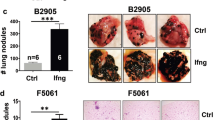
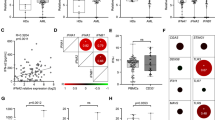
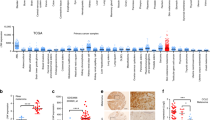
Abstract
Interferon alpha (IFNα) is widely used for treatment of melanoma and certain other malignancies. This cytokine as well as the related IFNβ exerts potent anti-tumorigenic effects; however, their efficacy in patients is often suboptimal. Here, we report that inflammatory signaling impedes the effects of IFNα/β. Melanoma cells can secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines that inhibit cellular responses to IFNα/β via activating the ligand-independent pathway for the phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitination and accelerated degradation of the IFNAR1 chain of type I IFN receptor. Catalytic activity of the p38 protein kinase was required for IFNAR1 downregulation and inhibition of IFNα/β signaling induced by proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin 1 (IL-1). Activation of p38 kinase inversely correlated with protein levels of IFNAR1 in clinical melanoma specimens. Inhibition of p38 kinase augmented the inhibitory effects of IFNα/β on cell viability and growth in vitro and in vivo. The roles of inflammation and p38 protein kinase in regulating cellular responses to IFNα/β in normal and tumor cells are discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaronson DS, Horvath CM . (2002). A road map for those who don’t know JAK-STAT. Science 296: 1653–1655.
Alonso-Curbelo D, Soengas MS . (2010). Self-killing of melanoma cells by cytosolic delivery of dsRNA: wiring innate immunity for a coordinated mobilization of endosomes, autophagosomes and the apoptotic machinery in tumor cells. Autophagy 6: 148–150.
Ascierto PA, Kirkwood JM . (2008). Adjuvant therapy of melanoma with interferon: lessons of the past decade. J Transl Med 6: 62.
Balkwill F, Mantovani A . (2010). Cancer and inflammation: implications for pharmacology and therapeutics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 87: 401–406.
Bennicelli JL, Elias J, Kern J, Guerry Dt . (1989). Production of interleukin 1 activity by cultured human melanoma cells. Cancer Res 49: 930–935.
Bhattacharya S, HuangFu WC, Liu J, Veeranki S, Baker DP, Koumenis C et al. (2010). Inducible priming phosphorylation promotes ligand-independent degradation of the IFNAR1 chain of type I interferon receptor. J Biol Chem 285: 2318–2325.
Bracarda S, Eggermont AM, Samuelsson J . (2010). Redefining the role of interferon in the treatment of malignant diseases. Eur J Cancer 46: 284–297.
Bregman H, Carroll PJ, Meggers E . (2006). Rapid access to unexplored chemical space by ligand scanning around a ruthenium center: discovery of potent and selective protein kinase inhibitors. J Am Chem Soc 128: 877–884.
Coccia EM, Uze G, Pellegrini S . (2006). Negative regulation of type I interferon signaling: facts and mechanisms. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 52: 77–87.
Fecher LA, Flaherty KT . (2009). Where are we with adjuvant therapy of stage III and IV melanoma in 2009? J Natl Compr Canc Netw 7: 295–304.
Germano G, Allavena P, Mantovani A . (2008). Cytokines as a key component of cancer-related inflammation. Cytokine 43: 374–379.
Goldman LA, Zafari M, Cutrone EC, Dang A, Brickelmeier M, Runkel L et al. (1999). Characterization of antihuman IFNAR-1 monoclonal antibodies: epitope localization and functional analysis. J Interferon Cytokine Res 19: 15–26.
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M . (2010). Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 140: 883–899.
Gu Y, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Linkov F, Koenig KL, Liu M, Velikokhatnaya L et al. (2009). Reproducibility of serum cytokines and growth factors. Cytokine 45: 44–49.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100: 57–70.
Huangfu WC, Qian J, Liu C, Rui H, Fuchs SY . (2010). Melanoma cell-secreted soluble factor that stimulates ubiquitination and degradation of the interferon alpha receptor and attenuates its signaling. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 23: 838–840.
Hui L, Bakiri L, Stepniak E, Wagner EF . (2007). p38alpha: a suppressor of cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Cell Cycle 6: 2429–2433.
Jinlian L, Yingbin Z, Chunbo W . (2007). p38 MAPK in regulating cellular responses to ultraviolet radiation. J Biomed Sci 14: 303–312.
Kaehler KC, Sondak VK, Schadendorf D, Hauschild A . (2010). Pegylated interferons: prospects for the use in the adjuvant and palliative therapy of metastatic melanoma. Eur J Cancer 46: 41–46.
Kock A, Schwarz T, Urbanski A, Peng Z, Vetterlein M, Micksche M et al. (1989). Expression and release of interleukin-1 by different human melanoma cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst 81: 36–42.
Kumar KG, Barriere H, Carbone CJ, Liu J, Swaminathan G, Xu P et al. (2007a). Site-specific ubiquitination exposes a linear motif to promote interferon-alpha receptor endocytosis. J Cell Biol 179: 935–950.
Kumar KG, Krolewski JJ, Fuchs SY . (2004). Phosphorylation and specific ubiquitin acceptor sites are required for ubiquitination and degradation of the IFNAR1 subunit of type I interferon receptor. J Biol Chem 279: 46614–46620.
Kumar KG, Liu J, Li Y, Yu D, Thomas-Tikhonenko A, Herlyn M et al. (2007b). Raf inhibitor stabilizes receptor for the type I interferon but inhibits its anti-proliferative effects in human malignant melanoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther 6: 1437–1441.
Kumar KG, Tang W, Ravindranath AK, Clark WA, Croze E, Fuchs SY . (2003). SCF(HOS) ubiquitin ligase mediates the ligand-induced down-regulation of the interferon-alpha receptor. EMBO J 22: 5480–5490.
Leiter U, Garbe C . (2008). Epidemiology of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer--the role of sunlight. Adv Exp Med Biol 624: 89–103.
Li Y, Clevenger CV, Minkovsky N, Kumar KG, Raghunath PN, Tomaszewski JE et al. (2006). Stabilization of prolactin receptor in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 25: 1896–1902.
Lin WW, Karin M . (2007). A cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J Clin Invest 117: 1175–1183.
Linkov F, Ferris RL, Yurkovetsky Z, Marrangoni A, Velikokhatnaya L, Gooding W et al. (2008). Multiplex analysis of cytokines as biomarkers that differentiate benign and malignant thyroid diseases. Proteomics Clin Appl 2: 1575–1585.
Liu J, Carvalho LP, Bhattacharya S, Carbone CJ, Kumar KG, Leu NA et al. (2009). Mammalian casein kinase 1alpha and its leishmanial ortholog regulate stability of IFNAR1 and type I interferon signaling. Mol Cell Biol 29: 6401–6412.
Liu J, Plotnikov A, Banerjee A, Suresh Kumar KG, Ragimbeau J, Marijanovic Z et al. (2008). Ligand-independent pathway that controls stability of interferon alpha receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 367: 388–393.
Liu J, Suresh Kumar KG, Yu D, Molton SA, McMahon M, Herlyn M et al. (2007). Oncogenic BRAF regulates beta-Trcp expression and NF-kappaB activity in human melanoma cells. Oncogene 26: 1954–1958.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F . (2008). Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454: 436–444.
Marijanovic Z, Ragimbeau J, Kumar KG, Fuchs SY, Pellegrini S . (2006). TYK2 activity promotes ligand-induced IFNAR1 proteolysis. Biochem J 397: 31–38.
Megason SG, McMahon AP . (2002). A mitogen gradient of dorsal midline Wnts organizes growth in the CNS. Development 129: 2087–2098.
Melnikova VO, Bar-Eli M . (2009). Inflammation and melanoma metastasis. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 22: 257–267.
Messina JL, Yu H, Riker AI, Munster PN, Jove RL, Daud AI . (2008). Activated stat-3 in melanoma. Cancer Control 15: 196–201.
Mocellin S, Pasquali S, Rossi CR, Nitti D . (2010). Interferon alpha adjuvant therapy in patients with high-risk melanoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 102: 493–501.
Moretti S, Pinzi C, Spallanzani A, Berti E, Chiarugi A, Mazzoli S et al. (1999). Immunohistochemical evidence of cytokine networks during progression of human melanocytic lesions. Int J Cancer 84: 160–168.
Nazarian RM, Prieto VG, Elder DE, Duncan LM . (2010). Melanoma biomarker expression in melanocytic tumor progression: a tissue microarray study. J Cutan Pathol 37 (Suppl 1): 41–47.
Okamoto M, Liu W, Luo Y, Tanaka A, Cai X, Norris DA et al. (2010). Constitutively active inflammasome in human melanoma cells mediating autoinflammation via caspase-1 processing and secretion of interleukin-1beta. J Biol Chem 285: 6477–6488.
Oxholm A, Oxholm P, Staberg B, Bendtzen K . (1988). Immunohistological detection of interleukin I-like molecules and tumour necrosis factor in human epidermis before and after UVB-irradiation in vivo. Br J Dermatol 118: 369–376.
Platanias LC . (2005). Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 5: 375–386.
Rigual NR, Popat SR, Jayaprakash V, Jaggernauth W, Wong M . (2008). Cutaneous head and neck melanoma: the old and the new. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 8: 403–412.
Roux PP, Blenis J . (2004). ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68: 320–344.
Sander B, Boeryd B . (1996). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in human primary malignant malanoma and it relationship to tumor infiltration by CD3+ cells. Int J Cancer 66: 42–47.
Smalley KS, Nathanson KL, Flaherty KT . (2009). Genetic subgrouping of melanoma reveals new opportunities for targeted therapy. Cancer Res 69: 3241–3244.
Soengas MS, Lowe SW . (2003). Apoptosis and melanoma chemoresistance. Oncogene 22: 3138–3151.
Spiegelman VS, Tang W, Katoh M, Slaga TJ, Fuchs SY . (2002). Inhibition of HOS expression and activities by Wnt pathway. Oncogene 21: 856–860.
Torisu H, Ono M, Kiryu H, Furue M, Ohmoto Y, Nakayama J et al. (2000). Macrophage infiltration correlates with tumor stage and angiogenesis in human malignant melanoma: possible involvement of TNFalpha and IL-1alpha. Int J Cancer 85: 182–188.
Uze G, Schreiber G, Piehler J, Pellegrini S . (2007). The receptor of the type I interferon family. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 316: 71–95.
Weber A, Wasiliew P, Kracht M . (2010). Interleukin-1 (IL-1) pathway. Sci Signal 3: cm1.
Yao K, Balch G, Winchester DJ . (2009). Multidisciplinary treatment of primary melanoma. Surg Clin North Am 89: 267–281, xi.
Yurkovetsky ZR, Kirkwood JM, Edington HD, Marrangoni AM, Velikokhatnaya L, Winans MT et al. (2007). Multiplex analysis of serum cytokines in melanoma patients treated with interferon-alpha2b. Clin Cancer Res 13: 2422–2428.
Zheng H, Qian J, Varghese B, Baker DP, Fuchs S . (2011). Ligand-stimulated downregulation of the alpha interferon receptor: role of protein kinase D2. Mol Cell Biol 31: 710–720.
Zwang Y, Yarden Y . (2006). p38 MAP kinase mediates stress-induced internalization of EGFR: implications for cancer chemotherapy. EMBO J 25: 4195–4206.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs M Gaestel, LM Duncan, RJ Davis, M Herlyn, M May, E Meggers, A Nebreda, J Ninomiya-Tsuji and Z Ronai for reagents. This work was supported by NIH grants CA092900 and CA142425 (to SYF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest except for Dr DP Baker who is an employee of BiogenIDEC, Inc. and owns stock of this company.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HuangFu, WC., Qian, J., Liu, C. et al. Inflammatory signaling compromises cell responses to interferon alpha. Oncogene 31, 161–172 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.221
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.221
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
TNF-α-induced down-regulation of type I interferon receptor contributes to acquired resistance of cervical squamous cancer to Cisplatin
The Journal of Antibiotics (2024)
-
Depression compromises antiviral innate immunity via the AVP-AHI1-Tyk2 axis
Cell Research (2022)
-
Targeting PARP11 to avert immunosuppression and improve CAR T therapy in solid tumors
Nature Cancer (2022)
-
Immune suppressive activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer requires inactivation of the type I interferon pathway
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts downregulate type I interferon receptor to stimulate intratumoral stromagenesis
Oncogene (2020)