Abstract
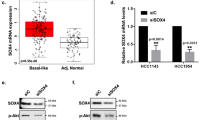
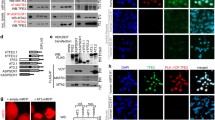
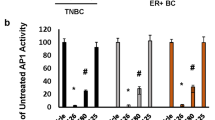
PIK3CA, which codes for the p110α catalytic subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K), is implicated as an oncogene. Despite importance of PIK3CA in cancer, little is known about what drives up its expression in tumor cells. We recently characterized the PIK3CA promoter and reported that it is transcriptionally silenced by the tumor suppressor protein p53. In the present study, we demonstrate that PIK3CA can be induced by the oncogenic transcription factor Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1). Three YB-1-responsive elements were identified on the PIK3CA promoter using chromatin immunoprecipitation and electrophoretic mobility shift assays. Interestingly, silencing YB-1 with siRNA in models of basal-like breast cancer decreased p110α protein levels regardless of whether PIK3CA was wild type, amplified or mutated. This decrease in p110α led to a reduction in PI3K activity and the downstream signaling primarily through p90 ribosomal S6 kinase and S6 ribosomal protein. Disruption in PIK3CA-dependent signaling suppressed cellular invasion correlative with loss of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA). Similarly, silencing YB-1 suppressed invasion and uPA production however this was reversible through the introduction of constitutively active PIK3CA. In conclusion, YB-1 is the first reported oncogene to induce the expression of PIK3CA through transcriptional control of its promoter.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anjum R, Blenis J . (2008). The RSK family of kinases: emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9: 747–758.
Astanehe A, Arenillas D, Wasserman WW, Leung PC, Dunn SE, Davies BR et al. (2008). Mechanisms underlying p53 regulation of PIK3CA transcription in ovarian surface epithelium and in ovarian cancer. J Cell Sci 121: 664–674.
Bachman KE, Argani P, Samuels Y, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S et al. (2004). The PIK3CA gene is mutated with high frequency in human breast cancers. Cancer Biol Ther 3: 772–775.
Bader AG, Kang S, Vogt PK . (2006). Cancer-specific mutations in PIK3CA are oncogenic in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 1475–1479.
Carriere A, Ray H, Blenis J, Roux PP . (2008). The RSK factors of activating the Ras/MAPK signaling cascade. Front Biosci 13: 4258–4275.
Clark DE, Errington TM, Smith JA, Frierson HF, Weber MJ, Lannigan DA . (2005). The serine/threonine protein kinase, p90 ribosomal S6 kinase, is an important regulator of prostate cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res 65: 3108–3116.
Deleeuw RJ, Zettl A, Klinker E, Haralambieva E, Trottier M, Chari R et al. (2007). Whole-genome analysis and HLA genotyping of enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma reveals 2 distinct lymphoma subtypes. Gastroenterology 132: 1902–1911.
Didier DK, Schiffenbauer J, Woulfe SL, Zacheis M, Schwartz BD . (1988). Characterization of the cDNA encoding a protein binding to the major histocompatibility complex class II Y box. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 7322–7326.
Dunn SE, Torres JV, Oh JS, Cykert DM, Barrett JC . (2001). Up-regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by insulin-like growth factor-I depends upon phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Cancer Res 61: 1367–1374.
Finkbeiner MR, Astanehe A, To K, Fotovati A, Davies AH, Zhao Y et al. (2009). Profiling YB-1 target genes uncovers a new mechanism for MET receptor regulation in normal and malignant human mammary cells. Oncogene 28: 1421–1431.
Ghoda L, Lin X, Greene WC . (1997). The 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (pp90rsk) phosphorylates the N-terminal regulatory domain of IkappaBalpha and stimulates its degradation in vitro. J Biol Chem 272: 21281–21288.
Gold MR, Duronio V, Saxena SP, Schrader JW, Aebersold R . (1994). Multiple cytokines activate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in hemopoietic cells: association of the enzyme with various tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. J Biol Chem 269: 5403–5412.
Gupta S, Ramjaun AR, Haiko P, Wang Y, Warne PH, Nicke B et al. (2007). Binding of ras to phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110alpha is required for ras-driven tumorigenesis in mice. Cell 129: 957–968.
Habibi G, Leung S, Law JH, Gelmon K, Masoudi H, Turbin D et al. (2008). Re-defining prognostic factors for breast cancer: YB-1 is a stronger predictor of relapse and disease specific survival than estrogen receptor or HER-2 across all tumor subtypes. Breast Cancer Res 10: R86.
Hollestelle A, Elstrodt F, Nagel JH, Kallemeijn WW, Schutte M . (2007). Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase or RAS pathway mutations in human breast cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer Res 5: 195–201.
Horn S, Bergholz U, Jucker M, McCubrey JA, Trumper L, Stocking C et al. (2008). Mutations in the catalytic subunit of class IA PI3K confer leukemogenic potential to hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 27: 4096–4106.
Hui RC, Gomes AR, Constantinidou D, Costa JR, Karadedou CT, Fernandez de Mattos S et al. (2008). The forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a increases phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt activity in drug-resistant leukemic cells through induction of PIK3CA expression. Mol Cell Biol 28: 5886–5898.
Isakoff SJ, Engelman JA, Irie HY, Luo J, Brachmann SM, Pearline RV et al. (2005). Breast cancer-associated PIK3CA mutations are oncogenic in mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res 65: 10992–11000.
Manning BD, Cantley LC . (2007). AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129: 1261–1274.
Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J, Baehner FL, Fevr T et al. (2006). A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 10: 515–527.
Rayet B, Gelinas C . (1999). Aberrant rel/nfkb genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene 18: 6938–6947.
Roux PP, Shahbazian D, Vu H, Holz MK, Cohen MS, Taunton J et al. (2007). RAS/ERK signaling promotes site-specific ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation via RSK and stimulates cap-dependent translation. J Biol Chem 282: 14056–14064.
Saal LH, Holm K, Maurer M, Memeo L, Su T, Wang X et al. (2005). PIK3CA mutations correlate with hormone receptors, node metastasis, and ERBB2, and are mutually exclusive with PTEN loss in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 65: 2554–2559.
Samuels Y, Velculescu VE . (2004). Oncogenic mutations of PIK3CA in human cancers. Cell Cycle 3: 1221–1224.
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S et al. (2004). High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 304: 554.
Shadeo A, Lam WL . (2006). Comprehensive copy number profiles of breast cancer cell model genomes. Breast Cancer Res 8: R9.
Shayesteh L, Lu Y, Kuo WL, Baldocchi R, Godfrey T, Collins C et al. (1999). PIK3CA is implicated as an oncogene in ovarian cancer. Nat Genet 21: 99–102.
She QB, Chandarlapaty S, Ye Q, Lobo J, Haskell KM, Leander KR et al. (2008). Breast tumor cells with PI3K mutation or HER2 amplification are selectively addicted to akt signaling. PLoS ONE 3: e3065.
Sliva D, Rizzo MT, English D . (2002). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and NF-kappaB regulate motility of invasive MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells by the secretion of urokinase-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem 277: 3150–3157.
Smith JA, Poteet-Smith CE, Xu Y, Errington TM, Hecht SM, Lannigan DA . (2005). Identification of the first specific inhibitor of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) reveals an unexpected role for RSK in cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res 65: 1027–1034.
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H et al. (2001). Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 10869–10874.
Stratford AL, Fry CJ, Desilets C, Davies AH, Cho YY, Li Y et al. (2008). Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) serine 102 is a downstream target of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) in basal-like breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 10: R99.
Stratford AL, Habibi G, Astanehe A, Jiang H, Hu K, Park E et al. (2007). Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is transcriptionally induced by the Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) and can be inhibited with Iressa in basal-like breast cancer, providing a potential target for therapy. Breast Cancer Res 9: R61.
Sunters A, Fernandez de Mattos S, Stahl M, Brosens JJ, Zoumpoulidou G, Saunders CA et al. (2003). FoxO3a transcriptional regulation of bim controls apoptosis in paclitaxel-treated breast cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem 278: 49795–49805.
Sutherland BW, Kucab J, Wu J, Lee C, Cheang MC, Yorida E et al. (2005). Akt phosphorylates the Y-box binding protein 1 at Ser102 located in the cold shock domain and affects the anchorage-independent growth of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 24: 4281–4292.
Ueki K, Fruman DA, Brachmann SM, Tseng YH, Cantley LC, Kahn CR . (2002). Molecular balance between the regulatory and catalytic subunits of phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulates cell signaling and survival. Mol Cell Biol 22: 965–977.
Vanhaesebroeck B, Alessi DR . (2000). The PI3K–PDK1 connection: more than just a road to PKB. Biochem J 346 (Part 3): 561–576.
Woo MM, Salamanca CM, Minor A, Auersperg N . (2007). An improved assay to quantitate the invasiveness of cells in modified Boyden chambers. in vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 43: 7–9.
Wu G, Xing M, Mambo E, Huang X, Liu J, Guo Z et al. (2005). Somatic mutation and gain of copy number of PIK3CA in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 7: R609–R616.
Wu J, Stratford AL, Astanehe A, Dunn SE . (2007). YB-1 is a transcription/translation factor that orchestrates the oncogenome by hardwiring signal transduction to gene expression. Trans Oncogen 2: 49–65.
Wu J, Lee C, Yokom D, Jiang H, Cheang MC, Yorida E et al. (2006). Disruption of the Y-box binding protein-1 results in suppression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and HER-2. Cancer Res 66: 4872–4879.
Yehiely F, Moyano JV, Evans JR, Nielsen TO, Cryns VL . (2006). Deconstructing the molecular portrait of basal-like breast cancer. Trends Mol Med 12: 537–544.
Zhang H, Liu G, Dziubinski M, Yang Z, Ethier SP, Wu G . (2008). Comprehensive analysis of oncogenic effects of PIK3CA mutations in human mammary epithelial cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 112: 217–227.
Zhao JJ, Cheng H, Jia S, Wang L, Gjoerup OV, Mikami A et al. (2006). The p110alpha isoform of PI3K is essential for proper growth factor signaling and oncogenic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 16296–16300.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of Canada (SED), RO1 CA114017-01A1 (SED and IB), Canadian Institute of Health Research (VD), Canadian Breast Cancer Research Alliance IDEA (WL). AA was supported by the Canadian Institute of Health Research MD/PhD and the Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research Studentships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Astanehe, A., Finkbeiner, M., Hojabrpour, P. et al. The transcriptional induction of PIK3CA in tumor cells is dependent on the oncoprotein Y-box binding protein-1. Oncogene 28, 2406–2418 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.81
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.81
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
H3K27 acetylation activated long noncoding RNA RP11-162G10.5 promotes breast cancer progression via the YBX1/GLO1 axis
Cellular Oncology (2023)
-
Long non-coding RNA MIR4435-2HG: a key molecule in progression of cancer and non-cancerous disorders
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
Reciprocal regulation of Daxx and PIK3CA promotes colorectal cancer cell growth
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
The YB-1/EZH2/amphiregulin signaling axis mediates LPA-induced breast cancer cell invasion
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2019)
-
Hypoxia-induced LncRNA-BX111 promotes metastasis and progression of pancreatic cancer through regulating ZEB1 transcription
Oncogene (2018)