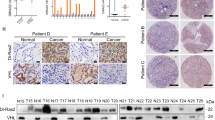
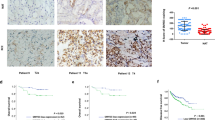
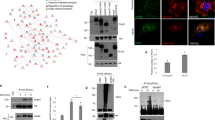
Abstract
von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor loss is associated with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) pathogenesis. Meanwhile, aberrant activation of the insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) signaling has been implicated in the development of highly invasive metastatic RCC. However, the link between VHL inactivation and RCC invasiveness is still unexplored. Here, we show that the receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) is a novel pVHL-interacting protein. pVHL competes with IGF-I receptor (IGF-IR) for binding to RACK1 thus potentially modulating the downstream IGF-I signal pathway. Upon IGF-I stimulation, pVHL-deficient RCC cells exhibit increased RACK1/IGF-IR binding and increased IGF-IR tyrosine kinase activity. pVHL-deficient RCC cells also demonstrate elevated PI3K/Akt signaling and matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity that culminates in enhanced cellular invasiveness, which can be partially suppressed by RACK1 small interfering RNA. Domain mapping analysis showed that the pVHL α-domain and the RACK1 WD 6–7 domains are critical for the interaction. Additionally, the RACK1 expression level is not regulated by pVHL expression status, suggesting that pVHL modifies RACK1 functions independent of the VHL/elongin E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Our data indicate that RACK1 serves as a direct mediator between loss of pVHL function and enhanced IGF-IR signaling pathway in RCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Alberghini A, Recalcati S, Tacchini L, Santambrogio P, Campanella A, Cairo G . (2005). Loss of the von Hippel Lindau tumor suppressor disrupts iron homeostasis in renal carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 280: 30120–30128.
Berns H, Humar R, Hengerer B, Kiefer FN, Battegay EJ . (2000). RACK1 is up-regulated in angiogenesis and human carcinomas. FASEB J 14: 2549–2558.
Brader S, Eccles SA . (2004). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling pathways in tumor progression, invasion and angiogenesis. Tumori 90: 2–8.
Brodt P, Fallavollita L, Khatib AM, Samani AA, Zhang D . (2001). Cooperative regulation of the invasive and metastatic phenotypes by different domains of the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor beta subunit. J Biol Chem 276: 33608–33615.
Brodt P, Samani A, Navab R . (2000). Inhibition of the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor expression and signaling: novel strategies for antimetastatic therapy. Biochem Pharmacol 60: 1101–1107.
Chang BY, Harte RA, Cartwright CA . (2002). RACK1: a novel substrate for the Src protein-tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 21: 7619–7629.
Cohen HT, McGovern FJ . (2005). Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 353: 2477–2490.
Datta K, Nambudripad R, Pal S, Zhou M, Cohen HT, Mukhopadhyay D . (2000). Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-I-mediated cell signaling by the von Hippel-Lindau gene product in renal cancer. J Biol Chem 275: 20700–20706.
Dunn SE, Ehrlich M, Sharp NJ, Reiss K, Solomon G, Hawkins R et al. (1998). A dominant negative mutant of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibits the adhesion, invasion, and metastasis of breast cancer. Cancer Res 58: 3353–3361.
Dupont J, Pierre A, Froment P, Moreau C . (2003). The insulin-like growth factor axis in cell cycle progression. Horm Metab Res 35: 740–750, -Dec.
Foster K, Prowse A, van den BA, Fleming S, Hulsbeek MM, Crossey PA et al. (1994). Somatic mutations of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumour suppressor gene in non-familial clear cell renal carcinoma. Hum Mol Genet 3: 2169–2173.
Gnarra JR, Tory K, Weng Y, Schmidt L, Wei MH, Li H et al. (1994). Mutations of the VHL tumour suppressor gene in renal carcinoma. Nat Genet 7: 85–90.
Gnarra JR, Zhou S, Merrill MJ, Wagner JR, Krumm A, Papavassiliou E et al. (1996). Post-transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA by the product of the VHL tumor suppressor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 10589–10594.
Hansen WJ, Ohh M, Moslehi J, Kondo K, Kaelin WG, Welch WJ . (2002). Diverse effects of mutations in exon II of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor gene on the interaction of pVHL with the cytosolic chaperonin and pVHL-dependent ubiquitin ligase activity. Mol Cell Biol 22: 1947–1960.
Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A, Tiwari RC, Ghafoor A et al. (2005). Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin 55: 10–30.
Kibel A, Iliopoulos O, DeCaprio JA, Kaelin Jr WG . (1995). Binding of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein to Elongin B and C. Science 269: 1444–1446.
Kiely PA, Leahy M, O'Gorman D, O'Connor R . (2005). RACK1-mediated integration of adhesion and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) signaling and cell migration are defective in cells expressing an IGF-I receptor mutated at tyrosines 1250 and 1251. J Biol Chem 280: 7624–7633.
Koochekpour S, Jeffers M, Wang PH, Gong C, Taylor GA, Roessler LM et al. (1999). The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene inhibits hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-induced invasion and branching morphogenesis in renal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 19: 5902–5912.
Kugler A, Hemmerlein B, Thelen P, Kallerhoff M, Radzun HJ, Ringert RH . (1998). Expression of metalloproteinase 2 and 9 and their inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 160: 1914–1918.
Kugler A . (1999). Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Anticancer Res 19: 1589–1592.
Li Z, Wang D, Na X, Schoen SR, Messing EM, Wu G . (2002). Identification of a deubiquitinating enzyme subfamily as substrates of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor. Bioche Biophys Res Commun 294: 700–709.
Liliental J, Chang DD . (1998). Rack1, a receptor for activated protein kinase C, interacts with integrin beta subunit. J Biol Chem 273: 2379–2383.
Liu YV, Baek JH, Zhang H, Diez R, Cole RN, Semenza GL . (2007). RACK1 competes with HSP90 for binding to HIF-1alpha and is required for O(2)-independent and HSP90 inhibitor-induced degradation of HIF-1alpha. Mol Cell 25: 207–217.
Long L, Navab R, Brodt P . (1998). Regulation of the Mr 72,000 type IV collagenase by the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 58: 3243–3247.
Loughran G, Huigsloot M, Kiely PA, Smith LM, Floyd S, Ayllon V et al. (2005). Gene expression profiles in cells transformed by overexpression of the IGF-I receptor. Oncogene 24: 6185–6193.
Macaulay VM . (1992). Insulin-like growth factors and cancer. Br J Cancer 65: 311–320.
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME et al. (1999). The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399: 271–275.
McCahill A, Warwicker J, Bolger GB, Houslay MD, Yarwood SJ . (2002). The RACK1 scaffold protein: a dynamic cog in cell response mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol 62: 1261–1273.
Min Y, Adachi Y, Yamamoto H, Imsumran A, Arimura Y, Endo T et al. (2005). Insulin-like growth factor I receptor blockade enhances chemotherapy and radiation responses and inhibits tumour growth in human gastric cancer xenografts. Gut 54: 591–600.
Mochly-Rosen D, Smith BL, Chen CH, Disatnik MH, Ron D . (1995). Interaction of protein kinase C with RACK1, a receptor for activated C-kinase: a role in beta protein kinase C mediated signal transduction. Biochem Soc Trans 23: 596–600.
Motzer RJ, Russo P . (2000). Systemic therapy for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 163: 408–417.
Na X, Duan HO, Messing EM, Schoen SR, Ryan CK, di Sant'Agnese PA et al. (2003). Identification of the RNA polymerase II subunit hsRPB7 as a novel target of the von Hippel-Lindau protein. EMBO J 22: 4249–4259.
O'Connor R . (2003). Regulation of IGF-I receptor signaling in tumor cells. Horm Metab Res 35: 771–777.
Ohh M, Park CW, Ivan M, Hoffman MA, Kim TY, Huang LE et al. (2000). Ubiquitination of hypoxia-inducible factor requires direct binding to the beta-domain of the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Nat Cell Biol 2: 423–427.
Ohh M, Yauch RL, Lonergan KM, Whaley JM, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Louis DN et al. (1998). The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein is required for proper assembly of an extracellular fibronectin matrix. Mol Cell 1: 959–968.
Pause A, Lee S, Worrell RA, Chen DY, Burgess WH, Linehan WM et al. (1997). The von Hippel-Lindau tumor-suppressor gene product forms a stable complex with human CUL-2, a member of the Cdc53 family of proteins. Pro Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 2156–2161.
Rajala RV, McClellan ME, Chan MD, Tsiokas L, Anderson RE . (2004). Interaction of the retinal insulin receptor beta-subunit with the p85 subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Biochemistry 43: 5637–5650.
Rodriguez MM, Ron D, Touhara K, Chen CH, Mochly-Rosen D . (1999). RACK1, a protein kinase C anchoring protein, coordinates the binding of activated protein kinase C and select pleckstrin homology domains in vitro. Biochemistry 38: 13787–13794.
Rosendahl A, Forsberg G . (2004). Influence of IGF-IR stimulation or blockade on proliferation of human renal cell carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol 25: 1327–1336.
Schips L, Zigeuner R, Ratschek M, Rehak P, Ruschoff J, Langner C . (2004). Analysis of insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 122: 931–937.
Sekharam M, Nasir A, Kaiser HE, Coppola D . (2003). Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor activates c-SRC and modifies transformation and motility of colon cancer in vitro. Anticancer Res 23: 1517–1524.
Shaw LM . (2001). Identification of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) and IRS-2 as signaling intermediates in the alpha6beta4 integrin-dependent activation of phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and promotion of invasion. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5082–5093.
Stawowy P, Kallisch H, Kilimnik A, Margeta C, Seidah NG, Chretien M et al. (2004). Proprotein convertases regulate insulin-like growth factor 1-induced membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in VSMCs via endoproteolytic activation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321: 531–538.
Steele MR, McCahill A, Thompson DS, MacKenzie C, Isaacs NW, Houslay MD et al. (2001). Identification of a surface on the beta-propeller protein RACK1 that interacts with the cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D5. Cell Signal 13: 507–513.
Tanno S, Tanno S, Mitsuuchi Y, Altomare DA, Xiao GH, Testa JR . (2001). AKT activation up-regulates insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression and promotes invasiveness of human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 61: 589–593.
Wang J, Gigliotti F, Bhagwat SP, Maggirwar SB, Wright TW . (2007). Pneumocystis stimulates MCP-1 production by alveolar epithelial cells through a JNK-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292: L1495–L1505.
Wang J, Gigliotti F, Maggirwar S, Johnston C, Finkelstein JN, Wright TW . (2005a). Pneumocystis carinii activates the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in alveolar epithelial cells. Infect Immun 73: 2766–2777.
Wang Y, Hailey J, Williams D, Wang Y, Lipari P, Malkowski M et al. (2005b). Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) signaling and tumor cell growth by a fully human neutralizing anti-IGF-IR antibody. Mol Cancer Ther 4: 1214–1221.
Yoon A, Hurta RA . (2001). Insulin like growth factor-1 selectively regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in malignant H-ras transformed cells. Mol Cell Biochem 223: 1–6.
Zagzag D, Krishnamachary B, Yee H, Okuyama H, Chiriboga L, Ali MA et al. (2005). Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha and CXCR4 expression in hemangioblastoma and clear cell-renal cell carcinoma: von Hippel-Lindau loss-of-function induces expression of a ligand and its receptor. Cancer Res 65: 6178–6188.
Zhang W, Zong CS, Hermanto U, Lopez-Bergami P, Ronai Z, Wang LH . (2006). RACK1 recruits STAT3 specifically to insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors for activation, which is important for regulating anchorage-independent growth. Mol Cell Biol 26: 413–424.
Zhou MI, Wang H, Foy RL, Ross JJ, Cohen HT . (2004). Tumor suppressor von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) stabilization of Jade-1 protein occurs through plant homeodomains and is VHL mutation dependent. Cancer Res 64: 1278–1286.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Patrick H Maxwell and Dr William G Kaelin Jr for their generous gifts of the RCC stable cell lines. We also thank Christopher R Silvers for his technical support. Funding: This work was supported in part by the James P Wilmot Cancer Center grant to X He.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, X., Wang, J., Messing, E. et al. Regulation of receptor for activated C kinase 1 protein by the von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor in IGF-I-induced renal carcinoma cell invasiveness. Oncogene 30, 535–547 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.427
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.427
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Insulin and insulin-like growth factors act as renal cell cancer intratumoral regulators
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2019)
-
RACK1 Silencing Induces Cell Apoptosis and Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma MHCC97-H Cells
Pathology & Oncology Research (2018)
-
The important role of the receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression
Journal of Translational Medicine (2016)
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling in renal cell carcinoma
BMC Cancer (2016)
-
RACK1, a versatile hub in cancer
Oncogene (2015)