Abstract
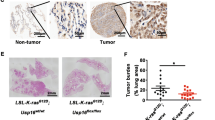
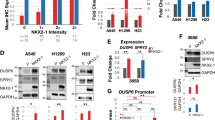
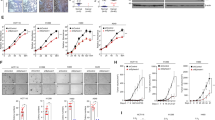
Rac1b, an alternative splice form of Rac1, has been previously shown to be upregulated in colon and breast cancer cells, suggesting an oncogenic role for Rac1b in these cancers. Our analysis of NSCLC tumor and matched normal tissue samples indicates Rac1b is upregulated in a significant fraction of lung tumors in correlation with mutational status of K-ras. To directly assess the oncogenic potential of Rac1b in vivo, we employed a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma, in which the expression of Rac1b can be conditionally activated specifically in the lung. Although expression of Rac1b alone is insufficient to drive tumor initiation, the expression of Rac1b synergizes with an oncogenic allele of K-ras resulting in increased cellular proliferation and accelerated tumor growth. Finally, we show that in contrast to our previous findings demonstrating a requirement for Rac1 in K-ras-driven cell proliferation, Rac1b is not required in this context. Given the partially overlapping spectrum of downstream effectors regulated by Rac1 and Rac1b, our findings further delineate the signaling pathways downstream of Rac1 that are required for K-ras driven tumorigenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wennerberg K, Der CJ . Rho-family GTPases: it's not only Rac and Rho (and I like it). J Cell Sci 2004; 117 (Pt 8): 1301–1312.
Ridley AJ, Paterson HF, Johnston CL, Diekmann D, Hall A . The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell 1992; 70: 401–410.
Nobes CD, Hall A . Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 1995; 81: 53–62.
Matos P, Collard JG, Jordan P . Tumor-related alternatively spliced Rac1b is not regulated by Rho-GDP dissociation inhibitors and exhibits selective downstream signaling. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 50442–50448.
Matos P, Jordan P . Expression of Rac1b stimulates NF-kappaB-mediated cell survival and G1/S progression. Exp Cell Res 2005; 305: 292–299.
Radisky DC, Levy DD, Littlepage LE, Liu H, Nelson CM, Fata JE et al. Rac1b and reactive oxygen species mediate MMP-3-induced EMT and genomic instability. Nature 2005; 436: 123–127.
Esufali S, Charames GS, Pethe VV, Buongiorno P, Bapat B . Activation of tumor-specific splice variant Rac1b by dishevelled promotes canonical Wnt signaling and decreased adhesion of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 2469–2479.
Schnelzer A, Prechtel D, Knaus U, Dehne K, Gerhard M, Graeff H et al. Rac1 in human breast cancer: overexpression, mutation analysis, and characterization of a new isoform, Rac1b. Oncogene 2000; 19: 3013–3020.
Jordan P, Brazao R, Boavida MG, Gespach C, Chastre E . Cloning of a novel human Rac1b splice variant with increased expression in colorectal tumors. Oncogene 1999; 18: 6835–6839.
Jackson EL, Willis N, Mercer K, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Montoya R et al. Analysis of lung tumor initiation and progression using conditional expression of oncogenic K-ras. Genes Dev 2001; 15: 3243–3248.
Kissil JL, Walmsley MJ, Hanlon L, Haigis KM, Bender Kim CF, Sweet-Cordero A et al. Requirement for Rac1 in a K-ras induced lung cancer in the mouse. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 8089–8094.
Fiegen D, Haeusler LC, Blumenstein L, Herbrand U, Dvorsky R, Vetter IR et al. Alternative splicing of Rac1 generates Rac1b, a self-activating GTPase. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 4743–4749.
Singh A, Karnoub AE, Palmby TR, Lengyel E, Sondek J, Der CJ . Rac1b, a tumor associated, constitutively active Rac1 splice variant, promotes cellular transformation. Oncogene 2004; 23: 9369–9380.
Matos P, Oliveira C, Velho S, Goncalves V, da Costa LT, Moyer MP et al. B-Raf(V600E) cooperates with alternative spliced Rac1b to sustain colorectal cancer cell survival. Gastroenterology 2008; 135: 899–906.
Lozano E, Frasa MA, Smolarczyk K, Knaus UG, Braga VM . PAK is required for the disruption of E-cadherin adhesion by the small GTPase Rac. J Cell Sci 2008; 121 (Pt 7): 933–938.
Dummler B, Ohshiro K, Kumar R, Field J . Pak protein kinases and their role in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2009; 28: 51–63.
Orlichenko L, Geyer R, Yanagisawa M, Khauv D, Radisky ES, Anastasiadis PZ et al. The 19-amino acid insertion in the tumor-associated splice isoform Rac1b confers specific binding to p120 catenin. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 19153–19161.
Walmsley MJ, Ooi SK, Reynolds LF, Smith SH, Ruf S, Mathiot A et al. Critical roles for Rac1 and Rac2 GTPases in B cell development and signaling. Science 2003; 302: 459–462.
Srinivas S, Watanabe T, Lin CS, William CM, Tanabe Y, Jessell TM et al. Cre reporter strains produced by targeted insertion of EYFP and ECFP into the ROSA26 locus. BMC Dev Biol 2001; 1: 4.
Johnson L, Mercer K, Greenbaum D, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Tuveson DA et al. Somatic activation of the K-ras oncogene causes early onset lung cancer in mice. Nature 2001; 410: 1111–1116.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Derek Radisky for sharing the pEYFP-C1-mRac1b vector and members of the Kissil and Albelda labs for technical assistance. We thank the Wistar Transgenics and Animal core facilities. This work was supported by Grant CA124495 (JLK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Licciulli, S., Avila, J. et al. The Rac1 splice form Rac1b promotes K-ras-induced lung tumorigenesis. Oncogene 32, 903–909 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.99
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.99
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RAC1B function is essential for breast cancer stem cell maintenance and chemoresistance of breast tumor cells
Oncogene (2023)
-
Met-RANTES preserves the blood–brain barrier through inhibiting CCR1/SRC/Rac1 pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2022)
-
The role of ROS in tumour development and progression
Nature Reviews Cancer (2022)
-
Negative regulation of TGFβ-induced apoptosis by RAC1B enhances intestinal tumourigenesis
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
RAC1B modulates intestinal tumourigenesis via modulation of WNT and EGFR signalling pathways
Nature Communications (2021)