Abstract
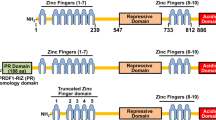
Friend leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia-1 (Fli-1), an E26 transformation specific (ETS) transcription factor, was isolated a quarter century ago through a retrovirus mutagenesis screen. Fli-1 has since been recognized to play critical roles in normal development and homeostasis. For example, it transcriptionally regulates genes that drive normal hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis. Indeed, Fli-1 is one of 10 key regulators of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell maintenance and differentiation. Aberrant expression of Fli-1 also underlies a number of virally induced leukemias, including Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia and various types of human cancers, and it is the target of chromosomal translocations in childhood Ewing's sarcoma. Abnormal expression of Fli-1 is important in the etiology of autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis. These studies establish Fli-1 as a strong candidate for drug development. Despite difficulties in targeting transcription factors, recent studies identified small-molecule inhibitors for Fli-1. Here we review past and ongoing research on Fli-1 with emphasis on its mechanistic function in autoimmune disease and malignant transformation. The significance of identifying Fli-1 inhibitors and their clinical applications for treatment of disease and cancer with deregulated Fli-1 expression are discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-David Y, Giddens EB, Bernstein A . Identification and mapping of a common proviral integration site Fli-1 in erythroleukemia cells induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87: 1332–1336.
Ben-David Y, Giddens EB, Letwin K, Bernstein A . Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev 1991; 5: 908–918.
Bergeron D, Poliquin L, Houde J, Barbeau B, Rassart E . Analysis of proviruses integrated in Fli-1 and Evi-1 regions in Cas-Br-E MuLV-induced non-T-, non-B-cell leukemias. Virology 1992; 191: 661–669.
Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B, Desmaze C, Melot T, Peter M et al. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature 1992; 359: 162–165.
Ordóñez JL, Osuna D, Herrero D, de Alava E, Madoz-Gúrpide J, Ordóñez JL et al. Advances in Ewing's sarcoma research: where are we now and what lies ahead? Cancer Res 2009; 69: 7140–7150.
Leavey PJ, Collier AB . Ewing sarcoma: prognostic criteria, outcomes and future treatment. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2008; 8: 617–624.
Riggi N, Stamenkovic I . The Biology of Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Lett 2007; 254: 1–10.
Owen LA, Lessnick SL . Identification of target genes in their native cellular context: an analysis of EWS/FLI in Ewing's sarcoma. Cell Cycle 2006; 5: 2049–2053.
Laudet V, Hänni C, Stéhelin D, Duterque-Coquillaud M . Molecular phylogeny of the ETS gene family. Oncogene 1999; 18: 1351–1359.
Schütte J, Moignard V, Göttgens B . Establishing the stem cell state: insights from regulatory network analysis of blood stem cell development. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2012; 4: 285–295.
Wilson NK, Foster SD, Wang X, Knezevic K, Schütte J, Kaimakis P et al. Combinatorial transcriptional control in blood stem/progenitor cells: genome-wide analysis of ten major transcriptional regulators. Cell Stem Cell 2010; 7: 532–544.
Wei GH, Badis G, Berger MF, Kivioja T, Palin K, Enge M et al. Genome-wide analysis of ETS-family DNA-binding in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J 2010; 29: 2147–2160.
Camões MJ, Paulo P, Ribeiro FR, Barros-Silva JD, Almeida M, Costa VL et al. Potential downstream target genes of aberrant ETS transcription factors are differentially affected in Ewing's sarcoma and prostate carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e49819.
Starck J, Weiss-Gayet M, Gonnet C, Guyot B, Vicat JM, Morlé F . Inducible Fli-1 gene deletion in adult mice modifies several myeloid lineage commitment decisions and accelerates proliferation arrest and terminal erythrocytic differentiation. Blood 2010; 116: 4795–4805.
Carmichael CL, Metcalf D, Henley KJ, Kruse EA, Di Rago L, Mifsud S et al. Hematopoietic overexpression of the transcription factor Erg induces lymphoid and erythro-megakaryocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 15437–15442.
Kruse EA, Loughran SJ, Baldwin TM, Josefsson EC, Ellis S, Watson DK et al. Dual requirement for the ETS transcription factors Fli-1 and Erg in hematopoietic stem cells and the megakaryocyte lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 13814–13819.
Pusztaszeri MP, Seelentag W, Bosman FT . Immunohistochemical expression of endothelial markers CD31, CD34, von Willebrand factor, and Fli-1 in normal human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 2006; 54: 385–395.
Hewett PW, Nishi K, Daft EL, Clifford MJ . Selective expression of erg isoforms in human endothelial cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2001; 33: 347–355.
Mélet F, Motro B, Rossi DJ, Zhang L, Bernstein A . Generation of a novel Fli-1 protein by gene targeting leads to a defect in thymus development and a delay in Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16: 2708–2718.
Tamir A, Howard J, Higgins RR, Li YJ, Berger L, Zacksenhaus E et al. Fli-1, an Ets-related transcription factor, regulates erythropoietin-induced erythroid proliferation and differentiation: evidence for direct transcriptional repression of the Rb gene during differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 4452–4464.
Zochodne B, Truong AH, Stetler K, Higgins RR, Howard J, Dumont D et al. Epo regulates erythroid proliferation and differentiation through distinct signaling pathways: implication for erythropoiesis and Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia. Oncogene 2000; 19: 2296–2304.
Masuya M, Moussa O, Abe T, Deguchi T, Higuchi T, Ebihara Y et al. Dysregulation of granulocyte, erythrocyte, and NK cell lineages in Fli-1 gene-targeted mice. Blood 2005; 105: 95–102.
Spyropoulos DD, Pharr PN, Lavenburg KR, Jackers P, Papas TS, Ogawa M et al. Hemorrhage, impaired hematopoiesis, and lethality in mouse embryos carrying a targeted disruption of the Fli1 transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 5643–5652.
Anderson MK, Hernandez-Hoyos G, Diamond RA, Rothenberg EV . Precise developmental regulation of Ets family transcription factors during specification and commitment to the T cell lineage. Development 1999; 126: 3131–3148.
Svenson JL, Chike-Harris K, Amria MY, Nowling TK . The mouse and human Fli1 genes are similarly regulated by Ets factors in T cells. Genes Immun 2010; 11: 161–172.
Hart A, Melet F, Grossfeld P, Chien K, Jones C, Tunnacliffe A et al. Fli-1 is required for murine vascular and megakaryocytic development and is hemizygously deleted in patients with thrombocytopenia. Immunity 2000; 13: 167–177.
Smeets MF, Chan AC, Dagger S, Bradley CK, Wei A, Izon DJ . Fli-1 overexpression in hematopoietic progenitors deregulates T cell development and induces pre-T cell lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e62346.
Zhang L, Eddy A, Teng YT, Fritzler M, Kluppel M, Melet F et al. An immunological renal disease in transgenic mice that overexpress Fli-1, a member of the ets family of transcription factor genes. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15: 6961–6970.
Moussa O, LaRue AC, Abangan RS Jr., Williams CR, Zhang XK, Masuya M et al. Thrombocytopenia in mice lacking the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain of the Ets transcription factor Fli1. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 5194–5206.
Zhang XK, Moussa O, LaRue A, Bradshaw S, Molano I, Spyropoulos DD et al. The transcription factor Fli-1 modulates marginal zone and follicular B cell development in mice. J Immunol 2008; 181: 1644–1654.
Bradshaw S, Zheng WJ, Tsoi LC, Gilkeson G, Zhang XK . A role for Fli-1 in B cell proliferation: implications for SLE pathogenesis. Clin Immunol 2008; 129: 19–30.
Okada Y, Nobori H, Shimizu M, Watanabe M, Yonekura M, Nakai T et al. Multiple ETS family proteins regulate PF4 gene expression by binding to the same ETS binding site. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e24837.
Krishnamurti L, Neglia JP, Nagarajan R, Berry SA, Lohr J, Hirsch B et al. Paris-Trousseau syndrome platelets in a child with Jacobsen's syndrome. Am J Hematol 2001; 66: 295–299.
Favier R, Jondeau K, Boutard P, Grossfeld P, Reinert P, Jones C et al. Paris-Trousseau syndrome: clinical, hematological, molecular data of ten new cases. Thromb Haemost 2003; 90: 893–897.
Wenger SL, Grossfeld PD, Siu BL, Coad JE, Keller FG, Hummel M . Molecular characterization of an 11q interstitial deletion in a patient with the clinical features of Jacobsen syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 2006; 140: 704–708.
Gosiengfiao Y, Horvat R, Thompson A . Transcription factors GATA-1 and Fli-1 regulate human HOXA10 expression in megakaryocytic cells. DNA Cell Biol 2007; 26: 577–587.
Stockley J, Morgan NV, Bem D, Lowe GC, Lordkipanidzé M, Dawood B et al. Enrichment of FLI1 and RUNX1 mutations in families with excessive bleeding and platelet dense granule secretion defects. Blood 2013; 122: 4090–4093.
Suzuki E, Williams S, Sato S, Gilkeson G, Watson DK, Zhang XK . The transcription factor Fli-1 regulates monocyte, macrophage and dendritic cell development in mice. Immunology 2013; 139: 318–327.
Remy P, Sénan F, Meyer D, Mager AM, Hindelang C . Overexpression of the Xenopus Xl-fli gene during early embryogenesis leads to anomalies in head and heart development and erythroid differentiation. Int J Dev Biol 1996; 40: 577–589.
Meyer D, Wolff CM, Stiegler P, Sénan F, Befort N, Befort JJ et al. Xl-fli, the Xenopus homologue of the fli-1 gene, is expressed during embryogenesis in a restricted pattern evocative of neural crest cell distribution. Mech Dev 1993; 44: 109–121.
Brown LA, Rodaway AR, Schilling TF, Jowett T, Ingham PW, Patient RK et al. Insights into early vasculogenesis revealed by expression of the ETS-domain transcription factor Fli-1 in wild-type and mutant zebrafish embryos. Mech Dev 2000; 90: 237–252.
Lawson ND, Weinstein BM . In vivo imaging of embryonic vascular development using transgenic zebrafish. Dev Biol 2002; 248: 307–318.
Pham VN, Lawson ND, Mugford JW, Dye L, Castranova D, Lo B et al. Combinatorial function of ETS transcription factors in the developing vasculature. Dev Biol 2007; 303: 772–783.
Liu F, Patient R . Genome-wide analysis of the zebrafish ETS family identifies three genes required for hemangioblast differentiation or angiogenesis. Circ Res 2008; 103: 1147–1154.
Liu F, Walmsley M, Rodaway A, Patient R . Fli1 acts at the top of the transcriptional network driving blood and endothelial development. Curr Biol 2008; 18: 1234–1240.
Li L, Chen D, Li J, Wang X, Wang N, Xu C et al. Aggf1 acts at the top of the genetic regulatory hierarchy in specification of hemangioblasts in zebrafish. Blood 2013; 123: 501–508.
Pimanda JE, Chan WY, Donaldson IJ, Bowen M, Green AR, Göttgens B . Endoglin expression in the endothelium is regulated by Fli-1, Erg, and Elf-1 acting on the promoter and a −8-kb enhancer. Blood 2006; 107: 4737–4745.
Landry JR, Kinston S, Knezevic K, Donaldson IJ, Green AR, Göttgens B . Fli1, Elf1, and Ets1 regulate the proximal promoter of the LMO2 gene in endothelial cells. Blood 2005; 106: 2680–2687.
Göttgens B, Broccardo C, Sanchez MJ, Deveaux S, Murphy G, Göthert JR et al. The scl +18/19 stem cell enhancer is not required for hematopoiesis: identification of a 5' bifunctional hematopoietic-endothelial enhancer bound by Fli-1 and Elf-1. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 1870–1883.
Göttgens B, Nastos A, Kinston S, Piltz S, Delabesse EC, Stanley M et al. Establishing the transcriptional programme for blood: the SCL stem cell enhancer is regulated by a multiprotein complex containing Ets and GATA factors. EMBO J 2002; 21: 3039–3050.
Heo SH, Choi YJ, Ryoo HM, Cho JY . Expression profiling of ETS and MMP factors in VEGF-activated endothelial cells: role of MMP-10 in VEGF-induced angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol 2010; 224: 734–742.
De Val S, Black BL . Transcriptional control of endothelial cell development. Dev Cell 2009; 16: 180–195.
McLaughlin F, Ludbrook VJ, Cox J, von Carlowitz I, Brown S, Randi AM . Combined genomic and antisense analysis reveals that the transcription factor Erg is implicated in endothelial cell differentiation. Blood 2001; 98: 3332–3339.
Ginsberg M, James D, Ding BS, Nolan D, Geng F, Butler JM et al. Efficient direct reprogramming of mature amniotic cells into endothelial cells by ETS factors and TGFβ suppression. Cell 2012; 151: 559–575.
Le Bras A, Samson C, Trentini M, Caetano B, Lelievre E, Mattot V et al. VE-statin/egfl7 expression in endothelial cells is regulated by a distal enhancer and a proximal promoter under the direct control of Erg and GATA-2. PLoS ONE 2010; 5: e12156.
Soncin F, Mattot V, Lionneton F, Spruyt N, Lepretre F, Begue A et al. VE-statin, an endothelial repressor of smooth muscle cell migration. EMBO J 2003; 22: 5700–5711.
Lelièvre E, Lionneton F, Mattot V, Spruyt N, Soncin F . Ets-1 regulates fli-1 expression in endothelial cells. Identification of ETS binding sites in the fli-1 gene promoter. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 25143–25151.
Georgiou P, Maroulakou I, Green J, Dantis P, Romanospica V, Kottaridis S et al. Expression of ets family of genes in systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjogren's syndrome. Int J Oncol 1996; 9: 9–18.
Zhang XK, Gallant S, Molano I, Moussa OM, Ruiz P, Spyropoulos DD et al. Decreased expression of the Ets family transcription factor Fli-1 markedly prolongs survival and significantly reduces renal disease in MRL/lpr mice. J Immunol 2004; 173: 6481–6489.
Mathenia J, Reyes-Cortes E, Williams S, Molano I, Ruiz P, Watson DK et al. Impact of Fli-1 transcription factor on autoantibody and lupus nephritis in NZM2410 mice. Clin Exp Immunol 2010; 162: 362–371.
Suzuki E, Karam E, Williams S, Watson DK, Gilkeson G, Zhang XK . Fli-1 transcription factor affects glomerulonephritis development by regulating expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in endothelial cells in the kidney. Clin Immunol 2012; 145: 201–208.
Molano I, Mathenia J, Ruiz P, Gilkeson GS, Zhang XK . Decreased expression of Fli-1 in bone marrow-derived haematopoietic cells significantly affects disease development in Murphy Roths Large/lymphoproliferation (MRL/lpr) mice. Clin Exp Immunol 2010; 160: 275–282.
Nowling TK, Fulton JD, Chike-Harris K, Gilkeson GS . Ets factors and a newly identified polymorphism regulate Fli1 promoter activity in lymphocytes. Mol Immunol 2008; 45: 1–12.
Morris EE, Amria MY, Kistner-Griffin E, Svenson JL, Kamen DL, Gilkeson GS et al. A GA microsatellite in the Fli1 promoter modulates gene expression and is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus patients without nephritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2010; 12: R212.
Sakthianandeswaren A, Curtis JM, Elso C, Kumar B, Baldwin TM, Lopaticki S et al. Fine mapping of Leishmania major susceptibility Locus lmr2 and evidence of a role for Fli1 in disease and wound healing. Infect Immun 2010; 78: 2734–2744.
Tani C, Bellando Randone S, Guiducci S, Della Rossa A . Systemic sclerosis: a critical digest of the recent literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2013; 31: 172–179.
Wang Y, Fan PS, Kahaleh B . Association between enhanced type I collagen expression and epigenetic repression of the FLI1 gene in scleroderma fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 2271–2279.
Asano Y, Bujor AM, Trojanowska M . The impact of Fli1 deficiency on the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. J Dermatol Sci 2010; 59: 153–162.
Asano Y, Stawski L, Hant F, Highland K, Silver R, Szalai G et al. Endothelial Fli1 deficiency impairs vascular homeostasis: a role in scleroderma vasculopathy. Am J Pathol 2010; 176: 1983–1998.
Bujor AM, Asano Y, Haines P, Lafyatis R, Trojanowska M . The c-Abl tyrosine kinase controls protein kinase Cδ-induced Fli-1 phosphorylation in human dermal fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 2011; 63: 1729–1737.
Asano Y, Trojanowska M . Phosphorylation of Fli1 at threonine 312 by protein kinase C delta promotes its interaction with p300/CREB-binding protein-associated factor and subsequent acetylation in response to transforming growth factor beta. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 1882–1894.
Asano Y, Czuwara J, Trojanowska M . Transforming growth factor-beta regulates DNA binding activity of transcription factor Fli1 by p300/CREB-binding protein-associated factor-dependent acetylation. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 34672–34683.
Noda S, Asano Y, Akamata K, Aozasa N, Taniguchi T, Takahashi T et al. Constitutive activation of c-Abl/protein kinase C-δ/Fli1 pathway in dermal fibroblasts derived from patients with localized scleroderma. Br J Dermatol 2012; 167: 1098–1105.
Elkareh J, Periyasamy SM, Shidyak A, Vetteth S, Schroeder J, Raju V et al. Marinobufagenin induces increases in procollagen expression in a process involving protein kinase C and Fli-1: implications for uremic cardiomyopathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2009; 296: F1219–F1226.
Haller ST, Kennedy DJ, Shidyak A, Budny GV, Malhotra D, Fedorova OV et al. Monoclonal antibody against marinobufagenin reverses cardiac fibrosis in rats with chronic renal failure. Am J Hypertens 2012; 25: 690–696.
Nikitina ER, Mikhailov AV, Nikandrova ES, Frolova EV, Fadeev AV, Shman VV et al. In preeclampsia endogenous cardiotonic steroids induce vascular fibrosis and impair relaxation of umbilical arteries. J Hypertens 2011; 29: 769–776.
Ott DE, Keller J, Rein A . 10A1 MuLV induces a murine leukemia that expresses hematopoietic stem cell markers by a mechanism that includes fli-1 integration. Virology 1994; 205: 563–568.
Prassad DD, Rao VN, Reddy ES . Structure and expression of human Fli-1 gene. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 5833–5837.
Watson DK, Smyth FE, Thompson DM, Cheng JQ, Testa JR, Papas TS et al. The ERGB/Fli-1 gene: isolation and characterization of a new member of the family of human ETS transcription factors. Cell Growth Differ 1992; 3: 705–713.
Ano S, Pereira R, Pironin M, Lesault I, Milley C, Lebigot I et al. Erythroblast transformation by FLI-1 depends upon its specific DNA binding and transcriptional activation properties. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 2993–3002.
Athanasiou M, Mavrothalassitis G, Sun-Hoffman L, Blair DG . FLI-1 is a suppressor of erythroid differentiation in human hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 2000; 14: 439–445.
Pereira R, Quang CT, Lesault I, Dolznig H, Beug H, Ghysdael J . FLI-1 inhibits differentiation and induces proliferation of primary erythroblasts. Oncogene 1999; 18: 1597–1608.
Lee CR, Cervi D, Truong AH, Li YJ, Sarkar A, Ben-David Y . Friend virus-induced erythroleukemias: a unique and well-defined mouse model for the development of leukemia. Anticancer Res 2003; 23: 2159–2166.
Torchia EC, Boyd K, Rehg JE, Qu C, Baker SJ . EWS/FLI-1 induces rapid onset of myeloid/erythroid leukemia in mice. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 7918–7934.
Lesault I, Quang CT, Frampton J, Ghysdael J . Direct regulation of BCL-2 by FLI-1 is involved in the survival of FLI-1-transformed erythroblasts. EMBO J 2002; 21: 694–703.
Truong AH, Cervi D, Lee J, Ben-David Y . Direct transcriptional regulation of MDM2 by Fli-1. Oncogene 2005; 24: 962–969.
Wong KS, Li YJ, Howard J, Ben-David Y . Loss of p53 in F-MuLV induced-erythroleukemias accelerates the acquisition of mutational events that confers immortality and growth factor independence. Oncogene 1999; 18: 5525–5534.
Li Y, Tanaka K, Fan X, Nakatani F, Li X, Nakamura T, Takasaki M et al. Inhibition of the transcriptional function of p53 by EWS-Fli1 chimeric protein in Ewing Family Tumors. Cancer Lett 2010; 294: 57–65.
Ban J, Bennani-Baiti IM, Kauer M, Schaefer KL, Poremba C, Jug G et al. EWS-FLI1 suppresses NOTCH-activated p53 in Ewing's sarcoma. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 7100–7109.
Lakhanpal GK, Vecchiarelli-Federico LM, Li YJ, Cui JW, Bailey ML, Spaner DE et al. The inositol phosphatase SHIP-1 is negatively regulated by Fli-1 and its loss accelerates leukemogenesis. Blood 2010; 116: 428–436.
Juban G, Giraud G, Guyot B, Belin S, Diaz JJ, Starck J et al. Spi-1 and Fli-1 directly activate common target genes involved in ribosome biogenesis in Friend erythroleukemic cells. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 2852–2864.
Klemsz MJ, Maki RA, Papayannopoulou T, Moore J, Hromas R . Characterization of the ets oncogene family member, fli-1. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 5769–5773.
Cui JW, Vecchiarelli-Federico LM, Li YJ, Wang GJ, Ben-David Y . Continuous Fli-1 expression plays an essential role in the proliferation and survival of F-MuLV-induced erythroleukemia and human erythroleukemia. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1311–1319.
Kornblau SM, Qiu YH, Zhang N, Singh N, Faderl S, Ferrajoli A et al. Abnormal expression of FLI1 protein is an adverse prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011; 118: 5604–5612.
Tyybäkinoja A, Saarinen-Pihkala U, Elonen E, Knuutila S . Amplified, lost, and fused genes in 11q23-25 amplicon in acute myeloid leukemia, an array-CGH study. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2006; 45: 257–264.
Kwiatkowski BA, Zielinska-Kwiatkowska AG, Bauer TR Jr., Hickstein DD . The ETS family member Tel antagonizes the Fli-1 phenotype in hematopoietic cells. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2000; 26: 84–90.
Kwiatkowski BA, Bastian LS, Bauer TR Jr., Tsai S, Zielinska-Kwiatkowska AG, Hickstein DD . The ets family member Tel binds to the Fli-1 oncoprotein and inhibits its transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 17525–17530.
Martens JH, Mandoli A, Simmer F, Wierenga BJ, Saeed S, Singh AA et al. ERG and FLI1 binding sites demarcate targets for aberrant epigenetic regulation by AML1-ETO in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2012; 120: 4038–4048.
Johnson AD, Pambuccian SE, Andrade RS, Dolan MM, Aslan DL . Ewing sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the esophagus: report of a case and review of literature. Int J Surg Pathol 2010; 18: 388–393.
Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Herrmann FR, Bshara W, Odunsi K, Terracciano L, Sauter G et al. Friend leukaemia integration-1 expression in malignant and benign tumours: a multiple tumour tissue microarray analysis using polyclonal antibody. J Clin Pathol 2007; 60: 694–700.
Sakurai T, Kondoh N, Arai M, Hamada J, Yamada T, Kihara-Negishi F et al. Functional roles of Fli-1, a member of the Ets family of transcription factors, in human breast malignancy. Cancer Sci 2007; 98: 1775–1784.
Torlakovic EE, Slipicevic A, Flørenes VA, Chibbar R, DeCoteau JF, Bilalovic N . Fli-1 expression in malignant melanoma. Histol Histopathol 2008; 23: 1309–1314.
Paula P, Barros-Silva JD, Ribeiro FR, Ramalho-Carvalho J, Jerónimo C, Henrique R et al. FLI1 is a novel ETS transcription factor involved in gene fusions in prostate cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012; 51: 240–249.
Cuda J, Mirzamani N, Kantipudi R, Robbins J, Welsch MJ, Sundram UN . Diagnostic utility of Fli-1 and D2-40 in distinguishing atypical fibroxanthoma from angiosarcoma. Am J Dermatopathol 2013; 35: 316–318.
Brown JG, Folpe AL, Rao P, Lazar AJ, Paner GP, Gupta R et al. Primary vascular tumors and tumor-like lesions of the kidney: a clinicopathologic analysis of 25 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2010; 34: 942–949.
Gill R, O'Donnell RJ, Horvai A . Utility of immunohistochemistry for endothelial markers in distinguishing epithelioid hemangioendothelioma from carcinoma metastatic to bone. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009; 133: 967–972.
Nagano A, Ohno T, Shimizu K, Hara A, Yamamoto T, Kawai G et al. EWS/Fli-1 chimeric fusion gene upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor-A. Int J Cancer 2010; 126: 2790–2798.
Shaked Y, Cervi D, Neuman M, Chen L, Klement G, Michaud CR et al. The splenic microenvironment is a source of proangiogenesis/inflammatory mediators accelerating the expansion of murine erythroleukemic cells. Blood 2005; 105: 4500–4507.
Boro A, Prêtre K, Rechfeld F, Thalhammer V, Oesch S, Wachtel M et al. Small-molecule screen identifies modulators of EWS/FLI1 target gene expression and cell survival in Ewing's sarcoma. Int J Cancer 2012; 131: 2153–2164.
Grohar PJ, Griffin LB, Yeung C, Chen QR, Pommier Y, Khanna C et al. Ecteinascidin 743 interferes with the activity of EWS-FLI1 in Ewing sarcoma cells. Neoplasia 2011; 13: 145–153.
Erkizan HV, Kong Y, Merchant M, Schlottmann S, Barber-Rotenberg JS, Yuan L et al. A small molecule blocking oncogenic protein EWS-FLI1 interaction with RNA helicase A inhibits growth of Ewing's sarcoma. Nat Med 2009; 15: 750–756.
Grohar PJ, Woldemichael GM, Griffin LB, Mendoza A, Chen QR, Yeung C et al. Identification of an inhibitor of the EWS-FLI1 oncogenic transcription factor by high-throughput screening. J Natl Cancer Inst 2011; 103: 962–978.
Li YJ, Zhao X, Vecchiarelli-Federico LM, Li Y, Datti A, Cheng Y et al. Drug-mediated inhibition of Fli-1 for the treatment of leukemia. Blood Cancer J 2012; 2: e54.
Bhatia S, Krailo MD, Chen Z, Burden L, Askin FB, Dickman PS et al. Therapy-related myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia after Ewing sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor of bone: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. Blood 2007; 109: 46–51.
Ladenstein R, Pötschger U, Le Deley MC, Whelan J, Paulussen M, Oberlin O et al. Primary disseminated multifocal Ewing sarcoma: results of the Euro-EWING 99 trial. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 3284–3291.
Miser JS, Krailo MD, Tarbell NJ, Link MP, Fryer CJ, Pritchard DJ et al. Treatment of metastatic Ewing's sarcoma or primitive neuroectodermal tumor of bone: evaluation of combination ifosfamide and etoposide–a Children's Cancer Group and Pediatric Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 2873–2876.
Zhang J, Guo H, Zhang H, Wang H, Qian G, Fan X et al. Putative tumor suppressor miR-145 inhibits colon cancer cell growth by targeting oncogene Friend leukemia virus integration 1 gene. Cancer 2011; 117: 86–95.
Ban J, Jug G, Mestdagh P, Schwentner R, Kauer M, Aryee DN et al. Hsa-mir-145 is the top EWS-FLI1-repressed microRNA involved in a positive feedback loop in Ewing's sarcoma. Oncogene 2011; 30: 2173–2180.
Bujor AM, Haines P, Padilla C, Christmann RB, Junie M, Sampaio-Barros PD et al. Ciprofloxacin has antifibrotic effects in scleroderma fibroblasts via downregulation of Dnmt1 and upregulation of Fli1. Int J Mol Med 2012; 30: 1473–1480.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Canadian Institute of Health Research to YB-D (MOP-110952), Canadian Breast Cancer Foundation to EZ, the Science and Technology Department of Guizhou Province innovation and project grants (6012, 4001) to YB-D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
These authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Luo, H., Liu, T. et al. The ets transcription factor Fli-1 in development, cancer and disease. Oncogene 34, 2022–2031 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.162
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.162
This article is cited by
-
FLI-1 is expressed in a wide variety of hematolymphoid neoplasms: a special concern in the differential diagnosis
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2024)
-
FLI1 regulates radiotherapy resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through TIE1-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
FLI1 and FRA1 transcription factors drive the transcriptional regulatory networks characterizing muscle invasive bladder cancer
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Current insights into the role of Fli-1 in hematopoiesis and malignant transformation
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
The microenvironment of pituitary adenomas: biological, clinical and therapeutical implications
Pituitary (2022)