Abstract
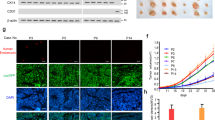
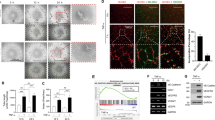
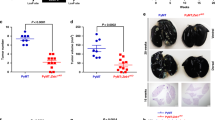
Recent studies suggested that cancer stem cells (CSCs) are capable of differentiating into endothelial cells and tumor endothelium may be derived from CSCs. But the mechanism remains unclear. We showed that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induced the expression of endothelial markers in breast cancer stem like cells (BCSLCs). In addition, the VEGF-treated BCSLCs formed capillary structure in matrigel and released vWF upon histamine treatment. The miR-27a expression was significantly increased in VEGF-treated BCSLCs. Antagonizing miR-27a by miR-27a anti-sense oligos (ASOs) in VEGF-treated BCSLCs led to decreased endothelial markers and function, while increasing miR-27a in BCSLCs resulted in enhanced endothelial properties. VEGF enhanced the transcription of miR-27a by increasing RUNX1 binding to miR-27a promoter. Increased miR-27a paralleled the reduced expression of ZBTB10, a known miR-27a target. Both expression of miR-27a and knockdown of ZBTB10 in BCSLCs promoted in vivo angiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Further, we demonstrated that VEGF-treated BCSLCs secreted more endogenous VEGF compared with undifferentiated BCSLCs. Thus, miR-27a promotes angiogenesis by mediating endothelial differentiation of BCSLCs and it may be a new target for anti-angiogenesis cancer therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
de Castro Junior G, Puglisi F, de Azambuja E, El Saghir NS, Awada A . Angiogenesis and cancer: a cross-talk between basic science and clinical trials (the "do ut des" paradigm). Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006; 59: 40–50.
Jain RK . Barriers to drug delivery in solid tumors. Sci Am 1994; 271: 58–65.
Jain RK . Determinants of tumor blood flow: a review. Cancer Res 1988; 48: 2641–2658.
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, Seftor EA, Gardner LM, Pe'er J et al. Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro: vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol 1999; 155: 739–752.
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Hess AR, Seftor RE . Vasculogenic mimicry and tumour-cell plasticity: lessons from melanoma. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 411–421.
Dome B, Hendrix MJ, Paku S, Tovari J, Timar J . Alternative vascularization mechanisms in cancer: pathology and therapeutic implications. Am J Pathol 2007; 170: 1–15.
Wang R, Chadalavada K, Wilshire J, Kowalik U, Hovinga KE, Geber A et al. Glioblastoma stem-like cells give rise to tumour endothelium. Nature 2010; 468: 829–833.
Ricci-Vitiani L, Pallini R, Biffoni M, Todaro M, Invernici G, Cenci T et al. Tumour vascularization via endothelial differentiation of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Nature 2010; 468: 824–828.
Shcherbata HR, Hatfield S, Ward EJ, Reynolds S, Fischer KA, Ruohola-Baker H . The MicroRNA pathway plays a regulatory role in stem cell division. Cell Cycle 2006; 5: 172–175.
Leonardo TR, Schultheisz HL, Loring JF, Laurent LC . The functions of microRNAs in pluripotency and reprogramming. Nat Cell Biol 2012; 14: 1114–1121.
Fang K, Qian F, Chen YQ . MicroRNAs as regulators in normal hematopoietic and leukemia stem cells: current concepts and clinical implications. Curr Mol Med 2012; 12: 536–546.
Liu C, Tang DG . MicroRNA regulation of cancer stem cells. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 5950–5954.
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong C et al. let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell 2007; 131: 1109–1123.
Mertens-Talcott SU, Chintharlapalli S, Li X, Safe S . The oncogenic microRNA-27a targets genes that regulate specificity protein transcription factors and the G2-M checkpoint in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 11001–11011.
Weigand M, Hantel P, Kreienberg R, Waltenberger J . Autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor signalling in breast cancer. Evidence from cell lines and primary breast cancer cultures in vitro. Angiogenesis 2005; 8: 197–204.
Tang W, Zhu J, Su S, Wu W, Liu Q, Su F et al. MiR-27 as a prognostic marker for breast cancer progression and patient survival. PLoS One 2012; 7: e51702.
Bussolati B, Grange C, Sapino A, Camussi G . Endothelial cell differentiation of human breast tumour stem/progenitor cells. J Cell Mol Med 2009; 13: 309–319.
Zhou Q, Gallagher R, Ufret-Vincenty R, Li X, Olson EN, Wang S . Regulation of angiogenesis and choroidal neovascularization by members of microRNA-23∼27∼24 clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 8287–8292.
Lee S, Chen TT, Barber CL, Jordan MC, Murdock J, Desai S et al. Autocrine VEGF signaling is required for vascular homeostasis. Cell 2007; 130: 691–703.
Stratman AN, Davis MJ, Davis GE . VEGF and FGF prime vascular tube morphogenesis and sprouting directed by hematopoietic stem cell cytokines. Blood 2011; 117: 3709–3719.
Ben-Ami O, Pencovich N, Lotem J, Levanon D, Groner Y . A regulatory interplay between miR-27a and Runx1 during megakaryopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 238–243.
Wang J, Zhao HP, Lin G, Xie CQ, Nie DS, Wang QR et al. In vitro hematopoietic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells induced by co-culture with human bone marrow stromal cells and low dose cytokines. Cell Biol Int 2005; 29: 654–661.
Fukumura D, Jain RK . Tumor microenvironment abnormalities: causes, consequences, and strategies to normalize. J Cell Biochem 2007; 101: 937–949.
Fukumura D, Jain RK . Tumor microvasculature and microenvironment: targets for anti-angiogenesis and normalization. Microvasc Res 2007; 74: 72–84.
Fukumura D, Duda DG, Munn LL, Jain RK . Tumor microvasculature and microenvironment: novel insights through intravital imaging in pre-clinical models. Microcirculation 2010; 17: 206–225.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the 973 Projects (2010CB912800, 2011CB504203) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, and grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (81072178, 81272894, 81230060, 81261140373, 81071788), Ministry of Education of China (20120171110075), a grant for Development of Important New Drugs from the Ministry of Health of China (2011ZX09102-010-02), grants from Guangdong Natural Science Fundation for Distinguished Young Scholar (S20120011199) and Foundation for the Author of National Excellent Doctoral Dissertation of PR China (FANEDD, 81000-3149001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, W., Yu, F., Yao, H. et al. miR-27a regulates endothelial differentiation of breast cancer stem like cells. Oncogene 33, 2629–2638 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.214
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.214
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Quantitative Changes in Pro-Oncogenic and Tumor-Suppressing MicroRNA in the Regional Lymph Node during Photodynamic Therapy of Experimental Breast Cancer
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (2024)
-
Identification of cancer stemness related miRNA(s) using integrated bioinformatics analysis and in vitro validation
3 Biotech (2021)
-
Snail promotes the generation of vascular endothelium by breast cancer cells
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
ZNFX1 anti-sense RNA 1 promotes the tumorigenesis of prostate cancer by regulating c-Myc expression via a regulatory network of competing endogenous RNAs
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2020)
-
High expression of microRNA20b is associated with malignant clinicopathological features and poor prognosis in breast phyllodes tumor
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2020)