Abstract
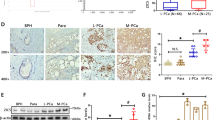
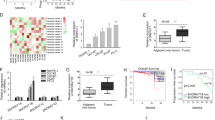
Characteristically, prostate cancer (PCa) cells exhibit marked decrease in intracellular zinc; however, the mechanism responsible is not clearly understood. HOXB13 is involved in PCa progression and is overexpressed in castration-resistant PCa. DNA microarray analysis of LNCaP Pca cells showed that ZnT zinc output transporters were strikingly upregulated among androgen-independent HOXB13 target genes. Furthermore, exogenous HOXB13 caused intracellular zinc concentrations to fall in PCa cells, stimulated NF-κB-mediated signaling by reducing inhibitor of NF-κB alpha (IκBα) and enhanced the nuclear translocation of RelA/p65. Human prostate tumors also exhibited strong inverse correlation between the protein expressions of HOXB13 and IκBα. Consequently, HOXB13 stimulated PCa cell invasion, and this was inhibited by the suppression of ZnT4. In addition, studies in a PC3 orthotopic mouse model of PCa metastasis showed that HOXB13 is a strong metastatic stimulator. Taken together, these results show that HOXB13 promotes PCa invasion and metastasis by decreasing intracellular zinc levels, thus stimulating NF-κB signals, and suggest that HOXB13 acts as a modulator of intracellular zinc levels that promotes the malignant characteristics of PCa.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abate-Shen C . Deregulated homeobox gene expression in cancer: cause or consequence? Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 777–785.
Economides KD, Capecchi MR . Hoxb13 is required for normal differentiation and secretory function of the ventral prostate. Development 2003; 130: 2061–2069.
Kim SD, Park RY, Kim YR, Kim IJ, Kang TW, Nam KI et al. HOXB13 is co-localized with androgen receptor to suppress androgen-stimulated prostate-specific antigen expression. Anat Cell Biol 2010; 43: 284–293.
Sreenath T, Orosz A, Fujita K, Bieberich CJ . Androgen-independent expression of hoxb-13 in the mouse prostate. Prostate 1999; 41: 203–207.
Kim YR, Oh KJ, Park RY, Xuan NT, Kang TW, Kwon DD et al. HOXB13 promotes androgen independent growth of LNCaP prostate cancer cells by the activation of E2F signaling. Mol Cancer 2010; 9: 124.
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013; 63: 11–30.
Chen CD, Welsbie DS, Tran C, Baek SH, Chen R, Vessella R et al. Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat Med 2004; 10: 33–39.
Linja MJ, Savinainen KJ, Saramaki OR, Tammela TL, Vessella RL, Visakorpi T . Amplification and overexpression of androgen receptor gene in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 3550–3555.
Edwards J, Krishna NS, Grigor KM, Bartlett JM . Androgen receptor gene amplification and protein expression in hormone refractory prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 2003; 89: 552–556.
Chen CD, Sawyers CL . NF-kappa B activates prostate-specific antigen expression and is upregulated in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 2862–2870.
Shukla S, Gupta S . Suppression of constitutive and tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activation and induction of apoptosis by apigenin in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells: correlation with down-regulation of NF-kappaB-responsive genes. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 3169–3178.
Suh J, Rabson AB . NF-kappaB activation in human prostate cancer: important mediator or epiphenomenon? J Cell Biochem 2004; 91: 100–117.
Sweeney C, Li L, Shanmugam R, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Jayaprakasan V, Baldridge LA et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB is constitutively activated in prostate cancer in vitro and is overexpressed in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 5501–5507.
Zhang L, Altuwaijri S, Deng F, Chen L, Lal P, Bhanot UK et al. NF-kappaB regulates androgen receptor expression and prostate cancer growth. Am J Pathol 2009; 175: 489–499.
Costello LC, Franklin RB . The clinical relevance of the metabolism of prostate cancer; zinc and tumor suppression: connecting the dots. Mol Cancer 2006; 5: 17.
Zaichick V, Sviridova TV, Zaichick SV . Zinc in the human prostate gland: normal, hyperplastic and cancerous. Int Urol Nephrol 1997; 29: 565–574.
Jung C, Kim RS, Zhang HJ, Lee SJ, Jeng MH . HOXB13 induces growth suppression of prostate cancer cells as a repressor of hormone-activated androgen receptor signaling. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 9185–9192.
Shaut CA, Saneyoshi C, Morgan EA, Knosp WM, Sexton DR, Stadler HS . HOXA13 directly regulates EphA6 and EphA7 expression in the genital tubercle vascular endothelia. Dev Dyn 2007; 236: 951–960.
Salsi V, Zappavigna V . Hoxd13 and Hoxa13 directly control the expression of the EphA7 Ephrin tyrosine kinase receptor in developing limbs. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 1992–1999.
Yamashita A, Hayashi N, Sugimura Y, Cunha GR, Kawamura J . Influence of diethylstilbestrol, Leuprolelin (a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analog), Finasteride (a 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor), and castration on the lobar subdivisions of the rat prostate. Prostate 1996; 29: 1–14.
Golovine K, Makhov P, Uzzo RG, Shaw T, Kunkle D, Kolenko VM . Overexpression of the zinc uptake transporter hZIP1 inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB and reduces the malignant potential of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 5376–5384.
Uzzo RG, Leavis P, Hatch W, Gabai VL, Dulin N, Zvartau N et al. Zinc inhibits nuclear factor-kappa B activation and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to cytotoxic agents. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 3579–3583.
Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB . NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 1998; 16: 225–260.
Ma XJ, Wang Z, Ryan PD, Isakoff SJ, Barmettler A, Fuller A et al. A two-gene expression ratio predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. Cancer Cell 2004; 5: 607–616.
Tricoli JV, Gumerlock PH, Yao JL, Chi SG, D’Souza SA, Nestok BR et al. Alterations of the retinoblastoma gene in human prostate adenocarcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1996; 15: 108–114.
Golovine K, Uzzo RG, Makhov P, Crispen PL, Kunkle D, Kolenko VM . Depletion of intracellular zinc increases expression of tumorigenic cytokines VEGF, IL-6 and IL-8 in prostate cancer cells via NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Prostate 2008; 68: 1443–1449.
Uzzo RG, Crispen PL, Golovine K, Makhov P, Horwitz EM, Kolenko VM . Diverse effects of zinc on NF-kappaB and AP-1 transcription factors: implications for prostate cancer progression. Carcinogenesis 2006; 27: 1980–1990.
Rosoff B . Studies of zinc in normal and neoplastic prostatic tissues. Prog Clin Biol Res 1981; 75A: 447–457.
Costello LC, Liu Y, Zou J, Franklin RB . Evidence for a zinc uptake transporter in human prostate cancer cells which is regulated by prolactin and testosterone. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 17499–17504.
McMahon RJ, Cousins RJ . Mammalian zinc transporters. J Nutr 1998; 128: 667–670.
Franklin RB, Feng P, Milon B, Desouki MM, Singh KK, Kajdacsy-Balla A et al. hZIP1 zinc uptake transporter down regulation and zinc depletion in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer 2005; 4: 32.
Zou J, Milon BC, Desouki MM, Costello LC, Franklin RB . hZIP1 zinc transporter down-regulation in prostate cancer involves the overexpression of ras responsive element binding protein-1 (RREB-1). Prostate 2011; 71: 1518–1524.
Palmiter RD, Huang L . Efflux and compartmentalization of zinc by members of the SLC30 family of solute carriers. Pflugers Arch 2004; 447: 744–751.
Michalczyk AA, Allen J, Blomeley RC, Ackland ML . Constitutive expression of hZnT4 zinc transporter in human breast epithelial cells. Biochem J 2002; 364: 105–113.
Ho LH, Ruffin RE, Murgia C, Li L, Krilis SA, Zalewski PD . Labile zinc and zinc transporter ZnT4 in mast cell granules: role in regulation of caspase activation and NF-kappaB translocation. J Immunol 2004; 172: 7750–7760.
Henshall SM, Afar DE, Rasiah KK, Horvath LG, Gish K, Caras I et al. Expression of the zinc transporter ZnT4 is decreased in the progression from early prostate disease to invasive prostate cancer. Oncogene 2003; 22: 6005–6012.
Murgia C, Vespignani I, Cerase J, Nobili F, Perozzi G . Cloning, expression, and vesicular localization of zinc transporter Dri 27/ZnT4 in intestinal tissue and cells. Am J Physiol 1999; 277: G1231–G1239.
Beck FW, Prasad AS, Butler CE, Sakr WA, Kucuk O, Sarkar FH . Differential expression of hZnT-4 in human prostate tissues. Prostate 2004; 58: 374–381.
Gilmore TD . The Rel/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway: introduction. Oncogene 1999; 18: 6842–6844.
Shukla S, MacLennan GT, Fu P, Patel J, Marengo SR, Resnick MI et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB/p65 (Rel A) is constitutively activated in human prostate adenocarcinoma and correlates with disease progression. Neoplasia 2004; 6: 390–400.
Suh J, Payvandi F, Edelstein LC, Amenta PS, Zong WX, Gelinas C et al. Mechanisms of constitutive NF-kappaB activation in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2002; 52: 183–200.
Huang S, Pettaway CA, Uehara H, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ . Blockade of NF-kappaB activity in human prostate cancer cells is associated with suppression of angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Oncogene 2001; 20: 4188–4197.
Muenchen HJ, Lin DL, Walsh MA, Keller ET, Pienta KJ . Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells through inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB by an IkappaBalpha ‘super-repressor’. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 1969–1977.
Jeon KI, Jeong JY, Jue DM . Thiol-reactive metal compounds inhibit NF-kappa B activation by blocking I kappa B kinase. J Immunol 2000; 164: 5981–5989.
Jung C, Ou YC, Yeung F, Frierson HF Jr., Kao C . Osteocalcin is incompletely spliced in non-osseous tissues. Gene 2001; 271: 143–150.
Jung C, Kim RS, Zhang H, Lee SJ, Sheng H, Loehrer PJ et al. HOXB13 is downregulated in colorectal cancer to confer TCF4-mediated transactivation. Br J Cancer 2005; 92: 2233–2239.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation through the Medical Research Center for Gene Regulation (2012-0009445), by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea Government (2010-0003838), and by a grant from the Chonnam National University Research Institute of Medical Sciences ((2010-CURIMS-DR011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YR., Kim, IJ., Kang, T. et al. HOXB13 downregulates intracellular zinc and increases NF-κB signaling to promote prostate cancer metastasis. Oncogene 33, 4558–4567 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.404
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.404
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular implications of HOX genes targeting multiple signaling pathways in cancer
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2022)
-
LncRNA SNHG14 regulates the DDP-resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cell through miR-133a/HOXB13 pathway
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2020)
-
Multiple roles of HOX proteins in Metastasis: Let me count the ways
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2020)
-
The Homeobox gene, HOXB13, Regulates a Mitotic Protein-Kinase Interaction Network in Metastatic Prostate Cancers
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Oncoprotein HBXIP enhances HOXB13 acetylation and co-activates HOXB13 to confer tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2018)