive migration/invasion contributing to increased mortality of cancer patients. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) expression is positively correlated with lung cancer malignancy. The mechanism underlying an elevated MMP9 expression is not clearly defined. We demonstrate here that the transcriptional modulator megakaryocytic leukemia 1 (MKL1) was activated by hypoxia and transforming growth factor (TGF-β), two prominent pro-malignancy factors, in cultured lung cancer cells. MKL1 levels were also increased in more invasive types of lung cancer in humans. Depletion of MKL1 in lung cancer cells attenuated migration and invasion both in vitro and in vivo. Overexpression of MKL1 potentiated the induction of MMP9 transcription by hypoxia and TGF-β, whereas MKL1 silencing diminished MMP9 expression. Of interest, MKL1 knockdown eliminated histone H3K4 methylation surrounding the MMP9 promoter. Further analyses revealed that MKL1 recruited ASH2, a component of the H3K4 methyltransferase complex, to activate MMP9 transcription. Depletion of ASH2 ameliorated cancer cell migration and invasion in an MMP9-dependent manner. Together our data indicate that MKL1 potentiates lung cancer cell migration and invasion by epigenetically activating MMP9 transcription.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ung YC, Maziak DE, Vanderveen JA, Smith CA, Gulenchyn K, Lacchetti C et al. 18Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer: a systematic review. J Natl Cancer Inst 2007; 99: 1753–1767.
Marcus PM, Bergstralh EJ, Fagerstrom RM, Williams DE, Fontana R, Taylor WF et al. Lung cancer mortality in the Mayo Lung Project: impact of extended follow-up. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000; 92: 1308–1316.
Pine SR, Ryan BM, Varticovski L, Robles AI, Harris CC . Microenvironmental modulation of asymmetric cell division in human lung cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 2195–2200.
Sun L, Li H, Chen J, Dehennaut V, Zhao Y, Yang Y et al. A SUMOylation-dependent pathway regulates SIRT1 transcription and lung cancer metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst 2013; 105: 887–898.
Moutsopoulos NM, Wen J, Wahl SM . TGF-beta and tumors—an ill-fated alliance. Curr Opin Immunol 2008; 20: 234–240.
Illman SA, Lehti K, Keski-Oja J, Lohi J . Epilysin (MMP-28) induces TGF-beta mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung carcinoma cells. J Cell Sci 2006; 119: 3856–3865.
Rintoul RC, Sethi T . The role of extracellular matrix in small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol 2001; 2: 437–442.
Cox G, Jones JL, O'Byrne KJ . Matrix metalloproteinase 9 and the epidermal growth factor signal pathway in operable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 2349–2355.
Sienel W, Hellers J, Morresi-Hauf A, Lichtinghagen R, Mutschler W, Jochum M et al. Prognostic impact of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in operable non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 2003; 103: 647–651.
Pinto CA, Carvalho PE, Antonangelo L, Garippo A, Da Silva AG, Soares F et al. Morphometric evaluation of tumor matrix metalloproteinase 9 predicts survival after surgical resection of adenocarcinoma of the lung. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 3098–3104.
Cock-Rada AM, Medjkane S, Janski N, Yousfi N, Perichon M, Chaussepied M et al. SMYD3 promotes cancer invasion by epigenetic upregulation of the metalloproteinase MMP-9. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 810–820.
Robert I, Aussems M, Keutgens A, Zhang X, Hennuy B, Viatour P et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene induction by a truncated oncogenic NF-kappaB2 protein involves the recruitment of MLL1 and MLL2 H3K4 histone methyltransferase complexes. Oncogene 2009; 28: 1626–1638.
Lin YW, Ren LL, Xiong H, Du W, Yu YN, Sun TT et al. Role of STAT3 and vitamin D receptor in EZH2-mediated invasion of human colorectal cancer. J Pathol 2013; 230: 277–290.
Ballerini P, Blaise A, Mercher T, Pellegrino B, Perot C, van den Akker J et al. A novel real-time RT-PCR assay for quantification of OTT-MAL fusion transcript reliable for diagnosis of t(1;22) and minimal residual disease (MRD) detection. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1193–1196.
Hampl V, Martin C, Aigner A, Hoebel S, Singer S, Frank N et al. Depletion of the transcriptional coactivators megakaryoblastic leukaemia 1 and 2 abolishes hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft growth by inducing oncogene-induced senescence. EMBO Mol Med 2013; 5: 1367–1382.
Gurbuz I, Ferralli J, Roloff T, Chiquet-Ehrismann R, Asparuhova MB . SAP domain-dependent Mkl1 signaling stimulates proliferation and cell migration by induction of a distinct gene set indicative of poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Mol Cancer 2014; 13: 22.
Medjkane S, Perez-Sanchez C, Gaggioli C, Sahai E, Treisman R . Myocardin-related transcription factors and SRF are required for cytoskeletal dynamics and experimental metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 257–268.
Yoshio T, Morita T, Tsujii M, Hayashi N, Sobue K . MRTF-A/B suppress the oncogenic properties of v-ras- and v-src-mediated transformants. Carcinogenesis 2010; 31: 1185–1193.
Fang F, Yang Y, Yuan Z, Gao Y, Zhou J, Chen Q et al. Myocardin-related transcription factor A mediates OxLDL-induced endothelial injury. Circ Res 2011; 108: 797–807.
Yang Y, Chen D, Yuan Z, Fang F, Cheng X, Xia J et al. Megakaryocytic leukemia 1 (MKL1) ties the epigenetic machinery to hypoxia-induced transactivation of endothelin-1. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41: 6005–6017.
Lockman K, Taylor JM, Mack CP . The histone demethylase, Jmjd1a, interacts with the myocardin factors to regulate SMC differentiation marker gene expression. Circ Res 2007; 101: e115–e123.
Zhou J, Zhang M, Fang H, El-Mounayri O, Rodenberg JM, Imbalzano AN et al. The SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex regulates myocardin-induced smooth muscle-specific gene expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2009; 29: 921–928.
Yang Y, Cheng X, Tian W, Zhou B, Wu X, Xu H et al. MRTF-A steers an epigenetic complex to activate endothelin-induced pro-inflammatory transcription in vascular smooth muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42: 10460–10472.
Tian W, Hao C, Fan Z, Weng X, Qin H, Wu X et al. Myocardin related transcription factor A programs epigenetic activation of hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol 2014; 62: 165–174.
Xu H, Wu X, Qin H, Tian W, Chen J, Sun L et al. Myocardin-related transcription factor A epigenetically regulates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2014, e-pub ahead of print 27 October 2014 doi:10.1681/ASN.2014070678.
Gilles L, Bluteau D, Boukour S, Chang Y, Zhang Y, Robert T et al. MAL/SRF complex is involved in platelet formation and megakaryocyte migration by regulating MYL9 (MLC2) and MMP9. Blood 2009; 114: 4221–4232.
Olson EN, Nordheim A . Linking actin dynamics and gene transcription to drive cellular motile functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 353–365.
Hiratsuka S, Nakamura K, Iwai S, Murakami M, Itoh T, Kijima H et al. MMP9 induction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 is involved in lung-specific metastasis. Cancer Cell 2002; 2: 289–300.
Hanna M, Liu H, Amir J, Sun Y, Morris SW, Siddiqui MA et al. Mechanical regulation of the proangiogenic factor CCN1/CYR61 gene requires the combined activities of MRTF-A and CREB-binding protein histone acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 23125–23136.
Shilatifard A . Molecular implementation and physiological roles for histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methylation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2008; 20: 341–348.
Shilatifard A . The COMPASS family of histone H3K4 methylases: mechanisms of regulation in development and disease pathogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem 2012; 81: 65–95.
Jakopovic M, Thomas A, Balasubramaniam S, Schrump D, Giaccone G, Bates SE . Targeting the epigenome in lung cancer: expanding approaches to epigenetic therapy. Front Oncol 2013; 3: 261.
Risch A, Plass C . Lung cancer epigenetics and genetics. Int J Cancer 2008; 123: 1–7.
Ma Z, Morris SW, Valentine V, Li M, Herbrick JA, Cui X et al. Fusion of two novel genes, RBM15 and MKL1, in the t(1;22)(p13;q13) of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet 2001; 28: 220–221.
Weinl C, Riehle H, Park D, Stritt C, Beck S, Huber G et al. Endothelial SRF/MRTF ablation causes vascular disease phenotypes in murine retinae. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 2193–2206.
Yu L, Weng X, Liang P, Dai X, Wu X, Xu H et al. MRTF-A mediates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory transcription by interacting with the COMPASS complex. J Cell Sci 2014; 127: 4645–4657.
Yuan Z, Chen J, Chen D, Xu G, Xia M, Xu Y et al. Megakaryocytic leukemia 1 (MKL1) regulates hypoxia induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. PLoS One 2014; 9: e83895.
Shaposhnikov D, Kuffer C, Storchova Z, Posern G . Myocardin related transcription factors are required for coordinated cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle 2013; 12: 1762–1772.
Shaposhnikov D, Descot A, Schilling J, Posern G . Myocardin-related transcription factor A regulates expression of Bok and Noxa and is involved in apoptotic signalling. Cell Cycle 2012; 11: 141–150.
Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Sugito N, Horio Y, Takahashi T . Histone modification in the TGFbetaRII gene promoter and its significance for responsiveness to HDAC inhibitor in lung cancer cell lines. Mol Carcinog 2005; 44: 233–241.
Zinn RL, Pruitt K, Eguchi S, Baylin SB, Herman JG . hTERT is expressed in cancer cell lines despite promoter DNA methylation by preservation of unmethylated DNA and active chromatin around the transcription start site. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 194–201.
Larrieu D, Ythier D, Brambilla C, Pedeux R . ING2 controls the G1 to S-phase transition by regulating p21 expression. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 3984–3990.
Kim J, Shin S, Subramaniam M, Bruinsma E, Kim TD, Hawse JR et al. Histone demethylase JARID1B/KDM5B is a corepressor of TIEG1/KLF10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010; 401: 412–416.
Zhou X, Sun H, Chen H, Zavadil J, Kluz T, Arita A et al. Hypoxia induces trimethylated H3 lysine 4 by inhibition of JARID1A demethylase. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 4214–4221.
Wan M, Liang J, Xiong Y, Shi F, Zhang Y, Lu W et al. The trithorax group protein Ash2l is essential for pluripotency and maintaining open chromatin in embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 5039–5048.
Lundin A, Driscoll B . Lung cancer stem cells: progress and prospects. Cancer Lett 2013; 338: 89–93.
Kaplan A, Spiller KJ, Towne C, Kanning KC, Choe GT, Geber A et al. Neuronal matrix metalloproteinase-9 is a determinant of selective neurodegeneration. Neuron 2014; 81: 333–348.
Yan XL, Jia YL, Chen L, Zeng Q, Zhou JN, Fu CJ et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma-associated mesenchymal stem cells promote hepatocarcinoma progression: role of the S100A4-miR155-SOCS1-MMP9 axis. Hepatology 2013; 57: 2274–2286.
Yang X, Pursell B, Lu S, Chang TK, Mercurio AM . Regulation of beta 4-integrin expression by epigenetic modifications in the mammary gland and during the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Sci 2009; 122: 2473–2480.
Chang C, Yang X, Pursell B, Mercurio AM . Id2 complexes with the SNAG domain of Snai1 inhibiting Snai1-mediated repression of integrin beta4. Mol Cell Biol 2013; 33: 3795–3804.
Tsai YP, Wu KJ . Epigenetic regulation of hypoxia-responsive gene expression: focusing on chromatin and DNA modifications. Int J Cancer 2014; 134: 249–256.
Wu MZ, Tsai YP, Yang MH, Huang CH, Chang SY, Chang CC et al. Interplay between HDAC3 and WDR5 is essential for hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 811–822.
Zhong Q, Kowluru RA . Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 by epigenetic modifications and the development of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 2013; 62: 2559–2568.
Kim JE, Kim HS, Shin YJ, Lee CS, Won C, Lee SA et al. LYR71, a derivative of trimeric resveratrol, inhibits tumorigenesis by blocking STAT3-mediated matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression. Exp Mol Med 2008; 40: 514–522.
Tang Z, Chen WY, Shimada M, Nguyen UT, Kim J, Sun XJ et al. SET1 and p300 act synergistically, through coupled histone modifications, in transcriptional activation by p53. Cell 2013; 154: 297–310.
Schaaij-Visser TB, de Wit M, Lam SW, Jimenez CR . The cancer secretome, current status and opportunities in the lung, breast and colorectal cancer context. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013; 1834: 2242–2258.
Chen Z, Fillmore CM, Hammerman PS, Kim CF, Wong KK . Non-small-cell lung cancers: a heterogeneous set of diseases. Nat Rev Cancer 2014; 14: 535–546.
Wood SL, Pernemalm M, Crosbie PA, Whetton AD . The role of the tumor-microenvironment in lung cancer-metastasis and its relationship to potential therapeutic targets. Cancer Treat Rev 2014; 40: 558–566.
Cen B, Selvaraj A, Burgess RC, Hitzler JK, Ma Z, Morris SW et al. Megakaryoblastic leukemia 1, a potent transcriptional coactivator for serum response factor (SRF), is required for serum induction of SRF target genes. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 6597–6608.
Lee SM, Vasishtha M, Prywes R . Activation and repression of cellular immediate early genes by serum response factor cofactors. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 22036–22049.
Takino T, Koshikawa N, Miyamori H, Tanaka M, Sasaki T, Okada Y et al. Cleavage of metastasis suppressor gene product KiSS-1 protein/metastin by matrix metalloproteinases. Oncogene 2003; 22: 4617–4626.
Basu S, Pathak S, Pathak SK, Bhattacharyya A, Banerjee A, Kundu M et al. Mycobacterium avium-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression occurs in a cyclooxygenase-2-dependent manner and involves phosphorylation- and acetylation-dependent chromatin modification. Cell Microbiol 2007; 9: 2804–2816.
Kong X, Fang M, Li P, Fang F, Xu Y . HDAC2 deacetylates class II transactivator and suppresses its activity in macrophages and smooth muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2009; 46: 292–299.
Tian W, Xu H, Fang F, Chen Q, Xu Y, Shen A . Brahma-related gene 1 bridges epigenetic regulation of proinflammatory cytokine production to steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2013; 58: 576–588.
Sun L, Li H, Chen J, Iwasaki Y, Kubota T, Matsuoka M et al. PIASy mediates hypoxia-induced SIRT1 transcriptional repression and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells. J Cell Sci 2013; 126: 3939–3947.
Chen D, Fang F, Yang Y, Chen J, Xu G, Xu Y et al. Brahma-related gene 1 (Brg1) epigenetically regulates CAM activation during hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Cardiovas Res 2013; 100: 363–373.
Fang F, Chen D, Yu L, Dai X, Yang Y, Tian W et al. Proinflammatory stimuli engage brahma related gene 1 and brahma in endothelial injury. Circ Res 2013; 113: 986–996.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported, in part, by grants from the National Basic Science Project of China (2012CB517503), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31270805, 31200645, 81402550, 91439106), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2012043, BK20140906, BK21041498), Education Commission of Jiangsu Province (14KJA31001), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of China (NCET-11-0991), Ministry of Education (212059, 20123234110008) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD). YX is a fellow at the Collaborative Innovative Center for Cardiovascular Translational Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, X., Yang, Y., Fan, Z. et al. MKL1 potentiates lung cancer cell migration and invasion by epigenetically activating MMP9 transcription. Oncogene 34, 5570–5581 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.14
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.14
This article is cited by
-
m6A-Mediated Upregulation of lncRNA CHASERR Promotes the Progression of Glioma by Modulating the miR-6893-3p/TRIM14 Axis
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)
-
M2PP: a novel computational model for predicting drug-targeted pathogenic proteins
BMC Bioinformatics (2022)
-
MKL-1-induced PINK1-AS overexpression contributes to the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via ALDOA-mediated glycolysis
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
PretiMeth: precise prediction models for DNA methylation based on single methylation mark
BMC Genomics (2020)
-
Bone marrow niche-derived extracellular matrix-degrading enzymes influence the progression of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Leukemia (2020)