Abstract
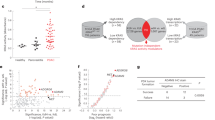
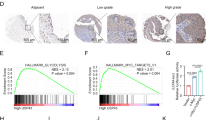
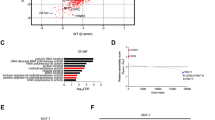
B-cell leukemia 3 (Bcl-3) is a member of the inhibitor of κB family, which regulates a wide range of biological processes by functioning as a transcriptional activator or as a repressor of target genes. As high levels of Bcl-3 expression and activation have been detected in different types of human cancer, Bcl-3 has been labeled a proto-oncogene. Our study uncovered a markedly upregulated Bcl-3 expression in human prostate cancer (PCa), where inflammatory cell infiltration was observed. Elevated Bcl-3 expression in PCa was dependent on the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6-mediated STAT3 activation. Microarray analyses, using Bcl-3 knockdown in PCa cells, identified the inhibitor of DNA-binding (Id) family of helix-loop-helix proteins as potential Bcl-3-regulated genes. Bcl-3 knockdown reduced the abundance of Id-1 and Id-2 proteins and boosted PCa cells to be more receptive to undergoing apoptosis following treatment with anticancer drug. Our data imply that inactivation of Bcl-3 may lead to sensitization of cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis, thus suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy in PCa treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Damber JE, Aus G . Prostate cancer. Lancet 2008; 371: 1710–1721.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E . Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 2010; 60: 277–300.
Coussens LM, Werb Z . Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002; 420: 860–867.
De Marzo AM, Platz EA, Sutcliffe S, Xu J, Gronberg H, Drake CG et al. Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 256–269.
Sottnik JL, Zhang J, Macoska JA, Keller ET . The PCa tumor microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron 2011; 4: 283–297.
Zha S, Gage WR, Sauvageot J, Saria EA, Putzi MJ, Ewing CM et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 is up-regulated in proliferative inflammatory atrophy of the prostate, but not in prostate carcinoma. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 8617–8623.
De Marzo AM, Marchi VL, Epstein JI, Nelson WG . Proliferative inflammatory atrophy of the prostate: implications for prostatic carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol 1999; 155: 1985–1992.
Correa P . Human gastric carcinogenesis: a multistep and multifactorial process—First American Cancer Society Award Lecture on Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 6735–6740.
Twillie DA, Eisenberger MA, Carducci MA, Hseih WS, Kim WY, Simons JW . Interleukin-6: a candidate mediator of human prostate cancer morbidity. Urology 1995; 45: 542–549.
Hobisch A, Rogatsch H, Hittmair A, Fuchs D, Bartsch G, Klocker H et al. Immunohistochemical localization of interleukin-6 and its receptor in benign, premalignant and malignant prostate tissue. J Pathol 2000; 191: 239–244.
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Muller-Newen G, Schaper F, Graeve L . Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem J. 1998; 334 (Part 2) 297–314.
Hobisch A, Ramoner R, Fuchs D, Godoy-Tundidor S, Bartsch G, Klocker H et al. Prostate cancer cells (LNCaP) generated after long-term interleukin 6 (IL-6) treatment express IL-6 and acquire an IL-6 partially resistant phenotype. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 2941–2948.
Smith PC, Keller ET . Anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody induces regression of human prostate cancer xenografts in nude mice. Prostate 2001; 48: 47–53.
Chung TD, Yu JJ, Kong TA, Spiotto MT, Lin JM . Interleukin-6 activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, which inhibits apoptosis in human prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate 2000; 42: 1–7.
Paule B, Terry S, Kheuang L, Soyeux P, Vacherot F, de la Taille A . The NF-kappaB/IL-6 pathway in metastatic androgen-independent prostate cancer: new therapeutic approaches? World J Urol 2007; 25: 477–489.
McKeithan TW, Rowley JD, Shows TB, Diaz MO . Cloning of the chromosome translocation breakpoint junction of the t(14;19) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987; 84: 9257–9260.
Cogswell PC, Guttridge DC, Funkhouser WK, Baldwin AS . Selective activation of NF-kappa B subunits in human breast cancer: potential roles for NF-kappa B2/p52 and for Bcl-3. Oncogene 2000; 19: 1123–1131.
Kuphal S, Shaw-Hallgren G, Eberl M, Karrer S, Aberger F, Bosserhoff AK et al. GLI1-dependent transcriptional repression of CYLD in basal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2011; 30: 4523–4530.
Massoumi R, Chmielarska K, Hennecke K, Pfeifer A, Fassler R . Cyld inhibits tumor cell proliferation by blocking Bcl-3-dependent NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2006; 125: 665–677.
Massoumi R, Kuphal S, Hellerbrand C, Haas B, Wild P, Spruss T et al. Down-regulation of CYLD expression by Snail promotes tumor progression in malignant melanoma. J Exp Med 2009; 206: 221–232.
Thornburg NJ, Pathmanathan R, Raab-Traub N . Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB p50 homodimer/Bcl-3 complexes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 8293–8301.
Choi HJ, Lee JM, Kim H, Nam HJ, Shin HJ, Kim D et al. Bcl3-dependent stabilization of CtBP1 is crucial for the inhibition of apoptosis and tumor progression in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010; 400: 396–402.
Kashatus D, Cogswell P, Baldwin AS . Expression of the Bcl-3 proto-oncogene suppresses p53 activation. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 225–235.
Rebollo A, Dumoutier L, Renauld JC, Zaballos A, Ayllon V, Martinez AC . Bcl-3 expression promotes cell survival following interleukin-4 deprivation and is controlled by AP1 and AP1-like transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 3407–3416.
Kuwata H, Watanabe Y, Miyoshi H, Yamamoto M, Kaisho T, Takeda K et al. IL-10-inducible Bcl-3 negatively regulates LPS-induced TNF-alpha production in macrophages. Blood 2003; 102: 4123–4129.
Wessells J, Baer M, Young HA, Claudio E, Brown K, Siebenlist U et al. BCL-3 and NF-kappaB p50 attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in macrophages. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 49995–50003.
Keutgens A, Shostak K, Close P, Zhang X, Hennuy B, Aussems M et al. The repressing function of the oncoprotein BCL-3 requires CtBP, while its polyubiquitination and degradation involve the E3 ligase TBLR1. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 4006–4021.
Brocke-Heidrich K, Kretzschmar AK, Pfeifer G, Henze C, Loffler D, Koczan D et al. Interleukin-6-dependent gene expression profiles in multiple myeloma INA-6 cells reveal a Bcl-2 family-independent survival pathway closely associated with Stat3 activation. Blood 2004; 103: 242–251.
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns HM, Muller-Newen G, Schaper F . Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J 2003; 374: 1–20.
Nadiminty N, Lou W, Sun M, Chen J, Yue J, Kung HJ et al. Aberrant activation of the androgen receptor by NF-kappaB2/p52 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 3309–3319.
Cai C, Jiang FN, Liang YX, He HC, Han ZD, Dai QS et al. Classical and alternative nuclear factor-κB pathways: a comparison among normal prostate, benign prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer. Pathol Oncol Res 2011; 17: 873–878.
Nadiminty N, Chun JY, Lou W, Lin X, Gao AC . NF-kappaB2/p52 enhances androgen-independent growth of human LNCaP cells via protection from apoptotic cell death and cell cycle arrest induced by androgen-deprivation. Prostate 2008; 68: 1725–1733.
Brocke-Heidrich K, Ge B, Cvijic H, Pfeifer G, Loffler D, Henze C et al. BCL3 is induced by IL-6 via Stat3 binding to intronic enhancer HS4 and represses its own transcription. Oncogene 2006; 25: 7297–7304.
Forootan SS, Wong YC, Dodson A, Wang X, Lin K, Smith PH et al. Increased Id-1 expression is significantly associated with poor survival of patients with prostate cancer. Hum Pathol 2007; 38: 1321–1329.
Zielinski AJ, Fong S, Allison J, Kawahara M, Coppe JP, Feiler H et al. The helix-loop-helix Id-1 inhibits PSA expression in prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2010; 126: 2490–2496.
Cheung HW, Ling MT, Tsao SW, Wong YC, Wang X . Id-1-induced Raf/MEK pathway activation is essential for its protective role against taxol-induced apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2004; 25: 881–887.
Hua H, Sarvetnick N . ID2 promotes the expansion and survival of growth-arrested pancreatic beta cells. Endocrine 2007; 32: 329–337.
Kim H, Chung H, Kim HJ, Lee JY, Oh MY, Kim Y et al. Id-1 regulates Bcl-2 and Bax expression through p53 and NF-kappaB in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2008; 112: 287–296.
Monticelli LA, Yang Y, Knell J, D'Cruz LM, Cannarile MA, Engel I et al. Transcriptional regulator Id2 controls survival of hepatic NKT cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 19461–19466.
Zhang H, Lawson WE, Polosukhin VV, Pozzi A, Blackwell TS, Litingtung Y et al. Inhibitor of differentiation 1 promotes endothelial survival in a bleomycin model of lung injury in mice. Am J Pathol 2007; 171: 1113–1126.
Ling MT, Wang X, Ouyang XS, Xu K, Tsao SW, Wong YC . Id-1 expression promotes cell survival through activation of NF-kappaB signalling pathway in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2003; 22: 4498–4508.
Wong YC, Zhang XM, Ling MT, Wang XH . Inactivation of ID-1 gene induces sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs. Adv Exp Med Biol 2008; 617: 565–572.
Zhang X, Ling MT, Wang Q, Lau CK, Leung SC, Lee TK et al. Identification of a novel inhibitor of differentiation-1 (ID-1) binding partner, caveolin-1, and its role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and resistance to apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 33284–33294.
Zhang X, Ling MT, Wang X, Wong YC . Inactivation of Id-1 in prostate cancer cells: a potential therapeutic target in inducing chemosensitization to taxol through activation of JNK pathway. Int J Cancer 2006; 118: 2072–2081.
Zhang X, Ling MT, Wong YC, Wang X . Evidence of a novel antiapoptotic factor: role of inhibitor of differentiation or DNA binding (Id-1) in anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. Cancer Sci 2007; 98: 308–314.
Acknowledgements
We thank Elise Nilsson for excellent technical assistance, Dr Zoran Culig (Innsbruck Medical University, Austria) for providing us the LNCaP-IL-6+ cells, Dr Takashi Tokino (Cancer Research Institute, Sapporo, Japan) for human Id-2 promoter luciferase reporter construct, Dr Roland M Schmid (Technical University Munich, Munich, Germany) for FLAG-Bcl-3 expression construct, Dr David Ulmert (Lund University, Lund, Sweden) for characterization of the human PCa tissue microarray and Dr Srinivas Veerla (SCIBLU, Lund University, Lund, Sweden) for microarray analysis and gene expression profiling. This work was supported by the Swedish Society for Medical Research, Swedish Cancer Foundation, Swedish Medical Research Council, Royal Physiographic Society in Lund, U-MAS Research Foundations, and funding from the European Research Council under the European Union's seventh framework program ERC grant agreement (260460 to RM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahlqvist, K., Saamarthy, K., Syed Khaja, A. et al. Expression of Id proteins is regulated by the Bcl-3 proto-oncogene in prostate cancer. Oncogene 32, 1601–1608 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.175
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.175
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Discovery of a small molecule that inhibits Bcl-3-mediated cyclin D1 expression in melanoma cells
BMC Cancer (2024)
-
Multifaceted roles for BCL3 in cancer: a proto-oncogene comes of age
Molecular Cancer (2024)
-
Multiple roles for Bcl-3 in mammary gland branching, stromal collagen invasion, involution and tumor pathology
Breast Cancer Research (2022)
-
The CDK1/TFCP2L1/ID2 cascade offers a novel combination therapy strategy in a preclinical model of bladder cancer
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
The Id-protein family in developmental and cancer-associated pathways
Cell Communication and Signaling (2017)