Abstract
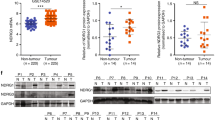
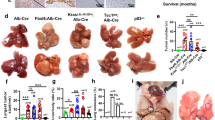
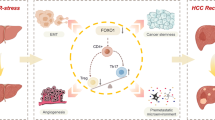
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is believed to arise from tumor-initiating cells (T-ICs), which are responsible for tumor relapse and metastases. Portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT) is raised from HCC and strongly correlated to a poor prognosis. However, the mechanism underling the formation of PVTT is largely unknown. Herein, we provide evidence that RNA polymerase II subunit 5 (RPB5)-mediating protein (RMP) was progressively upregulated in PVTT and overexpressed RMP appeared to increase T-ICs self-renewal. Moreover, RMP promoted metastases of PVTT cells and HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Knockdown of RMP attenuated T-ICs self-renewal and reversed epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in HCC and PVTT cells. The neutralizing assays suggested that interleukin-6 (IL-6) had an indispensable role in RMP regulating metastases and self-renewal of HCC cells. Furthermore, the transcription of IL-6 was verified to be modulated by RMP via interaction with p65 and RPB5, through which expanding the T-IC/cancer stem cell populations, as well as inducing EMT was promoted. These results suggested that RMP may promote PVTT formation by promoting IL-6 transcription. Thus, RMP serves as a potent factor contributed to develop PVTT and a promising therapeutic target for HCC patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM . Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 2010; 127: 2893–2917.
Portolani N, Coniglio A, Ghidoni S, Giovanelli M, Benetti A, Tiberio GA et al. Early and late recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Ann Surg 2006; 243: 229–235.
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M, Cleries R . Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology 2004; 127: S5–S16.
Weinstein IB . Cancer. Addiction to oncogenes–the Achilles heal of cancer. Science 2002; 297: 63–64.
He G, Karin M . NF-kappaB and STAT3—key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res 2011; 21: 159–168.
Naugler WE, Sakurai T, Kim S, Maeda S, Kim K, Elsharkawy AM et al. Gender disparity in liver cancer due to sex differences in MyD88-dependent IL-6 production. Science 2007; 317: 121–124.
Johnson C, Han Y, Hughart N, McCarra J, Alpini G, Meng F . Interleukin-6 and its receptor, key players in hepatobiliary inflammation and cancer. Transl Gastrointest Cancer 2012; 1: 58–70.
Yamashita T, Honda M, Nio K, Nakamoto Y, Takamura H, Tani T et al. Oncostatin m renders epithelial cell adhesion molecule-positive liver cancer stem cells sensitive to 5-Fluorouracil by inducing hepatocytic differentiation. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 4687–4697.
Lee TK, Castilho A, Cheung VC, Tang KH, Ma S, Ng IO . CD24(+) liver tumor-initiating cells drive self-renewal and tumor initiation through STAT3-mediated NANOG regulation. Cell Stem Cell 2011; 9: 50–63.
Dorjsuren D, Lin Y, Wei W, Yamashita T, Nomura T, Hayashi N et al. RMP, a novel RNA polymerase II subunit 5-interacting protein, counteracts transactivation by hepatitis B virus X protein. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 7546–7555.
Parusel CT, Kritikou EA, Hengartner MO, Krek W, Gotta M . URI-1 is required for DNA stability in C. elegans. Development 2006; 133: 621–629.
Theurillat JP, Metzler SC, Henzi N, Djouder N, Helbling M, Zimmermann AK et al. URI is an oncogene amplified in ovarian cancer cells and is required for their survival. Cancer Cell 2011; 19: 317–332.
Wei W, Dorjsuren D, Lin Y, Qin W, Nomura T, Hayashi N et al. Direct interaction between the subunit RAP30 of transcription factor IIF (TFIIF) and RNA polymerase subunit 5, which contributes to the association between TFIIF and RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 12266–12273.
Yang S, Wang H, Guo Y, Chen S, Zhang MY, Shen J et al. RMP plays distinct roles in the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and normal hepatic cells. Int J Biol Sci 2013; 9: 637–648.
Wang Q, Tan YX, Ren YB, Dong LW, Xie ZF, Tang L et al. Zinc finger protein ZBTB20 expression is increased in hepatocellular carcinoma and associated with poor prognosis. BMC Cancer 2011; 11: 271.
Baccelli I, Trumpp A . The evolving concept of cancer and metastasis stem cells. J Cell Biol 2012; 198: 281–293.
Ji J, Wang XW . Clinical implications of cancer stem cell biology in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Oncol 2012; 39: 461–472.
Spooren A, Kooijman R, Lintermans B, Van Craenenbroeck K, Vermeulen L, Haegeman G et al. Cooperation of NFkappaB and CREB to induce synergistic IL-6 expression in astrocytes. Cell Signal 2010; 22: 871–881.
Yoon S, Woo SU, Kang JH, Kim K, Kwon MH, Park S et al. STAT3 transcriptional factor activated by reactive oxygen species induces IL6 in starvation-induced autophagy of cancer cells. Autophagy 2010; 6: 1125–1138.
Zhang Y, Bharadwaj U, Logsdon CD, Chen C, Yao Q, Li M . ZIP4 regulates pancreatic cancer cell growth by activating IL-6/STAT3 pathway through zinc finger transcription factor CREB. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 1423–1430.
dGM Acker J, Cheynel I, Khazak V, Kedinger C, Vigneron M . Interactions between the human RNA polymerase II subunits. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 16815–16821.
Wang T, Hu HS, Feng YX, Shi J, Li N, Guo WX et al. Characterisation of a novel cell line (CSQT-2) with high metastatic activity derived from portal vein tumour thrombus of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer 2010; 102: 1618–1626.
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Wang G, Struhl K . Inducible formation of breast cancer stem cells and their dynamic equilibrium with non-stem cancer cells via IL6 secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 1397–1402.
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008; 133: 704–715.
Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE, Vesuna F, Raman V, Ramirez N et al. Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2009; 28: 2940–2947.
Xiang WQ, Feng WF, Ke W, Sun Z, Chen Z, Liu W . Hepatitis B virus X protein stimulates IL-6 expression in hepatocytes via a MyD88-dependent pathway. J Hepatol 2011; 54: 26–33.
He G, Dhar D, Nakagawa H, Font-Burgada J, Ogata H, Jiang Y et al. Identification of liver cancer progenitors whose malignant progression depends on autocrine IL-6 signaling. Cell 2013; 155: 384–396.
Jang JW, Oh BS, Kwon JH, You CR, Chung KW, Kay CS et al. Serum interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein as a prognostic indicator in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cytokine 2012; 60: 686–693.
Nakagawa H, Maeda S, Yoshida H, Tateishi R, Masuzaki R, Ohki T et al. Serum IL-6 levels and the risk for hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis C patients: an analysis based on gender differences. Int J Cancer 2009; 125: 2264–2269.
Wong VW, Yu J, Cheng AS, Wong GL, Chan HY, Chu ES et al. High serum interleukin-6 level predicts future hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Int J Cancer 2009; 124: 2766–2770.
Dong LW, Hou YJ, Tan YX, Tang L, Pan YF, Wang M et al. Prognostic significance of Beclin 1 in intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma. Autophagy 2011; 7: 1222–1229.
Wong CM, Yam JW, Ching YP, Yau TO, Leung TH, Jin DY et al. Rho GTPase-activating protein deleted in liver cancer suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 8861–8868.
Acknowledgements
We thank Liang Tang, Dong-Ping Hu, Shan-Na Huang, Dan-Dan Huang, Shan-Hua Tang, Lin-Na Guo and Huan-Lin Sun for technical assistance. We thank Dr Xiao-Ni Kong for providing luciferase reporter constructs and Ad-caSTAT3 virus. This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81370066, 81372355, 81001075, 91229205, BWS11J036), the Funds for Creative Research Groups of China (81221061) and the State Key Project for Liver Cancer (2012ZX10002–009, 2013ZX10002–010), Stem Cell and Medicine Research Center’s Innovation Research Program of the Second Military Medical University (SCMRC1306).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Pan, YF., Ding, ZW. et al. RMP promotes venous metastases of hepatocellular carcinoma through promoting IL-6 transcription. Oncogene 34, 1575–1583 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.84
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.84
This article is cited by
-
URI alleviates tyrosine kinase inhibitors-induced ferroptosis by reprogramming lipid metabolism in p53 wild-type liver cancers
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Portal vein tumor thrombosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanism and therapy
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2023)
-
Discovery of synthetic lethal interactions from large-scale pan-cancer perturbation screens
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Exosomal S100A4 derived from highly metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cells promotes metastasis by activating STAT3
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)
-
Detection of promoter methylation status of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) in tissue and plasma from Chinese patients with different hepatic diseases
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2018)