Abstract
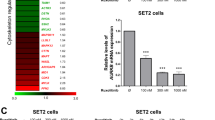
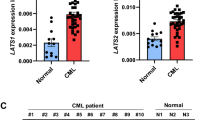
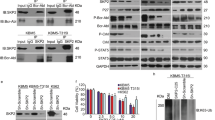
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) patients treated with imatinib mesylate (IM) become drug resistant by mutations within the kinase domain of Bcr–Abl, and by other changes that cause progression to advanced stage (blast crisis) and increased expression of the Lyn tyrosine kinase, the regulation of which is not understood yet. In Bcr–Abl+ cells inhibition of Jak2, a downstream target of Bcr–Abl, by either Jak2 inhibitors or Jak2-specific short interfering RNA (siRNA) reduced the level of the SET protein, and increased PP2A Ser/Thr phosphatase and Shp1 tyrosine phosphatase activities, which led to decreased levels of activated Lyn. Activation of PP2A combined with Jak2 inhibition enhanced the reduction of activated Lyn kinase compared with Jak2 inhibition alone. In contrast, inhibition of either PP2A or Shp1 combined with Jak2 inhibition interfered with the loss of Lyn kinase activation more so than Jak2 inhibition alone, indicating the involvement of PP2A and Shp1 in the inactivation of the Lyn kinase caused by Jak2 inhibition. Inhibition of Jak2 induced apoptosis and reduced colony formation in IM-sensitive and -resistant Bcr–Abl mutant cell lines. Jak2 inhibition also induced apoptosis in CML cells from blast crisis patients but not in normal hematopoietic cells. These results indicate that Lyn is downstream of Jak2, and Jak2 maintains activated Lyn kinase in CML through the SET–PP2A–Shp1 pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez RH, Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE . (2006). The role of Src in solid and hematologic malignancies: development of new-generation Src inhibitors. Cancer 107: 1918–1929.
Bruno O, Brullo C, Bondavalli F, Ranise A, Schenone S, Tognolini M et al. (2007). 2-Amino/azido/hydrazino-5-alkoxy-5H-[1]benzopyrano[4,3-d]pyrimidines: synthesis and pharmacological evaluation. Med Chem 3: 127–134.
Chu S, Holtz M, Gupta M, Bhatia R . (2004). BCR/ABL kinase inhibition by imatinib mesylate enhances MAP kinase activity in chronic myelogenous leukemia CD34+ cells. Blood 103: 3167–3174.
Dai Y, Rahmani M, Corey SJ, Dent P, Grant S . (2004). A Bcr/Abl-independent, Lyn-dependent form of imatinib mesylate (STI-571) resistance is associated with altered expression of Bcl-2. J Biol Chem 279: 34227–34239.
Donato NJ, Wu JY, Stapley J, Gallick G, Lin H, Arlinghaus R et al. (2003). BCR-ABL independence and LYN kinase overexpression in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells selected for resistance to STI571. Blood 101: 690–698.
Donato NJ, Wu JY, Stapley J, Lin H, Arlinghaus R, Aggarwal BB et al. (2004). Imatinib mesylate resistance through BCR-ABL independence in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res 22: 5766–5774.
Hu Y, Liu Y, Pelletier S, Buchdunger E, Warmuth M, Fabbro D et al. (2004). Requirement of Src kinases Lyn, Hck and Fgr for BCR-ABL1-induced B-lymphoblastic leukemia but not chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 36: 453–461.
Ilaria RL Jr, Hawley RG, Van Etten RA . (1999). Dominant negative mutants implicate STAT5 in myeloid cell proliferation and neutrophil differentiation. Blood 93: 4154–4166.
Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE, O'Brien S, Giles F, Garcia-Manero G, Faderl S et al. (2003). Imatinib mesylate therapy in newly diagnosed patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia: high incidence of early complete and major cytogenetic responses. Blood 101: 97–100.
Klejman A, Schreiner SJ, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Slupianek A, Wilson M, Smithgall TE et al. (2002). The Src family kinase Hck couples BCR/ABL to STAT5 activation in myeloid leukemia cells. EMBO J 21: 5766–5774.
Li L, Ren CH, Tahir SA, Ren C, Thompson TC . (2003). Caveolin-1 maintains activated Akt in prostate cancer cells through scaffolding domain binding site interactions with and inhibition of serine/threonine protein phosphatases PP1 and PP2A. Mol Cell Biol 23: 9389–9404.
Li M, Makkinje A, Damuni Z . (1996). The myeloid leukemia-associated protein SET is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A. J Biol Chem 271: 11059–11062.
Nawa M, Kanekura K, Hashimoto Y, Aiso S, Matsuoka M . (2008). A novel Akt/PKB-interacting protein promotes cell adhesion and inhibits familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked mutant SOD1-induced neuronal death via inhibition of PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of Akt/PKB. Cell Signal 20: 493–505.
Neviani P, Santhanam R, Trotta R, Notari M, Blaser BW, Liu S et al. (2005). The tumor suppressor PP2A is functionally inactivated in blast crisis CML through the inhibitory activity of the BCR/ABL-regulated SET protein. Cancer Cell 8: 355–368.
Nimmanapalli R, O’Bryan E, Huang M, Bali P, Burnette PK, Loughran T et al. (2002). Molecular characterization and sensitivity of STI-571 (imatinib mesylate, Gleevec)-resistant, Bcr-Abl-positive, human acute leukemia cells to SRC kinase inhibitor PD180970 and 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin. Cancer Res 62: 5761–5769.
O’Hare T, Corbin AS, Druker BJ . (2006). Targeted CML therapy: controlling drug resistance, seeking cure. Curr Opin Genet Dev 16: 92–99.
Pardanani A . (2008). AK2 inhibitor therapy in myeloproliferative disorders: rationale, preclinical studies and ongoing clinical trials. Leukemia 22: 23–30.
Pardanani A, Hood J, Lasho T, Levine RL, Martin MB, Noronha G et al. (2007). TG101209, a small molecule JAK2-selective kinase inhibitor potently inhibits myeloproliferative disorder-associated JAK2V617F and MPLW515L/K mutations. Leukemia 21: 1658–1668.
Pathak MK, Yi T . (2001). Sodium stibogluconate is a potent inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases and augments cytokine responses in hemopoietic cell lines. J Immunol 167: 3391–3397.
Perrotti D, Neviani P . (2006). ReSETting PP2A tumour suppressor activity in blast crisis and imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Cancer 95: 775–781.
Ptasznik A, Nakata Y, Kalota A, Emerson SG, Gewirtz AM . (2004). Short interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting the Lyn kinase induces apoptosis in primary, and drug-resistant, BCR-ABL1(+) leukemia cells. Nat Med 10: 1187–1189.
Puil L, Liu J, Gish G, Mbamalu G, Bowtell D, Pelicci PG et al. (1994). Bcr-Abl oncoproteins bind directly to activators of the Ras signalling pathway. EMBO J 13: 764–773.
Samanta AK, Lin H, Sun T, Kantarjian H, Arlinghaus RB . (2006). Janus kinase 2: a critical target in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res 66: 6468–6472.
Sandberg EM, Ma X, He K, Frank SJ, Ostrov DA, Sayeski PP . (2005). Identification of 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexabromocyclohexane as a small molecule inhibitor of jak2 tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation [correction of autophophorylation]. J Med Chem 48: 2526–2533.
Sattler M, Mohi MG, Pride YB, Quinnan LR, Malouf NA, Podar K et al. (2002). Critical role for Gab2 in transformation by BCR/ABL. Cancer Cell 1: 479–492.
Weisberg E, Manley PW, Breitenstein W, Bruggen J, Cowan-Jacob SW, Ray A et al. (2005). Characterization of AMN107, a selective inhibitor of native and mutant Bcr-Abl. Cancer Cell 7: 129–141.
Wilson-Rawls J, Xie S, Liu J, Laneuville P, Arlinghaus RB . (1996). P210 Bcr-Abl interacts with the interleukin 3 receptor beta(c) subunit and constitutively induces its tyrosine phosphorylation. Cancer Res 56: 3426–3430.
Wong S, Witte ON . (2004). The BCR-ABL story: bench to bedside and back. Annu Rev Immunol 22: 247–306.
Wu J, Meng F, Lu H, Kong L, Bornmann W, Peng Z et al. (2008). Lyn regulates BCR-ABL and Gab2 tyrosine phosphorylation and c-Cbl protein stability in imatinib resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood 7: 3821–3829.
Xie S, Lin H, Sun T, Arlinghaus RB . (2002). Jak2 is involved in c-Myc induction by Bcr-Abl. Oncogene 21: 7137–7146.
Xie S, Wang Y, Liu J, Sun T, Wilson MB, Smithgall TE et al. (2001). Involvement of Jak2 tyrosine phosphorylation in Bcr-Abl transformation. Oncogene 20: 6188–6195.
Yi T, Pathak MK, Lindner DJ, Ketterer ME, Farver C, Borden EC . (2002). Anticancer activity of sodium stibogluconate in synergy with IFNs. J Immunol 169: 5978–5985.
Yokota A, Kimura S, Masuda S, Ashihara E, Kuroda J, Sato K et al. (2007). INNO-406, a novel BCR-ABL/Lyn dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor, suppresses the growth of Ph+ leukemia cells in the central nervous system, and cyclosporine A augments its in vivo activity. Blood 109: 306–314.
Yokoyama N, Reich NC, Miller WT . (2001). Involvement of protein phosphatase 2A in the interleukin-3-stimulated Jak2-Stat5 signaling pathway. J Interferon Cytokine Res 21: 369–378.
Yokoyama N, Reich NC, Miller WT . (2003). Determinants for the interaction between Janus kinase 2 and protein phosphatase 2A. Arch Biochem Biophys 417: 87–95.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants CA49639 and CA093792 (RBA), CA095512 and DOD WB1XWH-07-1-0270 (DP), Leukemia Spore grant CA100632 (AKS), and Ladies Leukemia League (AKS). We thank Santhanam Ramasami, PhD in the Perrotti lab for his help in PP2A assay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samanta, A., Chakraborty, S., Wang, Y. et al. Jak2 inhibition deactivates Lyn kinase through the SET–PP2A–SHP1 pathway, causing apoptosis in drug-resistant cells from chronic myelogenous leukemia patients. Oncogene 28, 1669–1681 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.7
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pathogenesis and management of accelerated and blast phases of chronic myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2023)
-
Interfering B cell receptor signaling via SHP-1/p-Lyn axis shows therapeutic potential in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
miR-101 sensitizes K562 cell line to imatinib through Jak2 downregulation and inhibition of NF-κB target genes
Tumor Biology (2016)
-
Natural course and biology of CML
Annals of Hematology (2015)