Abstract
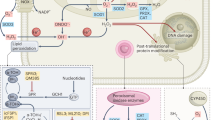
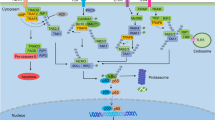
Elevated levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are found in most oncogenically transformed cells and are proposed to promote cellular transformation through mechanisms such as inhibition of phosphatases. BCR–ABL, the oncoprotein associated with the majority of chronic myeloid leukemias (CMLs), induces accumulation of intracellular ROS, causing enhanced signaling downstream of PI3K. Previously we have shown that the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) is activated by BCR–ABL expression and is required for BCR–ABL-mediated cellular transformation. Inhibition of IκB kinase (IKKβ) and NF-κB leads to cell death through an unknown mechanism. Here, we analyze the potential involvement of NF-κB in moderating BCR–ABL-induced ROS levels to protect from death. The data confirm that BCR–ABL promotes ROS and demonstrate that NF-κB prevents excessive levels. Inhibition of NF-κB leads to an increase in ROS levels and to cell death, which is at least partially controlled through ROS-induced c-Jun N-terminal kinase activity. The data demonstrate that one function for NF-κB in oncogenesis is the suppression of oncoprotein-induced ROS levels and that inhibition of NF-κB in some cancers, including CML, will increase ROS levels and promote cell death.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basseres DS, Baldwin AS . (2006). Nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibitor of kappaB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene 25: 6817–6830.
Benhar M, Engelberg D, Levitzki A . (2002). ROS, stress-activated kinases and stress signaling in cancer. EMBO Rep 3: 420–425.
Braun T, Carvalho G, Fabre C, Grosjean J, Fenaux P, Kroemer G . (2006). Targeting NF-kappaB in hematologic malignancies. Cell Death Differ 13: 748–758.
Chandra J, Tracy J, Loegering D, Flatten K, Verstovsek S, Beran M et al. (2006). Adaphostin-induced oxidative stress overcomes BCR/ABL mutation-dependent and -independent imatinib resistance. Blood 107: 2501–2506.
Cilloni D, Messa F, Arruga F, Defilippi I, Morotti A, Messa E et al. (2006). The NF-kappaB pathway blockade by the IKK inhibitor PS1145 can overcome imatinib resistance. Leukemia 20: 61–67.
Courtois G, Gilmore TD . (2006). Mutations in the NF-kappaB signaling pathway: implications for human disease. Oncogene 25: 6831–6843.
De Smaele E, Zazzeroni F, Papa S, Nguyen DU, Jin R, Jones J et al. (2001). Induction of gadd45beta by NF-kappaB downregulates pro-apoptotic JNK signalling. Nature 414: 308–313.
Dhanasekaran DN, Reddy EP . (2008). JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene 27: 6245–6251.
Diaz-Blanco E, Bruns I, Neumann F, Fischer JC, Graef T, Rosskopf M et al. (2007). Molecular signature of CD34(+) hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells of patients with CML in chronic phase. Leukemia 21: 494–504.
Duncan EA, Goetz CA, Stein SJ, Mayo KJ, Skaggs BJ, Ziegelbauer K et al. (2008). IkappaB kinase beta inhibition induces cell death in Imatinib-resistant and T315I Dasatinib-resistant BCR-ABL+ cells. Mol Cancer Ther 7: 391–397.
Felsher DW, Bishop JM . (1999). Transient excess of MYC activity can elicit genomic instability and tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 3940–3944.
Gupta S, Barrett T, Whitmarsh AJ, Cavanagh J, Sluss HK, Derijard B et al. (1996). Selective interaction of JNK protein kinase isoforms with transcription factors. EMBO J 15: 2760–2770.
Hamdane M, David-Cordonnier MH, D′Halluin JC . (1997). Activation of p65 NF-kappaB protein by p210BCR-ABL in a myeloid cell line. Oncogene 15: 2267–2275.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . (2004). Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 18: 2195–2224.
Hess P, Pihan G, Sawyers CL, Flavell RA, Davis RJ . (2002). Survival signaling mediated by c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase in transformed B lymphoblasts. Nat Genet 32: 201–205.
Hu MC, Lee DF, Xia W, Golfman LS, Ou-Yang F, Yang JY et al. (2004). IkappaB kinase promotes tumorigenesis through inhibition of forkhead FOXO3a. Cell 117: 225–237.
Iida T, Furuta A, Kawashima M, Nishida J, Nakabeppu Y, Iwaki T . (2001). Accumulation of 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine and increased expression of hMTH1 protein in brain tumors. Neuro Oncol 3: 73–81.
Irani K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Sollott SJ, Der CJ, Fearon ER et al. (1997). Mitogenic signaling mediated by oxidants in Ras-transformed fibroblasts. Science 275: 1649–1652.
Kamata H, Honda S, Maeda S, Chang L, Hirata H, Karin M . (2005). Reactive oxygen species promote TNFalpha-induced death and sustained JNK activation by inhibiting MAP kinase phosphatases. Cell 120: 649–661.
Kim JH, Chu SC, Gramlich JL, Pride YB, Babendreier E, Chauhan D et al. (2005). Activation of the PI3K/mTOR pathway by BCR-ABL contributes to increased production of reactive oxygen species. Blood 105: 1717–1723.
Lee DF, Kuo HP, Chen CT, Hsu JM, Chou CK, Wei Y et al. (2007). IKK beta suppression of TSC1 links inflammation and tumor angiogenesis via the mTOR pathway. Cell 130: 440–455.
Leppa S, Bohmann D . (1999). Diverse functions of JNK signaling and c-Jun in stress response and apoptosis. Oncogene 18: 6158–6162.
Mao X, Yu CR, Li WH, Li WX . (2008). Induction of apoptosis by shikonin through a ROS/JNK-mediated process in Bcr/Abl-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cells. Cell Res 18: 879–888.
Mitsushita J, Lambeth JD, Kamata T . (2004). The superoxide-generating oxidase Nox1 is functionally required for Ras oncogene transformation. Cancer Res 64: 3580–3585.
Naughton R, Quiney C, Turner SD, Cotter TG . (2009). Bcr-Abl-mediated redox regulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Leukemia 23: 1432–1440.
Pelicano H, Carney D, Huang P . (2004). ROS stress in cancer cells and therapeutic implications. Drug Resist Updat 7: 97–110.
Pham CG, Bubici C, Zazzeroni F, Papa S, Jones J, Alvarez K et al. (2004). Ferritin heavy chain upregulation by NF-kappaB inhibits TNFalpha-induced apoptosis by suppressing reactive oxygen species. Cell 119: 529–542.
Raitano AB, Halpern JR, Hambuch TM, Sawyers CL . (1995). The Bcr-Abl leukemia oncogene activates Jun kinase and requires Jun for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 11746–11750.
Reuther JY, Reuther GW, Cortez D, Pendergast AM, Baldwin Jr AS . (1998). A requirement for NF-kappaB activation in Bcr-Abl-mediated transformation. Genes Dev 12: 968–981.
Sakon S, Xue X, Takekawa M, Sasazuki T, Okazaki T, Kojima Y et al. (2003). NF-kappaB inhibits TNF-induced accumulation of ROS that mediate prolonged MAPK activation and necrotic cell death. EMBO J 22: 3898–3909.
Sattler M, Verma S, Shrikhande G, Byrne CH, Pride YB, Winkler T et al. (2000). The BCR/ABL tyrosine kinase induces production of reactive oxygen species in hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem 275: 24273–24278.
Sawyers CL . (1999). Chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 340: 1330–1340.
Schimmel M, Bauer G . (2002). Proapoptotic and redox state-related signaling of reactive oxygen species generated by transformed fibroblasts. Oncogene 21: 5886–5896.
Senthil K, Aranganathan S, Nalini N . (2004). Evidence of oxidative stress in the circulation of ovarian cancer patients. Clin Chim Acta 339: 27–32.
Shen HM, Liu ZG . (2006). JNK signaling pathway is a key modulator in cell death mediated by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Free Radic Biol Med 40: 928–939.
Suh YA, Arnold RS, Lassegue B, Shi J, Xu X, Sorescu D et al. (1999). Cell transformation by the superoxide-generating oxidase Nox1. Nature 401: 79–82.
Szatrowski TP, Nathan CF . (1991). Production of large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer Res 51: 794–798.
Tang F, Tang G, Xiang J, Dai Q, Rosner MR, Lin A . (2002). The absence of NF-kappaB-mediated inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation contributes to tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 22: 8571–8579.
Tang G, Minemoto Y, Dibling B, Purcell NH, Li Z, Karin M et al. (2001). Inhibition of JNK activation through NF-kappaB target genes. Nature 414: 313–317.
Toyokuni S, Okamoto K, Yodoi J, Hiai H . (1995). Persistent oxidative stress in cancer. FEBS Lett 358: 1–3.
Trachootham D, Alexandre J, Huang P . (2009). Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov 8: 579–591.
Trachootham D, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Demizu Y, Chen Z, Pelicano H et al. (2006). Selective killing of oncogenically transformed cells through a ROS-mediated mechanism by beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate. Cancer Cell 10: 241–252.
Vafa O, Wade M, Kern S, Beeche M, Pandita TK, Hampton GM et al. (2002). c-Myc can induce DNA damage, increase reactive oxygen species, and mitigate p53 function: a mechanism for oncogene-induced genetic instability. Mol Cell 9: 1031–1044.
Ventura JJ, Cogswell P, Flavell RA, Baldwin Jr AS, Davis RJ . (2004). JNK potentiates TNF-stimulated necrosis by increasing the production of cytotoxic reactive oxygen species. Genes Dev 18: 2905–2915.
Vogt PK . (2001). Jun, the oncoprotein. Oncogene 20: 2365–2377.
Weinberg F, Hamanaka R, Wheaton WW, Weinberg S, Joseph J, Lopez M et al. (2010). Mitochondrial metabolism and ROS generation are essential for Kras-mediated tumorigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 8788–8793.
Yu C, Minemoto Y, Zhang J, Liu J, Tang F, Bui TN, Xiang J, Lin A . (2004). JNK suppresses apoptosis via phosphorylation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2 family protein BAD. Mol Cell 13: 329–340.
Zhang H, Trachootham D, Lu W, Carew J, Giles FJ, Keating MJ et al. (2008). Effective killing of Gleevec-resistant CML cells with T315I mutation by a natural compound PEITC through redox-mediated mechanism. Leukemia 22: 1191–1199.
Zhou Y, Hileman EO, Plunkett W, Keating MJ, Huang P . (2003). Free radical stress in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and its role in cellular sensitivity to ROS-generating anticancer agents. Blood 101: 4098–4104.
Ziegelbauer K, Gantner F, Lukacs NW, Berlin A, Fuchikami K, Niki T et al. (2005). A selective novel low-molecular-weight inhibitor of IkappaB kinase-beta (IKK-beta) prevents pulmonary inflammation and shows broad anti-inflammatory activity. Br J Pharmacol 145: 178–192.
Acknowledgements
We thank Justina Chen for technical support and members of the Baldwin lab for advice and discussion. We acknowledge grant support from the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, from the NIH (CA73756 and CA75080), and from the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stein, S., Baldwin, A. NF-κB suppresses ROS levels in BCR–ABL+ cells to prevent activation of JNK and cell death. Oncogene 30, 4557–4566 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.156
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.156
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The potential role of hydrogen sulfide in cancer cell apoptosis
Cell Death Discovery (2024)
-
Investigation on the interaction behavior of afatinib, dasatinib, and imatinib docked to the BCR-ABL protein
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2021)
-
Ruxolitinib induces autophagy in chronic myeloid leukemia cells
Tumor Biology (2016)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: MiR-362-5p promotes the malignancy of chronic myelocytic leukaemia via down-regulation of GADD45α
Molecular Cancer (2015)