Abstract
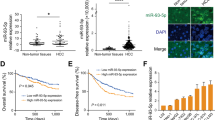
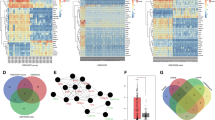
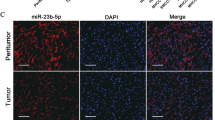
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are believed to have fundamental roles in tumorigenesis and have great potential for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. However, the roles of miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinogenesis are still not fully elucidated. We investigated the aberrantly expressed miRNAs involved in hepatoma by comparison of miRNA expression profiles in cancerous hepatocytes with normal primary human hepatocytes, and 37 dysregulated miRNAs were screened out by twofold change with a significant difference (P<0.05). Clustering analysis based on 13 miRNAs with changes over 15-folds showed that the miRNA expression patterns between the cancerous and normal hepatocytes were clearly different. Among the 13 miRNAs, we found that miR-375 was significantly downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of miR-375 in liver cancer cells decreased cell proliferation, clonogenicity, migration/invasion and also induced G1 arrest and apoptosis. To unveil the molecular mechanism of miR-375-mediated phenotype in hepatoma cells described above, we examined the putative targets using bioinformatics tools and found that astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) was a potential target of miR-375. Then we demonstrated that miR-375 bound directly to the 3′-untranslated region of AEG-1 and inhibited the expression of AEG-1. TaqMan quantitative reverse transcriptase–PCR and western blot analysis showed that miR-375 expression was inversely correlated with AEG-1 expression in HCC tissues. Knockdown of AEG-1 by RNAi in HCC cells, similar to miR-375 overexpression, suppressed tumor properties. Ectopic expression of AEG-1, conversely, could partially reverse the antitumor effects of miR-375. In a mouse model, therapeutic administration of cholesterol-conjugated 2′-O-methyl-modified miR-375 mimics (Chol-miR-375) could significantly suppress the growth of hepatoma xenografts in nude mice. In conclusion, our findings indicate that miR-375 targets AEG-1 in HCC and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo, and highlight the therapeutic potential of miR-375 in HCC treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Avissar M, Christensen BC, Kelsey KT, Marsit CJ . (2009). MicroRNA expression ratio is predictive of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15: 2850–2855.
Baek D, Villen J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP . (2008). The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 455: 64–71.
Braconi C, Patel T . (2008). MicroRNA expression profiling: a molecular tool for defining the phenotype of hepatocellular tumors. Hepatology 47: 1807–1809.
Budhu A, Jia HL, Forgues M, Liu CG, Goldstein D, Lam A et al. (2008). Identification of metastasis-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 47: 897–907.
Emdad L, Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Lee SG, Kang DC, Bruce JN et al. (2007). Astrocyte elevated gene-1: recent insights into a novel gene involved in tumor progression, metastasis and neurodegeneration. Pharmacol Ther 114: 155–170.
Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Fornari F, Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Liu CG et al. (2007). Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 67: 6092–6099.
Gramantieri L, Fornari F, Callegari E, Sabbioni S, Lanza G, Croce CM et al. (2008). MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 12: 2189–2204.
Hu G, Wei Y, Kang Y . (2009). The multifaceted role of MTDH7sol;AEG-1 in cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res 15: 5615–5620.
Huang YS, Dai Y, Yu XF, Bao SY, Yin YB, Tang M et al. (2008). Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues without viral hepatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23: 87–94.
Jian-bo X, Hui W, Yu-long H, Chang-hua Z, Long-juan Z, Shi-rong C et al. (2011). Astrocyte-elevated gene-1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Med Oncol 28: 455–462.
Jiang J, Gusev Y, Aderca I, Mettler TA, Nagorney DM, Brackett DJ et al. (2008). Association of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res 14: 419–427.
Kang DC, Su ZZ, Sarkar D, Emdad L, Volsky DJ, Fisher PB . (2005). Cloning and characterization of HIV-1-inducible astrocyte elevated gene-1, AEG-1. Gene 353: 8–15.
Kikuno N, Shiina H, Urakami S, Kawamoto K, Hirata H, Tanaka Y et al. (2007). Knockdown of astrocyte-elevated gene-1 inhibits prostate cancer progression through upregulation of FOXO3a activity. Oncogene 26: 7647–7655.
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Montgomery CL, Hwang HW et al. (2009). Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 137: 1005–1017.
Ladeiro Y, Couchy G, Balabaud C, Bioulac-Sage P, Pelletier L, Rebouissou S et al. (2008). MicroRNA profiling in hepatocellular tumors is associated with clinical features and oncogene/tumor suppressor gene mutations. Hepatology 47: 1955–1963.
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL et al. (2007). Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 120: 1046–1054.
Lee SG, Jeon HY, Su ZZ, Richards JE, Vozhilla N, Sarkar D et al. (2009). Astrocyte elevated gene-1 contributes to the pathogenesis of neuroblastoma. Oncogene 28: 2476–2484.
Lee SG, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Sarkar D, Fisher PB . (2006). Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is a target gene of oncogenic Ha-ras requiring phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and c-Myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 17390–17395.
Lee SG, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Sarkar D, Franke TF, Fisher PB . (2008). Astrocyte elevated gene-1 activates cell survival pathways through PI3K-Akt signaling. Oncogene 27: 1114–1121.
Li J, Zhang N, Song LB, Liao WT, Jiang LL, Gong LY et al. (2008). Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer progression and overall patient survival. Clin Cancer Res 14: 3319–3326.
Li Y, Tian B, Yang J, Zhao L, Wu X, Ye SL et al. (2004). Stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma cell model system with multiple metastatic potentials established through consecutive in vivo selection and studies on metastatic characteristics. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130: 460–468.
Liu AM, Poon RT, Luk JM . (2010). MicroRNA-375 targets Hippo-signaling effector YAP in liver cancer and inhibits tumor properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394: 623–627.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et al. (2005). MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435: 834–838.
Malarkey DE, Johnson K, Ryan L, Boorman G, Maronpot RR . (2005). New insights into functional aspects of liver morphology. Toxicol Pathol 33: 27–34.
Maruyama M, Totsugawa T, Kunieda T, Okitsu T, Shibata N, Takesue M et al. (2003). Hepatocyte isolation and transplantation in the pig. Cell Transplant 12: 593–598.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T . (2007). MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 133: 647–658.
Meng FY, Chen ZS, Han M, Hu XP, He XX, Liu Y et al. (2010). Porcine hepatocyte isolation and reversible immortalization mediated by retroviral transfer and site-specific recombination. World J Gastroenterol 16: 1660–1664.
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, Urashima T, Toyoda H, Okanoue T et al. (2006). Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene 25: 2537–2545.
Petri A, Lindow M, Kauppinen S . (2009). MicroRNA silencing in primates: towards development of novel therapeutics. Cancer Res 69: 393–395.
Poy MN, Eliasson L, Krutzfeldt J, Kuwajima S, Ma X, Macdonald PE et al. (2004). A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature 432: 226–230.
Santamaria E, Munoz J, Fernandez-Irigoyen J, Prieto J, Corrales FJ . (2007). Toward the discovery of new biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma by proteomics. Liver Int 27: 163–173.
Scherr M, Venturini L, Battmer K, Schaller-Schoenitz M, Schaefer D, Dallmann I et al. (2007). Lentivirus-mediated antagomir expression for specific inhibition of miRNA function. Nucleic Acids Res 35: e149.
Soutschek J, Akinc A, Bramlage B, Charisse K, Constien R, Donoghue M et al. (2004). Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature 432: 173–178.
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Gandhi V, Plunkett W, Sampath D, Calin GA . (2007). miRNAs and their potential for use against cancer and other diseases. Future Oncol 3: 521–537.
Tsukamoto Y, Nakada C, Noguchi T, Tanigawa M, Nguyen LT, Uchida T et al. (2010). MicroRNA-375 is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta. Cancer Res 70: 2339–2349.
Varnholt H, Drebber U, Schulze F, Wedemeyer I, Schirmacher P, Dienes HP et al. (2008). MicroRNA gene expression profile of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 47: 1223–1232.
Vester B, Wengel J . (2004). LNA (locked nucleic acid): high-affinity targeting of complementary RNA and DNA. Biochemistry 43: 13233–13241.
Yoo BK, Emdad L, Su ZZ, Villanueva A, Chiang DY, Mukhopadhyay ND et al. (2009). Astrocyte elevated gene-1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. J Clin Invest 119: 465–477.
Yu C, Chen K, Zheng H, Guo X, Jia W, Li M et al. (2009). Overexpression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) progression and pathogenesis. Carcinogenesis 30: 894–901.
Zhang B, Liu XX, He JR, Zhou CX, Guo M, He M et al. (2011). Pathologically decreased miR-26a antagonizes apoptosis and facilitates carcinogenesis by targeting MTDH and EZH2 in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 32: 2–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Xin Chen of University of California, San Francisco for critical review of the manuscript. This work was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (no. 2007CB512903) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81101824 and 30872237).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, XX., Chang, Y., Meng, FY. et al. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 31, 3357–3369 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.500
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.500
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multifunctional nanoplatforms application in the transcatheter chemoembolization against hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2023)
-
Rictor mediates p53 deactivation to facilitate the malignant transformation of hepatocytes and promote hepatocarcinogenesis
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
Comprehensive microRNA analysis across genome-edited colorectal cancer organoid models reveals miR-24 as a candidate regulator of cell survival
BMC Genomics (2022)
-
MALAT1-miRNAs network regulate thymidylate synthase and affect 5FU-based chemotherapy
Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
MicroRNA-375 represses tumor angiogenesis and reverses resistance to sorafenib in hepatocarcinoma
Cancer Gene Therapy (2021)