Abstract
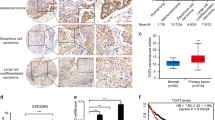
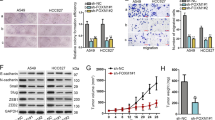
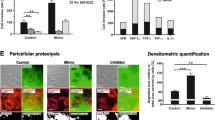
Fibulins (FBLNs), a family of extracellular matrix proteins, have recently been shown to act as tumor suppressors or activators in different cancers, and the underlying molecular mechanisms of their action in cancer remain unclear. We have previously shown that the expression of FBLN3 is suppressed by promoter hypermethylation and is associated with invasiveness in aggressive non-small cell lung cancer. In this study, we evaluated the roles and signaling mechanism of FBLN3 in lung cancer stem cells (CSCs). Forced expression of FBLN3 suppressed invasion and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells and decreased the expression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) activators, including N-cadherin and Snail. Stemness activities of lung adenocarcinoma cells were also suppressed by FBLN3 as indicated by a decrease in spheroid formation and the levels of stemness markers such as Sox2 and β-catenin. These effects of FBLN3 were mediated by the glycogen synthase kinase-3β, GSK3β/β-catenin pathway, and the upstream regulators of GSK3β, including phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R), were inactivated by FBLN3. Moreover, IGF1R was shown to be a direct target of FBLN3, which competitively inhibited insulin-like growth factor (IGF) action. To confirm the effect of FBLN3 on lung CSCs, aldehyde dehydrogenase-positive (ALDH+) A549 lung CSCs were sorted and treated with recombinant FBLN3 protein. FBLN3 clearly suppressed EMT, stemness activity and the over-activated IGF1R/PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway of the ALDH+ CSC subpopulation. In addition, injection of recombinant FBLN3 protein around subcutaneous xenografts established with ALDH+ CSCs in athymic nude mice significantly suppressed tumor growth and progression. Overall, our results show that FBLN3 suppresses both EMT and self-renewal of the lung CSCs by modulating the IGF1R/PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway and that FBLN3 would be useful as an alternative CSC therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esposito L, Conti D, Ailavajhala R, Khalil N, Giordano A . Lung cancer: are we up to the challenge? Curr Genomics 2010; 11: 513–518.
Heist RS, Christiani D . EGFR-targeted therapies in lung cancer: predictors of response and toxicity. Pharmacogenomics 2009; 10: 59–68.
Alison MR, Lin WR, Lim SM, Nicholson LJ . Cancer stem cells: in the line of fire. Cancer Treat Rev 2012; 38: 589–598.
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008; 133: 704–715.
Rivera C, Rivera S, Loriot Y, Vozenin MC, Deutsch E . Lung cancer stem cell: new insights on experimental models and preclinical data. J Oncol 2011; 2011: 549181.
Bonnet D, Dick JE . Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med 1997; 3: 730–737.
Korkaya H, Wicha MS . Selective targeting of cancer stem cells: a new concept in cancer therapeutics. BioDrugs 2007; 21: 299–310.
Perona R, Lopez-Ayllon BD, de Castro Carpeno J, Belda-Iniesta C . A role for cancer stem cells in drug resistance and metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 2011; 13: 289–293.
Li J, Zhou BP . Activation of beta-catenin and Akt pathways by Twist are critical for the maintenance of EMT associated cancer stem cell-like characters. BMC Cancer 2011; 11: 49.
de Vega S, Iwamoto T, Yamada Y . Fibulins: multiple roles in matrix structures and tissue functions. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009; 66: 1890–1902.
Schiemann WP, Blobe GC, Kalume DE, Pandey A, Lodish HF . Context-specific effects of fibulin-5 (DANCE/EVEC) on cell proliferation, motility, and invasion. Fibulin-5 is induced by transforming growth factor-beta and affects protein kinase cascades. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 27367–27377.
Yue W, Sun Q, Landreneau R, Wu C, Siegfried JM, Yu J et al. Fibulin-5 suppresses lung cancer invasion by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 6339–6346.
Hu B, Thirtamara-Rajamani KK, Sim H, Viapiano MS . Fibulin-3 is uniquely upregulated in malignant gliomas and promotes tumor cell motility and invasion. Mol Cancer Res 2009; 7: 1756–1770.
Hu Y, Pioli PD, Siegel E, Zhang Q, Nelson J, Chaturbedi A et al. EFEMP1 suppresses malignant glioma growth and exerts its action within the tumor extracellular compartment. Mol Cancer 2011; 10: 123.
Kim EJ, Lee SY, Woo MK, Choi SI, Kim TR, Kim MJ et al. Fibulin-3 promoter methylation alters the invasive behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines via MMP-7 and MMP-2 regulation. Int J Oncol 2012; 40: 402–408.
Sung JM, Cho HJ, Yi H, Lee CH, Kim HS, Kim DK et al. Characterization of a stem cell population in lung cancer A549 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 371: 163–167.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA . Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009; 139: 871–890.
Araki K, Shimura T, Suzuki H, Tsutsumi S, Wada W, Yajima T et al. E/N-cadherin switch mediates cancer progression via TGF-beta-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Cancer 2011; 105: 1885–1893.
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, Thompson EW . The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol 2006; 172: 973–981.
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A et al. The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 1487–1495.
Vuoriluoto K, Haugen H, Kiviluoto S, Mpindi JP, Nevo J, Gjerdrum C et al. Vimentin regulates EMT induction by Slug and oncogenic H-Ras and migration by governing Axl expression in breast cancer. Oncogene 2011; 30: 1436–1448.
Biddle A, Mackenzie IC . Cancer stem cells and EMT in carcinoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2012; 31: 285–293.
Lee J, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Li A, Su Q, Donin NM et al. Tumor stem cells derived from glioblastomas cultured in bFGF and EGF more closely mirror the phenotype and genotype of primary tumors than do serum-cultured cell lines. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 391–403.
Pastrana E, Silva-Vargas V, Doetsch F . Eyes wide open: a critical review of sphere-formation as an assay for stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2011; 8: 486–498.
O'Brien CA, Kreso A, Jamieson CH . Cancer stem cells and self-renewal. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 3113–3120.
Fuxe J, Vincent T, Garcia de Herreros A . Transcriptional crosstalk between TGF-beta and stem cell pathways in tumor cell invasion: role of EMT promoting Smad complexes. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 2363–2374.
Jiang YG, Luo Y, He DL, Li X, Zhang LL, Peng T et al. Role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human prostate cancer induced by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Int J Urol 2007; 14: 1034–1039.
Hwang CF, Chien CY, Huang SC, Yin YF, Huang CC, Fang FM et al. Fibulin-3 is associated with tumour progression and a poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinomas and inhibits cell migration and invasion via suppressed AKT activity. J Pathol 2010; 222: 367–379.
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Koutsilieris M . The Akt pathway: molecular targets for anti-cancer drug development. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2004; 4: 235–256.
Desbois-Mouthon C, Cadoret A, Blivet-Van Eggelpoel MJ, Bertrand F, Cherqui G, Perret C et al. Insulin and IGF-1 stimulate the beta-catenin pathway through two signalling cascades involving GSK-3beta inhibition and Ras activation. Oncogene 2001; 20: 252–259.
Doble BW, Woodgett JR . Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in cell fate and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Cells Tissues Organs 2007; 185: 73–84.
Cappuzzo F, Tallini G, Finocchiaro G, Wilson RS, Ligorio C, Giordano L et al. Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) expression and survival in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Ann Oncol 2010; 21: 562–567.
Engelman JA, Janne PA, Mermel C, Pearlberg J, Mukohara T, Fleet C et al. ErbB-3 mediates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in gefitinib-sensitive non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 3788–3793.
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y, Dennis PA . Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 3986–3997.
Morrison R, Schleicher SM, Sun Y, Niermann KJ, Kim S, Spratt DE et al. Targeting the mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy with the cancer stem cell hypothesis. J Oncol 2011; 2011: 941876.
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M et al. ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell 2007; 1: 555–567.
Ucar D, Cogle CR, Zucali JR, Ostmark B, Scott EW, Zori R et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity as a functional marker for lung cancer. Chem Biol Interact 2009; 178: 48–55.
Jiang T, Collins BJ, Jin N, Watkins DN, Brock MV, Matsui W et al. Achaete-scute complex homologue 1 regulates tumor-initiating capacity in human small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 845–854.
Ischenko I, Seeliger H, Schaffer M, Jauch KW, Bruns CJ . Cancer stem cells: how can we target them? Curr Med Chem 2008; 15: 3171–3184.
Gorelik E, Lokshin A, Levina V . Lung cancer stem cells as a target for therapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2010; 10: 164–171.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Misaghian N, Chappell WH, Basecke J et al. Targeting the cancer initiating cell: the ultimate target for cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Des 2012; 18: 1784–1795.
Prud'homme GJ . Cancer stem cells and novel targets for antitumor strategies. Curr Pharm Des 2012; 18: 2838–2849.
Hu B, Nandhu MS, Sim H, Agudelo-Garcia PA, Saldivar JC, Dolan CE et al. Fibulin-3 promotes glioma growth and resistance through a novel paracrine regulation of Notch signaling. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 3873–3885.
Camaj P, Seeliger H, Ischenko I, Krebs S, Blum H, De Toni EN et al. EFEMP1 binds the EGF receptor and activates MAPK and Akt pathways in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Biol Chem 2009; 390: 1293–1302.
Wang R, Zhang YW, Chen LB . Aberrant promoter methylation of FBLN3 gene and clinicopathological significance in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2010; 69: 239–244.
Pollak M . Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 915–928.
Yang J, Ylipaa A, Sun Y, Zheng H, Chen K, Nykter M et al. Genomic and molecular characterization of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor identifies the IGF1R pathway as a primary target for treatment. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 7563–7573.
Ivanova NB, Dimos JT, Schaniel C, Hackney JA, Moore KA, Lemischka IR . A stem cell molecular signature. Science 2002; 298: 601–604.
Bendall SC, Stewart MH, Menendez P, George D, Vijayaragavan K, Werbowetski-Ogilvie T et al. IGF and FGF cooperatively establish the regulatory stem cell niche of pluripotent human cells in vitro. Nature 2007; 448: 1015–1021.
Jones RA, Campbell CI, Wood GA, Petrik JJ, Moorehead RA . Reversibility and recurrence of IGF-IR-induced mammary tumors. Oncogene 2009; 28: 2152–2162.
Shan J, Shen J, Liu L, Xia F, Xu C, Duan G et al. Nanog regulates self-renewal of cancer stem cells through the insulin-like growth factor pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012; 56: 1004–1014.
Bill A, Schmitz A, Konig K, Heukamp LC, Hannam JS, Famulok M . Anti-proliferative effect of cytohesin inhibition in gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells. PloS One 2012; 7: e41179.
Desbois-Mouthon C, Baron A, Blivet-Van Eggelpoel MJ, Fartoux L, Venot C, Bladt F et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibition induces a resistance mechanism via the epidermal growth factor receptor/HER3/AKT signaling pathway: rational basis for cotargeting insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 5445–5456.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial supports from the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (Nuclear Research and Development Program) of the Republic of Korea and basic program of Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, I., Kim, S., Choi, S. et al. Fibulin-3-mediated inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and self-renewal of ALDH+ lung cancer stem cells through IGF1R signaling. Oncogene 33, 3908–3917 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.373
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.373
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A Pilot Urinary Proteome Study Reveals Widespread Influences of Circadian Rhythm Disruption by Sleep Deprivation
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2023)
-
Role of IGF-1R in epithelial–mesenchymal transdifferentiation of human peritoneal mesothelial cells
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (2022)
-
Fibulin-3 knockout mice demonstrate corneal dysfunction but maintain normal retinal integrity
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
Tescalcin/c-Src/IGF1Rβ-mediated STAT3 activation enhances cancer stemness and radioresistant properties through ALDH1
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Fibulin-3 knockdown inhibits cervical cancer cell growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo
Scientific Reports (2018)