Abstract
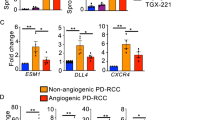
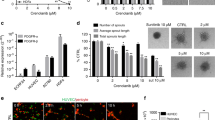
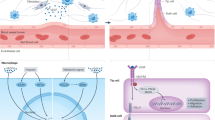
The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib has been approved for first-line treatment of patients with metastatic renal cancer and is currently being trialled in other cancers. However, the effectiveness of this anti-angiogenic agent is limited by the presence of innate and acquired drug resistance. By screening a panel of candidate growth factors we identified fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) as a potent regulator of endothelial cell sensitivity to sunitinib. We show that FGF2 supports endothelial proliferation and de novo tubule formation in the presence of sunitinib and that FGF2 can suppress sunitinib-induced retraction of tubules. Importantly, these effects of FGF2 were ablated by PD173074, a small molecule inhibitor of FGF receptor signalling. We also show that FGF2 can stimulate pro-angiogenic signalling pathways in endothelial cells despite the presence of sunitinib. Finally, analysis of clinical renal-cancer samples demonstrates that a large proportion of renal cancers strongly express FGF2. We suggest that therapeutic strategies designed to simultaneously target both VEGF and FGF2 signalling may prove more efficacious than sunitinib in renal cancer patients whose tumours express FGF2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams TJ, Lee LB, Murray LJ, Pryer NK, Cherrington JM . (2003). SU11248 inhibits KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta in preclinical models of human small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2: 471–478.
Bergers G, Song S, Meyer-Morse N, Bergsland E, Hanahan D . (2003). Benefits of targeting both pericytes and endothelial cells in the tumor vasculature with kinase inhibitors. J Clin Invest 111: 1287–1295.
Bergers G, Hanahan D . (2008). Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 8: 592–603.
Britten CD, Kabbinavar F, Hecht JR, Bello CL, Li J, Baum C et al. (2008). A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of sunitinib administered daily for 2 weeks, followed by a 1-week off period. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 61: 515–524.
Bryant DM, Stow JL . (2005). Nuclear translocation of cell-surface receptors: lessons from fibroblast growth factor. Traffic 6: 947–954.
Casanovas O, Hicklin DJ, Bergers G, Hanahan D . (2005). Drug resistance by evasion of antiangiogenic targeting of VEGF signaling in late-stage pancreatic islet tumors. Cancer Cell 8: 299–309.
Crawford Y, Kasman I, Yu L, Zhong C, Wu X, Modrusan Z et al. (2009). PDGF-C mediates the angiogenic and tumorigenic properties of fibroblasts associated with tumors refractory to anti-VEGF treatment. Cancer Cell 15: 21–34.
Cross MJ, Claesson-Welsh L . (2001). FGF and VEGF function in angiogenesis: signalling pathways, biological responses and therapeutic inhibition. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22: 201–207.
Ebos JM, Lee CR, Kerbel RS . (2009). Tumor and host-mediated pathways of resistance and disease progression in response to antiangiogenic therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15: 5020–5025.
Eguchi J, Nomata K, Kanda S, Igawa T, Taide M, Koga S et al. (1992). Gene expression and immunohistochemical localization of basic fibroblast growth factor in renal cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 183: 937–944.
Eliceiri BP, Klemke R, Stromblad S, Cheresh DA . (1998). Integrin alphavbeta3 requirement for sustained mitogen-activated protein kinase activity during angiogenesis. J Cell Biol 140: 1255–1263.
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ . (2008). VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer 8: 579–591.
Faivre S, Delbaldo C, Vera K, Robert C, Lozahic S, Lassau N et al. (2006). Safety, pharmacokinetic, and antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel oral multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol 24: 25–35.
Faivre S, Demetri G, Sargent W, Raymond E . (2007). Molecular basis for sunitinib efficacy and future clinical development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6: 734–745.
Ferrara N . (2002). VEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 795–803.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J . (2003). The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9: 669–676.
Ferrara N, Hillan KJ, Gerber HP, Novotny W . (2004). Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3: 391–400.
Ferrara N, Kerbel RS . (2005). Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 438: 967–974.
Fischer C, Jonckx B, Mazzone M, Zacchigna S, Loges S, Pattarini L et al. (2007). Anti-PlGF inhibits growth of VEGF(R)-inhibitor-resistant tumors without affecting healthy vessels. Cell 131: 463–475.
Fukata S, Inoue K, Kamada M, Kawada C, Furihata M, Ohtsuki Y et al. (2005). Levels of angiogenesis and expression of angiogenesis-related genes are prognostic for organ-specific metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 103: 931–942.
Giavazzi R, Sennino B, Coltrini D, Garofalo A, Dossi R, Ronca R et al. (2003). Distinct role of fibroblast growth factor-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor on tumor growth and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 162: 1913–1926.
Gualandris A, Rusnati M, Belleri M, Nelli EE, Bastaki M, Molinari-Tosatti MP et al. (1996). Basic fibroblast growth factor overexpression in endothelial cells: an autocrine mechanism for angiogenesis and angioproliferative diseases. Cell Growth Differ 7: 147–160.
Hanahan D, Folkman J . (1996). Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86: 353–364.
Huang D, Ding Y, Li Y, Luo WM, Zhang ZF, Snider J et al. (2010a). Sunitinib acts primarily on tumor endothelium rather than tumor cells to inhibit the growth of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 70: 1053–1062.
Huang D, Ding Y, Zhou M, Rini BI, Petillo D, Qian CN et al. (2010b). Interleukin-8 mediates resistance to antiangiogenic agent sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 70: 1063–1071.
Joy A, Moffett J, Neary K, Mordechai E, Stachowiak EK, Coons S et al. (1997). Nuclear accumulation of FGF-2 is associated with proliferation of human astrocytes and glioma cells. Oncogene 14: 171–183.
Karaman MW, Herrgard S, Treiber DK, Gallant P, Atteridge CE, Campbell BT et al. (2008). A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol 26: 127–132.
Kerbel R, Folkman J . (2002). Clinical translation of angiogenesis inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 727–739.
Kerbel RS . (2008). Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 358: 2039–2049.
Mancuso MR, Davis R, Norberg SM, O′Brien S, Sennino B, Nakahara T et al. (2006). Rapid vascular regrowth in tumors after reversal of VEGF inhibition. J Clin Invest 116: 2610–2621.
Mavria G, Vercoulen Y, Yeo M, Paterson H, Karasarides M, Marais R et al. (2006). ERK-MAPK signaling opposes Rho-kinase to promote endothelial cell survival and sprouting during angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 9: 33–44.
Mendel DB, Laird AD, Xin X, Louie SG, Christensen JG, Li G et al. (2003). In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin Cancer Res 9: 327–337.
Meyer RD, Latz C, Rahimi N . (2003). Recruitment and activation of phospholipase Cgamma1 by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 are required for tubulogenesis and differentiation of endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 278: 16347–16355.
Mohammadi M, Froum S, Hamby JM, Schroeder MC, Panek RL, Lu GH et al. (1998). Crystal structure of an angiogenesis inhibitor bound to the FGF receptor tyrosine kinase domain. Embo J 17: 5896–5904.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O et al. (2007). Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356: 115–124.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Oudard S et al. (2009). Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 27: 3584–3590.
Nakatsu MN, Hughes CC . (2008). An optimized three-dimensional in vitro model for the analysis of angiogenesis. Methods Enzymol 443: 65–82.
Nanus DM, Schmitz-Drager BJ, Motzer RJ, Lee AC, Vlamis V, Cordon-Cardo C et al. (1993). Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in primary human renal tumors: correlation with poor survival. J Natl Cancer Inst 85: 1597–1599.
O'Farrell AM, Abrams TJ, Yuen HA, Ngai TJ, Louie SG, Yee KW et al. (2003). SU11248 is a novel FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potent activity in vitro and in vivo. Blood 101: 3597–3605.
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L . (2006). VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 359–371.
Pardo OE, Latigo J, Jeffery RE, Nye E, Poulsom R, Spencer-Dene B et al. (2009). The fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor PD173074 blocks small cell lung cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 69: 8645–8651.
Pepper MS, Ferrara N, Orci L, Montesano R . (1992). Potent synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in the induction of angiogenesis in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 189: 824–831.
Pintucci G, Moscatelli D, Saponara F, Biernacki PR, Baumann FG, Bizekis C et al. (2002). Lack of ERK activation and cell migration in FGF-2-deficient endothelial cells. FASEB J 16: 598–600.
Presta M, Tiberio L, Rusnati M, Dell′Era P, Ragnotti G . (1991). Basic fibroblast growth factor requires a long-lasting activation of protein kinase C to induce cell proliferation in transformed fetal bovine aortic endothelial cells. Cell Regul 2: 719–726.
Presta M, Dell′Era P, Mitola S, Moroni E, Ronca R, Rusnati M . (2005). Fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast growth factor receptor system in angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16: 159–178.
Ravaud A, Hawkins R, Gardner JP, von der Maase H, Zantl N, Harper P et al. (2008). Lapatinib versus hormone therapy in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: a randomized phase III clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 26: 2285–2291.
Relf M, LeJeune S, Scott PA, Fox S, Smith K, Leek R et al. (1997). Expression of the angiogenic factors vascular endothelial cell growth factor, acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor, tumor growth factor beta-1, platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor, placenta growth factor, and pleiotrophin in human primary breast cancer and its relation to angiogenesis. Cancer Res 57: 963–969.
Rini BI, Atkins MB . (2009). Resistance to targeted therapy in renal-cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol 10: 992–1000.
Schweigerer L, Neufeld G, Friedman J, Abraham JA, Fiddes JC, Gospodarowicz D . (1987). Capillary endothelial cells express basic fibroblast growth factor, a mitogen that promotes their own growth. Nature 325: 257–259.
Slaton JW, Inoue K, Perrotte P, El-Naggar AK, Swanson DA, Fidler IJ et al. (2001). Expression levels of genes that regulate metastasis and angiogenesis correlate with advanced pathological stage of renal cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol 158: 735–743.
Turner N, Grose R . (2010). Fibroblast growth factor signalling: from development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10: 116–129.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Alan Ashworth, Clare Isacke and Nicholas Turner for critical comments on the paper and Breakthrough Breast Cancer for research funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Thomas Powles is the recipient of an educational research grant from Pfizer Global Pharmaceuticals. The other authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welti, J., Gourlaouen, M., Powles, T. et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2 regulates endothelial cell sensitivity to sunitinib. Oncogene 30, 1183–1193 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.503
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.503
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Candidate biomarkers for treatment benefit from sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma using mass spectrometry-based (phospho)proteomics
Clinical Proteomics (2023)
-
VEGF-B prevents excessive angiogenesis by inhibiting FGF2/FGFR1 pathway
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Cancer combination therapies by angiogenesis inhibitors; a comprehensive review
Cell Communication and Signaling (2022)
-
Capillary morphogenesis gene 2 (CMG2) mediates growth factor-induced angiogenesis by regulating endothelial cell chemotaxis
Angiogenesis (2022)
-
Metastasis-associated fibroblasts promote angiogenesis in metastasized pancreatic cancer via the CXCL8 and the CCL2 axes
Scientific Reports (2020)