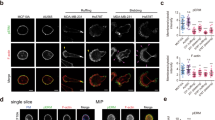
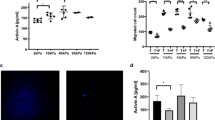
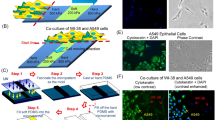
Abstract
Microenvironmental clues are critical to cell behavior. One of the key elements of migration is the generation and response to forces. Up to now, there is no definitive concept on how the generation and responses to cellular forces influence cancer-cell behavior. Here, we show that expression of receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase alpha (RPTPα) in human SW480 colon cancer cells sets a threshold for the response to matrix forces by changing cellular contractility. This can be explained as an RPTPα-mediated increase in contractility with a consecutive increase in number and size of adhesion sites and stress fibers. These effects are mediated through myosin light chain kinase and largely independent of Rho/Rho-kinase (ROCK) signaling. In addition, we report that RPTPα influences spreading on low-rigidity surfaces, binding of collagen-coated beads and expression of RPTPα is required for invasion into the chorioallantoic membrane. These data suggest that force-responsive proteins such as RPTPα can influence cancer-cell behavior and identify potential targets for cancer therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAM:
-
chorioallantoic membrane
- CSK:
-
C-terminal Src kinase
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- FC:
-
focal contact
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- MLCK:
-
myosin light chain kinase
- MLC:
-
myosin light chain
- MYPT1:
-
myosin phosphatase target subunit isoform 1
- ROCK:
-
Rho kinase
- RPTPα:
-
receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase alpha
- SFK:
-
Src family kinases
- TMA:
-
Tissue micro-array
- YFP:
-
yellow fluorescent protein
References
Ardini E, Agresti R, Tagliabue E, Greco M, Aiello P, Yang LT et al. (2000). Expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha (RPTPalpha) in human breast cancer correlates with low tumor grade, and inhibits tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 19: 4979–4987.
Balaban NQ, Schwarz US, Riveline D, Goichberg P, Tzur G, Sabanay I et al. (2001). Force and focal adhesion assembly: a close relationship studied using elastic micropatterned substrates. Nat Cell Biol 3: 466–472.
Benoliel AM, Pirro N, Marin V, Consentino B, Pierres A, Vitte J et al. (2003). Correlation between invasiveness of colorectal tumor cells and adhesive potential under flow. Anticancer Res 23: 4891–4896.
Berndt A, Luo X, Bohmer FD, Kosmehl H . (1999). Expression of the transmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase RPTPalpha in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Histochem Cell Biol 111: 399–403.
Bodrikov V, Leshchyns'ka I, Sytnyk V, Overvoorde J, den Hertog J, Schachner M . (2005). RPTPalpha is essential for NCAM-mediated p59fyn activation and neurite elongation. J Cell Biol 168: 127–139.
Choquet D, Felsenfeld DP, Sheetz MP . (1997). Extracellular matrix rigidity causes strengthening of integrin-cytoskeleton linkages. Cell 88: 39–48.
den Hertog J, Pals CE, Peppelenbosch MP, Tertoolen LG, de Laat SW, Kruijer W . (1993). Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha activates pp60c-src and is involved in neuronal differentiation. EMBO J 12: 3789–3798.
Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE . (2006). Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126: 677–689.
Han B, Bai XH, Lodyga M, Xu J, Yang BB, Keshavjee S et al. (2004). Conversion of mechanical force into biochemical signaling. J Biol Chem 279: 54793–54801.
Harder KW, Moller NP, Peacock JW, Jirik FR . (1998). Protein-tyrosine phosphatase alpha regulates Src family kinases and alters cell-substratum adhesion. J Biol Chem 273: 31890–31900.
Harris AK, Stopak D, Wild P . (1981). Fibroblast traction as a mechanism for collagen morphogenesis. Nature 290: 249–251.
Ingber DE . (2003). Mechanobiology and diseases of mechanotransduction. Ann Med 35: 564–577.
Jiang G, Huang AH, Cai Y, Tanase M, Sheetz MP . (2006). Rigidity sensing at the leading edge through alphavbeta3 integrins and RPTPalpha. Biophys J 90: 1804–1809.
Kostic A, Sheetz MP . (2006). Fibronectin rigidity response through Fyn and p130Cas recruitment to the leading edge. Mol Biol Cell 17: 2684–2695.
Kunzi-Rapp K, Genze F, Kufer R, Reich E, Hautmann RE, Gschwend JE . (2001). Chorioallantoic membrane assay: vascularized 3-dimensional cell culture system for human prostate cancer cells as an animal substitute model. J Urol 166: 1502–1507.
Lee W, Sodek J, McCulloch CA . (1996). Role of integrins in regulation of collagen phagocytosis by human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol 168: 695–704.
Munevar S, Wang Y, Dembo M . (2001). Traction force microscopy of migrating normal and H-ras transformed 3T3 fibroblasts. Biophys J 80: 1744–1757.
Paszek MJ, Zahir N, Johnson KR, Lakins JN, Rozenberg GI, Gefen A et al. (2005). Tensional homeostasis and the malignant phenotype. Cancer Cell 8: 241–254.
Petrone A, Sap J . (2000). Emerging issues in receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase function: lifting fog or simply shifting? J Cell Sci 113: 2345–2354.
Sahai E, Marshall CJ . (2002). ROCK and Dia have opposing effects on adherens junctions downstream of Rho. Nat Cell Biol 4: 408–415.
Sawada Y, Tamada M, Dubin-Thaler BJ, Cherniavskaya O, Sakai R, Tanaka S et al. (2006). Force sensing by mechanical extension of the Src family kinase substrate p130Cas. Cell 127: 1015–1026.
Su J, Muranjan M, Sap J . (1999). Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha activates Src-family kinases and controls integrin-mediated responses in fibroblasts. Curr Biol 9: 505–511.
Tabiti K, Smith DR, Goh HS, Pallen CJ . (1995). Increased mRNA expression of the receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha in late stage colon carcinomas. Cancer Lett 93: 239–248.
Thamilselvan V, Basson MD . (2004). Pressure activates colon cancer cell adhesion by inside-out focal adhesion complex and actin cytoskeletal signaling. Gastroenterology 126: 8–18.
Totsukawa G, Wu Y, Sasaki Y, Hartshorne DJ, Yamakita Y, Yamashiro S et al. (2004). Distinct roles of MLCK and ROCK in the regulation of membrane protrusions and focal adhesion dynamics during cell migration of fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 164: 427–439.
von Wichert G, Jiang G, Kostic A, DeVos K, Sap J, Sheetz MP . (2003). RPTP-alpha acts as a transducer of mechanical force on alphav/beta3-integrin-cytoskeleton linkages. J Cell Biol 161: 143–153.
Wang Y, Botvinick EL, Zhao Y, Berns MW, Usami S, Tsien RY et al. (2005). Visualizing the mechanical activation of Src. Nature 434: 1040–1045.
Wang YL, Pelham Jr RJ . (1998). Preparation of a flexible, porous polyacrylamide substrate for mechanical studies of cultured cells. Methods Enzymol 298: 489–496.
Wells RG . (2008). The role of matrix stiffness in regulating cell behavior. Hepatology 47: 1394–1400.
Wozniak MA, Desai R, Solski PA, Der CJ, Keely PJ . (2003). ROCK-generated contractility regulates breast epithelial cell differentiation in response to the physical properties of a three-dimensional collagen matrix. J Cell Biol 163: 583–595.
Wu CW, Kao HL, Li AF, Chi CW, Lin WC . (2006). Protein tyrosine-phosphatase expression profiling in gastric cancer tissues. Cancer Lett 242: 95–103.
Zeng L, D'Alessandri L, Kalousek MB, Vaughan L, Pallen CJ . (1999). Protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha (PTPalpha) and contactin form a novel neuronal receptor complex linked to the intracellular tyrosine kinase fyn. J Cell Biol 147: 707–714.
Zeng L, Si X, Yu WP, Le HT, Ng KP, Teng RM et al. (2003). PTP alpha regulates integrin-stimulated FAK autophosphorylation and cytoskeletal rearrangement in cell spreading and migration. J Cell Biol 160: 137–146.
Zheng XM, Wang Y, Pallen CJ . (1992). Cell transformation and activation of pp60c-src by overexpression of a protein tyrosine phosphatase. Nature 359: 336–339.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the DFG to GvW and FO and the Deutsche Krebshilfe to GvW and TS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krndija, D., Schmid, H., Eismann, JL. et al. Substrate stiffness and the receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase alpha regulate spreading of colon cancer cells through cytoskeletal contractility. Oncogene 29, 2724–2738 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.25
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.25
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Biophysics in tumor growth and progression: from single mechano-sensitive molecules to mechanomedicine
Oncogene (2023)
-
Multicellular contractility contributes to the emergence of mesothelioma nodules
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
The regulatory roles of phosphatases in cancer
Oncogene (2014)