Abstract
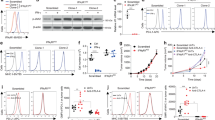
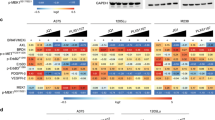
Melanoma is an aggressive skin cancer that carries an extremely poor prognosis when local invasion, nodal spread or systemic metastasis has occurred. Recent advances in melanoma biology have revealed that RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signaling has a pivotal role in governing disease progression and treatment resistance. Proof-of-concept clinical studies have shown that direct BRAF inhibition yields impressive responses in advanced disease but these are short-lived as treatment resistance rapidly emerges. Therefore, there is a pressing need to develop new targeted strategies for BRAF mutant melanoma. As such, oncolytic viruses represent a promising cancer-specific approach with significant activity in melanoma. This study investigated interactions between genetically-modified vaccinia virus (GLV-1h68) and radiotherapy in melanoma cell lines with BRAF mutant, Ras mutant or wild-type genotype. Preclinical studies revealed that GLV-1h68 combined with radiotherapy significantly increased cytotoxicity and apoptosis relative to either single agent in V600DBRAF/V600EBRAF mutant melanoma in vitro and in vivo. The mechanism of enhanced cytotoxicity with GLV-1h68/radiation (RT) was independent of viral replication and due to attenuation of JNK, p38 and ERK MAPK phosphorylation specifically in BRAF mutant cells. Further studies showed that JNK pathway inhibition sensitized BRAF mutant cells to GLV-1h68-mediated cell death, mimicking the effect of RT. GLV-1h68 infection activated MAPK signaling in V600DBRAF/V600EBRAF mutant cell lines and this was associated with TNF-α secretion which, in turn, provided a prosurvival signal. Combination GLV-1h68/RT (or GLV-1h68/JNK inhibition) caused abrogation of TNF-α secretion. These data provide a strong rationale for combining GLV-1h68 with irradiation in V600D/EBRAF mutant tumors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harrington KJ, Karapanagiotou EM, Roulstone V, Twigger KR, White CL, Vidal L et al. Two-stage phase I dose-escalation study of intratumoral reovirus type 3 dearing and palliative radiotherapy in patients with advanced cancers. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 3067–3077.
Comins C, Spicer J, Protheroe A, Roulstone V, Twigger K, White CM et al. REO-10: a phase I study of intravenous reovirus and docetaxel in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 5564–5572.
Andrade AA, Silva PN, Pereira AC, De Sousa LP, Ferreira PC, Gazzinelli RT et al. The vaccinia virus-stimulated mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is required for virus multiplication. Biochem J. 2004; 381 (Pt 2): 437–446.
de Magalhaes JC, Andrade AA, Silva PN, Sousa LP, Ropert C, Ferreira PC et al. A mitogenic signal triggered at an early stage of vaccinia virus infection: implication of MEK/ERK and protein kinase A in virus multiplication. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 38353–38360.
Dent P, Yacoub A, Fisher PB, Hagan MP, Grant S . MAPK pathways in radiation responses. Oncogene 2003; 22: 5885–5896.
Ascierto ML, Worschech A, Yu Z, Adams S, Reinboth J, Chen NG et al. Permissivity of the NCI-60 cancer cell lines to oncolytic Vaccinia Virus GLV-1h68. BMC Cancer 2011; 11: 451.
Yu YA, Galanis C, Woo Y, Chen N, Zhang Q, Fong Y et al. Regression of human pancreatic tumor xenografts in mice after a single systemic injection of recombinant vaccinia virus GLV-1h68. Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8: 141–151.
Gentschev I, Stritzker J, Hofmann E, Weibel S, Yu YA, Chen N et al. Use of an oncolytic vaccinia virus for the treatment of canine breast cancer in nude mice: preclinical development of a therapeutic agent. Cancer Gene Ther 2009; 16: 320–328.
Yu Z, Li S, Brader P, Chen N, Yu YA, Zhang Q et al. Oncolytic vaccinia therapy of squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2009; 8: 45.
Lin SF, Price DL, Chen CH, Brader P, Li S, Gonzalez L et al. Oncolytic vaccinia virotherapy of anaplastic thyroid cancer in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93: 4403–4407.
Kelly KJ, Woo Y, Brader P, Yu Z, Riedl C, Lin SF et al. Novel oncolytic agent GLV-1h68 is effective against malignant pleural mesothelioma. Hum Gene Ther 2008; 19: 774–782.
Zhang Q, Yu YA, Wang E, Chen N, Danner RL, Munson PJ et al. Eradication of solid human breast tumors in nude mice with an intravenously injected light-emitting oncolytic vaccinia virus. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 10038–10046.
Khan N, Khan MK, Almasan A, Singh AD, Macklis R . The evolving role of radiation therapy in the management of malignant melanoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2011; 80: 645–654.
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 2507–2516.
Mansfield D, Pencavel T, Kyula JN, Zaidi S, Roulstone V, Thway K et al. Oncolytic Vaccinia virus and radiotherapy in head and neck cancer. Oral oncology 2012; 49: 108–118.
Buck E, Eyzaguirre A, Brown E, Petti F, McCormack S, Haley JD et al. Rapamycin synergizes with the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib in non-small-cell lung, pancreatic, colon, and breast tumors. Mol Cancer Ther 2006; 5: 2676–2684.
Greco WR, Bravo G, Parsons JC . The search for synergy: a critical review from a response surface perspective. Pharmacol Reviews 1995; 47: 331–385.
Bliss CI . The calculation of microbial assays. Bacteriol Reviews 1956; 20: 243–258.
Wullaert A, Heyninck K, Beyaert R . Mechanisms of crosstalk between TNF-induced NF-kappaB and JNK activation in hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 2006; 72: 1090–1101.
Gray-Schopfer VC, Karasarides M, Hayward R, Marais R . Tumor necrosis factor-alpha blocks apoptosis in melanoma cells when BRAF signaling is inhibited. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 122–129.
Gray-Schopfer V, Wellbrock C, Marais R . Melanoma biology and new targeted therapy. Nature 2007; 445: 851–857.
Chudnovsky Y, Khavari PA, Adams AE . Melanoma genetics and the development of rational therapeutics. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 813–824.
Pandha HS, Heinemann L, Simpson GR, Melcher A, Prestwich R, Errington F et al. Synergistic effects of oncolytic reovirus and cisplatin chemotherapy in murine malignant melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 6158–6166.
Tawbi HA, Kirkwood JM . Management of metastatic melanoma. Semin Oncol. 2007; 34: 532–545.
King AJ, Patrick DR, Batorsky RS, Ho ML, Do HT, Zhang SY et al. Demonstration of a genetic therapeutic index for tumors expressing oncogenic BRAF by the kinase inhibitor SB-590885. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 11100–11105.
Tsai J, Lee JT, Wang W, Zhang J, Cho H, Mamo S et al. Discovery of a selective inhibitor of oncogenic B-Raf kinase with potent antimelanoma activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 3041–3046.
Heidorn SJ, Milagre C, Whittaker S, Nourry A, Niculescu-Duvas I, Dhomen N et al. Kinase-dead BRAF and oncogenic RAS cooperate to drive tumor progression through CRAF. Cell 2010; 140: 209–221.
Amaravadi RK, Schuchter LM, McDermott DF, Kramer A, Giles L, Gramlich K et al. Phase II trial of temozolomide and sorafenib in advanced melanoma patients with or without brain metastases. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 7711–7718.
Maki RG, D'Adamo DR, Keohan ML, Saulle M, Schuetze SM, Undevia SD et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with metastatic or recurrent sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 3133–3140.
Toyoizumi T, Mick R, Abbas AE, Kang EH, Kaiser LR, Molnar-Kimber KL . Combined therapy with chemotherapeutic agents and herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP34.5 mutant (HSV-1716) in human non-small cell lung cancer. Hum Gene Ther 1999; 10: 3013–3029.
Post DE, Devi NS, Li Z, Brat DJ, Kaur B, Nicholson A et al. Cancer therapy with a replicating oncolytic adenovirus targeting the hypoxic microenvironment of tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 8603–8612.
Heinemann L, Simpson GR, Boxall A, Kottke T, Relph KL, Vile R et al. Synergistic effects of oncolytic reovirus and docetaxel chemotherapy in prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 2011; 11: 221.
Gutermann A, Mayer E, von Dehn-Rothfelser K, Breidenstein C, Weber M, Muench M et al. Efficacy of oncolytic herpesvirus NV1020 can be enhanced by combination with chemotherapeutics in colon carcinoma cells. Hum Gene Ther 2006; 17: 1241–1253.
Twigger K, Vidal L, White CL, De Bono JS, Bhide S, Coffey M et al. Enhanced in vitro and in vivo cytotoxicity of combined reovirus and radiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 912–923.
Pawlik TM, Nakamura H, Mullen JT, Kasuya H, Yoon SS, Chandrasekhar S et al. Prodrug bioactivation and oncolysis of diffuse liver metastases by a herpes simplex virus 1 mutant that expresses the CYP2B1 transgene. Cancer 2002; 95: 1171–1181.
Tyminski E, Leroy S, Terada K, Finkelstein DM, Hyatt JL, Danks MK et al. Brain tumor oncolysis with replication-conditional herpes simplex virus type 1 expressing the prodrug-activating genes, CYP2B1 and secreted human intestinal carboxylesterase, in combination with cyclophosphamide and irinotecan. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 6850–6857.
Raki M, Kanerva A, Ristimaki A, Desmond RA, Chen DT, Ranki T et al. Combination of gemcitabine and Ad5/3-Delta24, a tropism modified conditionally replicating adenovirus, for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Gene Ther 2005; 12: 1198–1205.
Soares JA, Leite FG, Andrade LG, Torres AA, De Sousa LP, Barcelos LS et al. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway early during vaccinia and cowpox virus infections is required for both host survival and viral replication. J Virol 2009; 83: 6883–6899.
Wang G, Barrett JW, Stanford M, Werden SJ, Johnston JB, Gao X et al. Infection of human cancer cells with myxoma virus requires Akt activation via interaction with a viral ankyrin-repeat host range factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 4640–4645.
Moore RJ, Owens DM, Stamp G, Arnott C, Burke F, East N et al. Mice deficient in tumor necrosis factor-alpha are resistant to skin carcinogenesis. Nature Medicine 1999; 5: 828–831.
Beyaert R, Van Loo G, Heyninck K, Vandenabeele P . Signaling to gene activation and cell death by tumor necrosis factor receptors and Fas. Int Rev Cytol 2002; 214: 225–272.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 2004; 18: 2195–2224.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Khin Thway and Dr Michelle Wilkinson for their assistance with data acquisition and analysis. This work was supported in part by research grants from the Myfanwy Townsend Melanoma Research Fund and the Cotswold Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Aladar Szalay is president and a shareholder of GeneLux corporation. Kevin Harrington receives funding from GeneLux corporation in support of laboratory research. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kyula, J., Khan, A., Mansfield, D. et al. Synergistic cytotoxicity of radiation and oncolytic Lister strain vaccinia in V600D/EBRAF mutant melanoma depends on JNK and TNF-α signaling. Oncogene 33, 1700–1712 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.112
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.112
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Therapy with oncolytic viruses: progress and challenges
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
Oncolytic vaccinia virus GLV-1h68 exhibits profound antitumoral activities in cell lines originating from neuroendocrine neoplasms
BMC Cancer (2020)
-
MALT1 promotes melanoma progression through JNK/c-Jun signaling
Oncogenesis (2017)
-
Oncolytic vaccinia virus as a vector for therapeutic sodium iodide symporter gene therapy in prostate cancer
Gene Therapy (2016)
-
The tumour microenvironment after radiotherapy: mechanisms of resistance and recurrence
Nature Reviews Cancer (2015)