Abstract
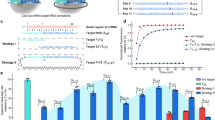
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A), also known as p21Cip1/Waf1, is a master downstream effector of tumor suppressors. In this study, we experimentally demonstrate through a high-throughput luciferase reporter screen that p21Cip1/Waf1 can be directly targeted by nearly 28 microRNAs (miRNAs). The results were further confirmed by a series of mutational analyses and luciferase reporter assays. These 28 miRNAs can substantially inhibit p21Cip1/Waf1 expression, predominantly at translational level. Many of these miRNAs were upregulated in cancers and might serve as modulators of oncogenesis. Furthermore, 8 of these 28 p21-regulating miRNAs are located in the chromosome 19 miRNA cluster, the largest miRNA gene cluster in humans, and they can clearly promote cell proliferation and cell-cycle progression in choriocarcinoma cells. In conclusion, our screening strategy provides an alternative approach to uncovering miRNA modulators of an individual mRNA, and it has identified multiple miRNAs that can suppress p21Cip1/Waf1 expression by directly targeting its 3′ untranslated region.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas T, Dutta A . (2009). p21 in cancer: intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat Rev Cancer 9: 400–414.
Ambros V . (2004). The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431: 350–355.
Bartel DP . (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297.
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O et al. (2005). Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet 37: 766–770.
Bortolin-Cavaille ML, Dance M, Weber M, Cavaille J . (2009). C19MC microRNAs are processed from introns of large Pol-II, non-protein-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res 37: 3464–3473.
Gartel AL, Tyner AL . (1999). Transcriptional regulation of the p21((WAF1/CIP1)) gene. Exp Cell Res 246: 280–289.
Gottardo F, Liu CG, Ferracin M, Calin GA, Fassan M, Bassi P et al. (2007). Micro-RNA profiling in kidney and bladder cancers. Urol Oncol 25: 387–392.
Guled M, Lahti L, Lindholm PM, Salmenkivi K, Bagwan I, Nicholson AG et al. (2009). CDKN2A, NF2, and JUN are dysregulated among other genes by miRNAs in malignant mesothelioma-A miRNA microarray analysis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 48: 615–623.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K, Elledge SJ . (1993). The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell 75: 805–816.
Hausser J, Berninger P, Rodak C, Jantscher Y, Wirth S, Zavolan M . (2009). MirZ: an integrated microRNA expression atlas and target prediction resource. Nucleic Acids Res 37: 266–W272.
Ivanovska I, Ball AS, Diaz RL, Magnus JF, Kibukawa M, Schelter JM et al. (2008). MicroRNAs in the miR-106b family regulate p21/CDKN1A and promote cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol 28: 2167–2174.
Jongen-Lavrencic M, Sun SM, Dijkstra MK, Valk PJ, Lowenberg B . (2008). MicroRNA expression profiling in relation to the genetic heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 111: 5078–5085.
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ et al. (2005). Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37: 495–500.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP . (2005). Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120: 15–20.
Lionetti M, Biasiolo M, Agnelli L, Todoerti K, Mosca L, Fabris S et al. (2009). Identification of microRNA expression patterns and definition of a microRNA/mRNA regulatory network in distinct molecular groups of multiple myeloma. Blood 114: e20–e26.
Lv K, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Wang K, Jia Y, Sun S . (2008). Allele-specific targeting of hsa-miR-657 to human IGF2R creates a potential mechanism underlying the association of ACAA-insertion/deletion polymorphism with type 2 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374: 101–105.
Martin-Caballero J, Flores JM, Garcia-Palencia P, Serrano M . (2001). Tumor susceptibility of p21(Waf1/Cip1)-deficient mice. Cancer Res 61: 6234–6238.
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, Shah MH, Nicoloso MS, de Martino I et al. (2008). E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell 13: 272–286.
Topley GI, Okuyama R, Gonzales JG, Conti C, Dotto GP . (1999). p21(WAF1/Cip1) functions as a suppressor of malignant skin tumor formation and a determinant of keratinocyte stem-cell potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 9089–9094.
van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Qi X, Richardson JA, Hill J, Olson EN . (2007). Control of stress-dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a microRNA. Science 316: 575–579.
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R et al. (2006). A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell 124: 1169–1181.
Wong TS, Liu XB, Wong BY, Ng RW, Yuen AP, Wei WI . (2008). Mature miR-184 as potential oncogenic microRNA of squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. Clin Cancer Res 14: 2588–2592.
Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, Casso D, Kobayashi R, Beach D . (1993). p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature 366: 701–704.
Acknowledgements
We are most grateful for Dr T Didier's gifts of the pWPXL, psPAX2 and pMD2.G lentivirus plasmids. This work was supported by grants from the Science & Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (07DJ14006), the Ministry of Health of China (2008ZX10002-017), the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of China (2007-170) and the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (200802480076).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Huang, S., Ding, J. et al. Multiple microRNAs modulate p21Cip1/Waf1 expression by directly targeting its 3′ untranslated region. Oncogene 29, 2302–2308 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.34
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.34
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Phenome-wide association study on miRNA-related sequence variants: the UK Biobank
Human Genomics (2023)
-
Discerning the Prospects of miRNAs as a Multi-Target Therapeutic and Diagnostic for Alzheimer’s Disease
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
The microRNA cluster C19MC confers differentiation potential into trophoblast lineages upon human pluripotent stem cells
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Role of MicroRNAs, Aptamers in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegenerative Disorders
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
Differential microRNA expression profile in blood of children with Down syndrome suggests a role in immunological dysfunction
Human Cell (2022)