Abstract
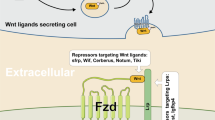
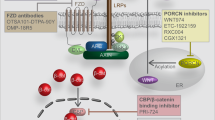
Developmental and cancer models show Wnt/β-catenin-dependent signaling mediates diverse phenotypic outcomes in the pancreas that are dictated by context, duration and strength of activation. While generally assumed to be pro-tumorigenic, it is unclear to what extent dysregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling impacts tumor progression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC). In the present study, Wnt/β-catenin activity was characterized across a spectrum of PDAC cell lines and primary tumors. Reporter and gene expression-based assays revealed wide heterogeneity in Wnt/β-catenin transcriptional activity across PDAC cell lines and patient tumors, as well as variable responsiveness to exogenous Wnt ligand stimulation. An experimentally generated, pancreas-specific gene expression signature of Wnt/β-catenin transcriptional activation was used to stratify pathway activation across a cohort of resected, early-stage PDAC tumors (N=41). In this cohort, higher Wnt/β-catenin activation was found to significantly correlate with lymphvascular invasion and worse disease-specific survival (median survival time 20.3 versus 43.9 months, log-rank P=0.03). Supporting the importance of Wnt ligand in mediating autocrine Wnt signaling, Wnt/β-catenin activity was significantly inhibited in PDAC cell lines by WLS gene silencing and the small-molecule inhibitor IWP-2, both of which functionally block Wnt ligand processing and secretion. Transcriptional profiling revealed elevated expression of WNT7B occurred in PDAC cell lines with high levels of cell autonomous Wnt/β-catenin activity. Gene-knockdown studies in AsPC-1 and HPAF-2 cell lines confirmed WNT7B-mediated cell autonomous Wnt/β-catenin activation, as well as an anchorage-independent growth phenotype. Our findings indicate WNT7B can serve as a primary determinant of differential Wnt/β-catenin activation in PDAC. Disrupting the interaction between Wnt ligands and their receptors may be a particularly suitable approach for therapeutic modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in PDAC and other cancer contexts where Wnt activation is mediated by ligand expression rather than mutations in canonical pathway members.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH, Goggins M . Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2011; 378: 607–620.
Hong SM, Park JY, Hruban RH, Goggins M . Molecular signatures of pancreatic cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011; 135: 716–727.
Maitra A, Hruban RH . Pancreatic cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 2008; 3: 157–188.
American_Cancer_Society, Cancer Facts & Figures 2012. Cancer. American Cancer Society, New York, 2012, pp 1–66.
Donahue T, Tran L, Hill R, Li Y, Kovochich A, Calvopina J et al. Intergrative survival-based molecular profiling of human pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 1352–1363.
Jones S, Zhang X, Parsons DW, Lin JC, Leary RJ, Angenendt P et al. Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global genomic analyses. Science 2008; 321: 1801–1806.
Vincent A, Omura N, Hong SM, Jaffe A, Eshleman J, Goggins M . Genome-wide analysis of promoter methylation associated with gene expression profile in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 4341–4354.
Clevers H, Nusse R . Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012; 149: 1192–1205.
Angers S, Moon RT . Proximal events in Wnt signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10: 468–477.
Chien AJ, Conrad WH, Moon RTA . Wnt survival guide: from flies to human disease. J Invest Dermatol 2009; 129: 1614–1627.
Lucero OM, Dawson DW, Moon RT, Chien AJ . A re-evaluation of the ‘oncogenic’ nature of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in melanoma and other cancers. Curr Oncol Rep 2010; 12: 314–318.
Caca K, Kolligs FT, Ji X, Hayes M, Qian J, Yahanda A et al. Beta- and gamma-catenin mutations, but not E-cadherin inactivation, underlie T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor transcriptional deregulation in gastric and pancreatic cancer. Cell Growth Differ 1999; 10: 369–376.
Gerdes B, Ramaswamy A, Simon B, Pietsch T, Bastian D, Kersting M et al. Analysis of beta-catenin gene mutations in pancreatic tumors. Digestion 1999; 60: 544–548.
Biankin AV, Waddell N, Kassahn KS, Gingras MC, Muthuswamy LB, Johns AL et al. Pancreatic cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon guidance pathway genes. Nature 2012; 491: 399–405.
Pasca di Magliano M, Biankin AV, Heiser PW, Cano DA, Gutierrez PJ, Deramaudt T et al. Common activation of canonical Wnt signaling in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. PLoS One 2007; 2: e1155.
White BD, Chien AJ, Dawson DW . Dysregulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in gastrointestinal cancers. Gastroenterology 2012; 142: 219–232.
Zeng G, Germinaro M, Micsenyi A, Monga NK, Bell A, Sood A et al. Aberrant Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia 2006; 8: 279–289.
Nawroth R, van Zante A, Cervantes S, McManus M, Hebrok M, Rosen SD . Extracellular sulfatases, elements of the Wnt signaling pathway, positively regulate growth and tumorigenicity of human pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One 2007; 2: e392.
Wang L, Heidt DG, Lee CJ, Yang H, Logsdon CD, Zhang L et al. Oncogenic function of ATDC in pancreatic cancer through Wnt pathway activation and beta-catenin stabilization. Cancer Cell 2009; 15: 207–219.
Zhong Y, Wang Z, Fu B, Pan F, Yachida S, Dhara M et al. GATA6 activates Wnt signaling in pancreatic cancer by negatively regulating the Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1. PLoS One 2011; 6: e22129.
Morris JPt, Wang SC, Hebrok M . KRAS, Hedgehog, Wnt and the twisted developmental biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 683–695.
Biechele TL, Moon RT . Assaying beta-catenin/TCF transcription with beta-catenin/TCF transcription-based reporter constructs. Methods Mol Biol 2008; 468: 99–110.
Jho EH, Zhang T, Domon C, Joo CK, Freund JN, Costantini F . Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 1172–1183.
Chang JT, Gatza ML, Lucas JE, Barry WT, Vaughn P, Nevins JR . SIGNATURE: a workbench for gene expression signature analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 2011; 12: 443.
Chen B, Dodge ME, Tang W, Lu J, Ma Z, Fan CW et al. Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol 2009; 5: 100–107.
Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, Cheung A, Stegmeier F, Michaud GA et al. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature 2009; 461: 614–620.
Port F, Basler K . Wnt trafficking: new insights into Wnt maturation, secretion and spreading. Traffic 2010; 11: 1265–1271.
Yu M, Ting DT, Stott SL, Wittner BS, Ozsolak F, Paul S et al. RNA sequencing of pancreatic circulating tumour cells implicates WNT signalling in metastasis. Nature 2012; 487: 510–513.
Lowe AW, Olsen M, Hao Y, Lee SP, Taek Lee K, Chen X et al. Gene expression patterns in pancreatic tumors, cells and tissues. PLoS One 2007; 2: e323.
Heiser PW, Cano DA, Landsman L, Kim GE, Kench JG, Klimstra DS et al. Stabilization of beta-catenin induces pancreas tumor formation. Gastroenterology 2008; 135: 1288–1300.
Morris JPt, Cano DA, Sekine S, Wang SC, Hebrok M . Beta-catenin blocks Kras-dependent reprogramming of acini into pancreatic cancer precursor lesions in mice. J Clin Invest 2010; 120: 508–520.
Froeling FE, Feig C, Chelala C, Dobson R, Mein CE, Tuveson DA et al. Retinoic acid-induced pancreatic stellate cell quiescence reduces paracrine Wnt-beta-catenin signaling to slow tumor progression. Gastroenterology 2011; 141: 1486–1497.
Froeling FE, Mirza TA, Feakins RM, Seedhar A, Elia G, Hart IR et al. Organotypic culture model of pancreatic cancer demonstrates that stromal cells modulate E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and Ezrin expression in tumor cells. Am J Pathol 2009; 175: 636–648.
Chien AJ, Moon RT . WNTS and WNT receptors as therapeutic tools and targets in human disease processes. Front Biosci 2007; 12: 448–457.
Gurney A, Axelrod F, Bond CJ, Cain J, Chartier C, Donigan L et al. Wnt pathway inhibition via the targeting of Frizzled receptors results in decreased growth and tumorigenicity of human tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 11717–11722.
Kovochich AN, Arensman MD, Lay AR, Rao NP, Donahue T, Li X et al. HOXB7 promotes invasion and predicts survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2013; 119: 529–539.
Liu N, Furukawa T, Kobari M, Tsao MS . Comparative phenotypic studies of duct epithelial cell lines derived from normal human pancreas and pancreatic carcinoma. Am J Pathol 1998; 153: 263–269.
Li C, Wong WH . Model-based analysis of oligonucleotide arrays: expression index computation and outlier detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 31–36.
Acknowledgements
DWD was supported by an American Cancer Society Research Scholar Grant, an American Association for Cancer Research/Pancreatic Cancer Action Network Career Development Award in memory of Seena Magowitz and a Research Services Research Fund Grant from the UCLA Department of Pathology. AJC was supported by a Career Development Award (1K08128565) from the NCI/NIH and Bridge Funding from the University of Washington Office of the Provost. MDA was supported by the UCLA Tumor Biology Program (USHHS Ruth L. Kirschstein Institutional National Research Service Award # T32 CA009056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arensman, M., Kovochich, A., Kulikauskas, R. et al. WNT7B mediates autocrine Wnt/β-catenin signaling and anchorage-independent growth in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 33, 899–908 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.23
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.23
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cancer associated fibroblasts serve as an ovarian cancer stem cell niche through noncanonical Wnt5a signaling
npj Precision Oncology (2024)
-
PDHB-AS suppresses cervical cancer progression and cisplatin resistance via inhibition on Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
CSTF2 mediated mRNA N6-methyladenosine modification drives pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma m6A subtypes
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Activation of WNT7b autocrine eases metastasis of colorectal cancer via epithelial to mesenchymal transition and predicts poor prognosis
BMC Cancer (2021)
-
EphA2 super-enhancer promotes tumor progression by recruiting FOSL2 and TCF7L2 to activate the target gene EphA2
Cell Death & Disease (2021)