Abstract
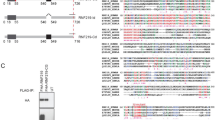
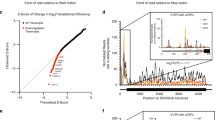
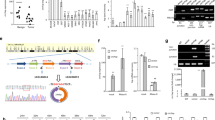
Pdcd4 is a novel tumor suppressor protein that functions in the nucleus and the cytoplasm, and appears to be involved in the regulation of transcription and translation. In the cytoplasm, Pdcd4 has been implicated in the suppression of translation of mRNAs containing structured 5′-untranslated regions; however, the mechanisms that recruit Pdcd4 to specific target mRNAs and the identities of these mRNAs are mostly unknown. In this study, we have identified c-myb mRNA as the first natural translational target mRNA of Pdcd4. We have found that translational suppression of c-myb mRNA by Pdcd4 is dependent on sequences located within the c-myb-coding region. Furthermore, we have found that the N-terminal domain of Pdcd4 has an important role in targeting Pdcd4 to c-myb RNA by mediating preferential RNA binding to the Pdcd4-responsive region of c-myb mRNA. Overall, our work demonstrates for the first time that Pdcd4 is directly involved in translational suppression of a natural mRNA and provides the first evidence for a key role of the RNA-binding domain in targeting Pdcd4 to a specific mRNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afonja O, Juste D, Das S, Matsuhashi S, Samuels HH . (2004). Induction of PDCD4 tumor suppressor gene expression by RAR agonists, antiestrogen and HER-2/neu antagonist in breast cancer cells. Evidence for a role in apoptosis. Oncogene 23: 8135–8145.
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S et al. (2008). MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27: 2128–2136.
Appl H, Klempnauer K-H . (2002). Targeted disruption of c-myb in the chicken pre B-cell line DT40. Oncogene 21: 3076–3081.
Bitomsky N, Böhm M, Klempnauer K-H . (2004). Transformation suppressor protein Pdcd4 interferes with JNK-mediated phosphorylation of c-Jun and recruitment of the coactivator p300 by c-Jun. Oncogene 23: 7484–7493.
Bitomsky N, Wethkamp N, Marikkannu R, Klempnauer K-H . (2008). siRNA-mediated knock-down of Pdcd4 expression causes up-regulation of p21(Waf1/Cip1) expression. Oncogene 27: 4820–4829.
Böhm M, Sawicka K, Siebrasse JP, Brehmer-Fastnacht A, Peters R, Klempnauer K-H . (2003). The transformation suppressor protein Pdcd4 shuttles between nucleus and cytoplasm and binds RNA. Oncogene 22: 4905–4910.
Chang JH, Cho YH, Sohn SY, Choi JM, Kim A, Kim YC et al. (2009). Crystal structure of the eIF4A-PDCD4 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 3148–3153.
Chen Y, Knosel T, Kristiansen G, Pietas A, Garber ME, Matsuhashi S et al. (2003). Loss of PDCD4 expression in human lung cancer correlates with tumour progression and prognosis. J Pathol 200: 640–646.
Cmarik JL, Min H, Hegamyer G, Zhan S, Kulesz-Martin M, Yoshinaga H et al. (1999). Differentially expressed protein Pdcd4 inhibits tumor promoter-induced neoplastic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 14037–14042.
Dorello NV, Peschiamoli A, Guardavaccaro D, Colburn NH, Sherman NE, Pagano M . (2006). S6K1- and betaTRCP-mediated degradation of PDCD4 promotes protein translation and cell growth. Science 314: 467–471.
Ercikan-Abali EA, Banerjee D, Waltham MC, Skacel N, Scotto KW, Bertino JR . (1997). Dihydrofolate reductase protein inhibits its own translation by binding to dihydrofolate reductase mRNA sequences within the coding region. Biochemistry 36: 12317–12322.
Evan GI, Lewis GK, Bishop JM . (1984). Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specic for products of avian oncogene myb. Mol Cell Biol 4: 2843–2850.
Foos G, Grimm S, Klempnauer K-H . (1992). Functional antagonism between members of the myb family: B-myb inhibits v-myb induced gene activation. EMBO J 11: 4619–4629.
Hafner M, Landthaler M, Burger L, Khorshid M, Hausser J, Berninger P et al. (2010). Transcriptome-wide identification of RNA-binding protein and microRNA target sites by PAR-CLIP. Cell 141: 129–141.
Hogan DJ, Riordan DP, Gerber AP, Herschlag D, Brown PO . (2008). Diverse RNA-binding proteins interact with functionally related sets of RNAs, suggesting an extensive regulatory system. PLos Biol 6: e255.
Lancaster AM, Jan E, Sarnow P . (2006). Initiation factor-independent translation mediated by the hepatitis C virus internal ribosomal entry site. RNA 12: 894–902.
Lankat-Buttgereit B, Göke R . (2009). The tumor suppressor Pdcd4: recent advances in the elucidation of function and regulation. Biol Cell 101: 309–317.
LaRonde-LeBlanc N, Santhanam AN, Baker AR, Wlodawer A, Colburn NH . (2007). Structural basis for inhibition of translation by the tumor suppressor Pdcd4. Mol Cell Biol 27: 147–156.
Leupold JH, Yang HS, Colburn NH, Asangani I, Post S, Allgayer H . (2007). Tumor suppressor Pdcd4 inhibits invasion/intravasation and regulates urokinase receptor (u-PAR) gene expression via Sp-transcription factors. Oncogene 26: 4550–4562.
Lin X, Parsels LA, Voeller DM, Allegra CJ, Maley GF, Maley F et al. (2000). Characterization of a cis-acting regulatory element in the protein coding region of thymidylate synthase mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28: 1381–1389.
Loh PG, Yang HS, Walsh MA, Wang Q, Wang X, Cheng Z et al. (2009). Structural basis for translational inhibition by the tumour suppressor Pdcd4. EMBO J 28: 274–285.
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, Klinge CM, Ramos KS, Colburn NH . (2008). MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene 27: 4373–4379.
Mink S, Kerber U, Klempnauer K-H . (1996). Interaction of C/EBPβ and v-Myb is required for synergistic activation of the mim-1 gene. Mol Cell Biol 16: 1316–1325.
Mudduluru G, Medved F, Grobholz R, Jost C, Gruber A, Leupold JH et al. (2007). Loss of programmed cell death 4 expression marks adenoma-carcinoma transition, correlates inversely with phosphorylated protein kinase B, and is an independent prognostic factor in resected colorectal cancer. Cancer 110: 1697–1707.
Nottrott S, Simard MJ, Richter JD . (2006). Human let-7a miRNA blocks protein production on actively translating polyribosomes. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13: 1108–1114.
Petersen CP, Bordeleau M-E, Pelletier J, Sharp PA . (2006). Short RNAs repress translation after initiation in mammalian cells. Mol Cell 21: 533–542.
Plachetka A, Chayka O, Wilczek C, Melnik S, Bonifer C, Klempnauer K-H . (2008). C/EBPβ induces chromatin opening at a cell-type-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol 28: 2102–2112.
Prechtel AT, Chemnitz J, Schirmer S, Ehlers C, Langbein-Detsch I, Stülke J et al. (2006). Expression of CD83 is regulated by HuR via a novel cis-active coding region element. J Biol Chem 281: 10912–10925.
Ramsay RG, Gonda TJ . (2008). Myb function in normal and cancer cells. Nat Rev Cancer 8: 523–534.
Schlichter U, Burk O, Worpenberg S, Klempnauer K-H . (2001a). The chicken Pdcd4 gene is regulated by v-Myb. Oncogene 20: 231–239.
Schlichter U, Kattmann D, Appl H, Miethe J, Brehmer-Fastnacht A, Klempnauer K-H . (2001b). Identification of the myb-inducible promoter of the chicken Pdcd4 gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1520: 99–104.
Shibahara K, Asano M, Ishida Y, Aoki T, Koike T, Honjo T. . (1995). Isolation of a novel mouse gene MA-3 that is induced upon programmed cell death. Gene 166: 297–301.
Singh P, Marikkannu R, Bitomsky N, Klempnauer K-H . (2009). Disruption of the Pdcd4 tumor suppressor gene in chicken DT40 cells reveals its role in the DNA-damage response. Oncogene 28: 3758–3764.
Sleeman JP . (1993). Xenopus A-myb is expressed during early spermatogenesis. Oncogene 8: 1931–1941.
Suzuki C, Garces RG, Edmonds KA, Hiller S, Hyberts SG, Marintchev A et al. (2008). PDCD4 inhibits translation initiation by binding to eIF4A using both its MA3 domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 3274–3279.
Waters LC, Strong SL, Ferlemann E, Oka O, Muskett FW, Veverka V et al. (2011). Structure of the tandem MA-3 region of Pdcd4 and characterization of its interactions with eIF4A and eIF4G: molecular mechanisms of a tumour suppressor. J Biol Chem 285: 17270–17280.
Waters LC, Veverka V, Böhm M, Schmedt T, Choong PT, Muskett FW et al. (2007). Structure of the C-terminal MA-3 domain of the tumour suppressor protein Pdcd4 and characterization of its interaction with eIF4A. Oncogene 26: 4941–4950.
Wedeken L, Ohnheiser J, Hirschi B, Wethkamp N, Klempnauer K-H . (2010). Association of tumor suppressor protein Pdcd4 with ribosomes is mediated by protein-protein and protein-RNA interactions. Genes Cancer 1: 293–301.
Yang HS, Cho MH, Zacowicz H, Hegamyer G, Sonenberg N, Colburn N . (2004). A novel function of the MA-3 domains in transformation and translation suppressor Pdcd4 is essential for its binding to eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A. Mol Cell Biol 24: 3894–3906.
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Komar AA, Zheng X, Merrick WC, Costes S et al. (2003a). The transformation suppressor Pdcd4 is a novel eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A binding protein that inhibits translation. Mol Cell Biol 23: 26–37.
Yang HS, Knies JL, Stark C, Colburn NH . (2003b). Pdcd4 suppresses tumor phenotype in JB6 cells by inhibiting AP-1 transactivation. Oncogene 22: 3712–3720.
Zhang H, Ozaki I, Mizuta T, Hamajima H, Yasutake T, Eguchi Y et al. (2006). Involvement of programmed cell death 4 in transforming growth factor-beta1-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 25: 6101–6112.
Zhang Y, Yang S, Liu M, Song C, Wu N, Ling P et al. (2010). Interaction between thymidylate synthase and its cognate mRNA in zebrafish embryos. PLos One 5: e10618.
Acknowledgements
We thank M Hentze and D Ostareck for providing plasmids. This work was supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe (10–1716), the Wilhelm-Sander-Stiftung (2004.088.1) and the Wellcome Trust. PS and LW were supported by the Graduate School of Chemistry (GSC-MS) at the University of Münster.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P., Wedeken, L., Waters, L. et al. Pdcd4 directly binds the coding region of c-myb mRNA and suppresses its translation. Oncogene 30, 4864–4873 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.202
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.202
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The molecular basis of translation initiation and its regulation in eukaryotes
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2024)
-
The brain targeted delivery of programmed cell death 4 specific siRNA protects mice from CRS-induced depressive behavior
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Programmed cell death 4 as an endogenous suppressor of BDNF translation is involved in stress-induced depression
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
PDCD4 controls the G1/S-phase transition in a telomerase-immortalized epithelial cell line and affects the expression level and translation of multiple mRNAs
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Cytoplasmic localization of programmed cell death 4 contributes to its anti-apoptotic function
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2018)