Abstract
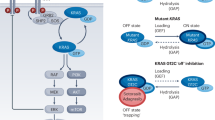
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been documented to have substantial clinical benefits to non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation. TKI resistance occurs in nearly all patients who receive TKI-targeting therapy, resulting in a modest overall survival benefit. Therefore, establishing a biomarker for early prediction and exploring the mechanism of primary TKI resistance is essential for improving the therapeutic efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer patients. In this study, we provide evidence indicating that paxillin (PXN) overexpression may confer TKI resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer cells. Mechanistically, PXN-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) activation is responsible for TKI resistance via decreased Bcl2-interacting mediator of cell death (BIM) and increased Mcl-1 expression due to modulating their protein stabilities by phosphorylation of BIM at serine 69 and Mcl-1 at threonine 163. The mechanistic action in the cell model was further confirmed by the observation of xenograft tumors in nude mice, revealing that the PXN-mediated TKI resistance was conquered by ERK inhibitor (AZD6244) and Bcl-2 family inhibitor (obatoclax), but the TKI resistance overcome by AZD6244 is more effective than that of obatoclax. Therefore, we suggest that PXN expression may be useful in predicting primary TKI resistance, and combining TKI with ERK inhibitors may clinically benefit EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients whose tumors exhibit high PXN expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013; 63: 11–30.
Pao W, Chmielecki J . Rational, biologically based treatment of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 760–774.
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA . Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 169–181.
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 786–792.
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA, Riely GJ, Somwar R, Zakowski MF et al. Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Med 2005; 2: e73.
Sharma SV, Lee DY, Li B, Quinlan MP, Takahashi F, Maheswaran S et al. A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 2010; 141: 69–80.
Engelman JA, Mukohara T, Zejnullahu K, Lifshits E, Borras AM, Gale CM et al. Allelic dilution obscures detection of a biologically significant resistance mutation in EGFR-amplified lung cancer. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 2695–2706.
Huang MH, Lee JH, Chang YJ, Tsai HH, Lin YL, Lin AM et al. MEK inhibitors reverse resistance in epidermal growth factor receptor mutation lung cancer cells with acquired resistance to gefitinib. Mol Oncol 2013; 7: 112–120.
Ochi N, Takigawa N, Harada D, Yasugi M, Ichihara E, Hotta K et al. Src mediates ERK reactivation in gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Cell Res 2014; 322: 168–177.
Kim HR, Lee SY, Hyun DS, Lee MK, Lee HK, Choi CM et al. Detection of EGFR mutations in circulating free DNA by PNA-mediated PCR clamping. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2013; 32: 50.
Song JY, Kim CS, Lee JH, Jang SJ, Lee SW, Hwang JJ et al. Dual inhibition of MEK1/2 and EGFR synergistically induces caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in EGFR inhibitor-resistant lung cancer cells via BIM upregulation. Invest New Drugs 2013; 31: 1458–1465.
Ewings KE, Wiggins CM, Cook SJ . Bim and the pro-survival Bcl-2 proteins: opposites attract, ERK repels. Cell Cycle 2007; 6: 2236–2240.
Wu DW, Wu TC, Wu JY, Cheng YW, Chen YC, Lee MC et al. Phosphorylation of paxillin confers cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via activating ERK-mediated Bcl-2 expression. Oncogene 2013; 33: 4385–4395.
de Bruin EC, Cowell C, Warne PH, Jiang M, Saunders RE, Melnick MA et al. Reduced NF1 expression confers resistance to EGFR inhibition in lung cancer. Cancer Discov 2014; 4: 606–619.
Luciano F, Jacquel A, Colosetti P, Herrant M, Cagnol S, Pages G et al. Phosphorylation of Bim-EL by Erk1/2 on serine 69 promotes its degradation via the proteasome pathway and regulates its proapoptotic function. Oncogene 2003; 22: 6785–6793.
Booy EP, Henson ES, Gibson SB . Epidermal growth factor regulates Mcl-1 expression through the MAPK-Elk-1 signalling pathway contributing to cell survival in breast cancer. Oncogene 2011; 30: 2367–2378.
Zhao J, Xin M, Wang T, Zhang Y, Deng X . Nicotine enhances the antiapoptotic function of Mcl-1 through phosphorylation. Mol Cancer Res 2009; 7: 1954–1961.
Nifoussi SK, Vrana JA, Domina AM, De Biasio A, Gui J, Gregory MA et al. Thr 163 phosphorylation causes Mcl-1 stabilization when degradation is independent of the adjacent GSK3-targeted phosphodegron, promoting drug resistance in cancer. PLoS One 2012; 7: e47060.
Liao M, Zhao J, Wang T, Duan J, Zhang Y, Deng X . Role of bile salt in regulating Mcl-1 phosphorylation and chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer 2011; 10: 44.
Hubner A, Barrett T, Flavell RA, Davis RJ . Multisite phosphorylation regulates Bim stability and apoptotic activity. Mol Cell 2008; 30: 415–425.
Nguyen M, Marcellus RC, Roulston A, Watson M, Serfass L, Murthy Madiraju SR et al. Small molecule obatoclax (GX15-070) antagonizes MCL-1 and overcomes MCL-1-mediated resistance to apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 19512–19517.
Vela L, Gonzalo O, Naval J, Marzo I . Direct interaction of Bax and Bak proteins with Bcl-2 homology domain 3 (BH3)-only proteins in living cells revealed by fluorescence complementation. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 4935–4946.
Faber AC, Corcoran RB, Ebi H, Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Chung E et al. BIM expression in treatment-naive cancers predicts responsiveness to kinase inhibitors. Cancer Discov 2011; 1: 352–365.
Garofalo M, Romano G, Di Leva G, Nuovo G, Jeon YJ, Ngankeu A et al. EGFR and MET receptor tyrosine kinase-altered microRNA expression induces tumorigenesis and gefitinib resistance in lung cancers. Nat Med 2012; 18: 74–82.
Costa DB, Kobayashi S, Tenen DG, Huberman MS . Pooled analysis of the prospective trials of gefitinib monotherapy for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer 2007; 58: 95–103.
Ng KP, Hillmer AM, Chuah CT, Juan WC, Ko TK, Teo AS et al. A common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nat Med 2012; 18: 521–528.
Wang J, Zhou JY, Wu GS . Bim protein degradation contributes to cisplatin resistance. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 22384–22392.
Costa DB, Halmos B, Kumar A, Schumer ST, Huberman MS, Boggon TJ et al. BIM mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med 2007; 4: 1669–1679.
Wu DW, Tsai LH, Chen PM, Lee MC, Wang L, Chen CY et al. Loss of TIMP-3 promotes tumor invasion via elevated IL-6 production and predicts poor survival and relapse in HPV-infected non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Pathol 2012; 181: 1796–1806.
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by grants from the National Health Research Institute (NHRI-EX103-10328BI) and the National Science Council (NSC100-2314-B-038-043-MY3) of Taiwan, ROC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, DW., Chen, CY., Chu, CL. et al. Paxillin confers resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant lung cancers via modulating BIM and Mcl-1 protein stability. Oncogene 35, 621–630 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.120
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.120
This article is cited by
-
Bcl-2 inhibition combined with PPARα activation synergistically targets leukemic stem cell-like cells in acute myeloid leukemia
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
DeepInsight-3D architecture for anti-cancer drug response prediction with deep-learning on multi-omics
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Long non-coding RNA CASC9 promotes gefitinib resistance in NSCLC by epigenetic repression of DUSP1
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Long noncoding RNA PXN-AS1-L promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression via regulating PXN
Cancer Cell International (2019)
-
The MBNL3 splicing factor promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing PXN expression through the alternative splicing of lncRNA-PXN-AS1
Nature Cell Biology (2017)