Abstract
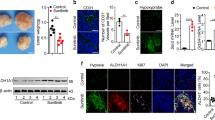
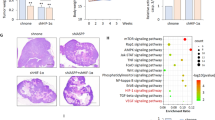
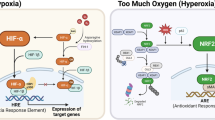
The expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) correlates with poor clinical outcomes and confers resistance to the apoptosis of the tumor cells that are exposed to hypoxia. Presently, the mechanism underlying this phenomenon is poorly understood. In this study we provide evidence that transglutaminase 2 (TG2), an enzyme that catalyses protein crosslinking reactions, is a transcriptional target of HIF-1 to enhance the survival of hypoxic cells. We found that hypoxia induces TG2 expression through an HIF-1 dependent pathway and concurrently activates intracellular TG2. The hypoxic cells overexpressing TG2 showed resistance to apoptosis. Conversely, the hypoxic cells treated with either TG2 inhibitor or small interfering RNA (siRNA) became sensitive to apoptosis. Activation of TG2 in response to hypoxic stress inhibited caspase-3 activity by forming crosslinked multimer, resulting in insoluble aggregates. TG2 also activates nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathway after hypoxic stress, and thereby induces the expression of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 2. The anti-apoptotic role of TG2 was further confirmed in vivo using xenografts in athymic mice. Our results indicate that TG2 is an anti-apoptotic mediator of HIF-1 through modulating both apoptosis and survival pathways and may confer a selective growth advantage to tumor cells. These findings suggest that the inhibition of TG2 may offer a novel strategy for anticancer therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Abbreviations
- HIF-1:
-
hypoxia-inducible factor-1
- HRE:
-
hypoxia-response element
- TG:
-
transglutaminase
- BP:
-
5′-(biotinamido)pentylamine
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- MDC:
-
monodansylcadaverine
References
Aggarwal BB . (2004). Nuclear factor-kappaB: the enemy within. Cancer Cell 6: 203–208.
Antonyak MA, Miller AM, Jansen JM, Boehm JE, Balkman CE, Wakshlag JJ et al. (2004). Augmentation of tissue transglutaminase expression and activation by epidermal growth factor inhibit doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 279: 41461–41467.
Antonyak MA, Jansen JM, Miller AM, Ly TK, Endo M, Cerione RA . (2006). Two isoforms of tissue transglutaminase mediate opposing cellular fates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 18609–18614.
Baldwin AS . (2001). Control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-κB. J Clin Invest 107: 241–246.
Baylin SB . (1997). Tying it all together: epigenetics, genetic, cell cycle, and cancer. Science 277: 1948–1949.
Brown JM, Wilson WR . (2004). Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 437–447.
Brunelle JK, Chandel NS . (2002). Oxygen deprivation induced cell death: an update. Apoptosis 7: 475–482.
Bubici C, Papa S, Dean K, Franzoso G . (2006). Mutual cross-talk between reactive oxygen species and nuclear factor-kappa B: molecular basis and biological significance. Oncogene 25: 6731–6748.
Choi K, Siegel M, Piper JL, Yuan L, Cho E, Strnad P et al. (2005). Chemistry and biology of dihydroisoxazole derivatives: selective inhibitors of human transglutaminase 2. Chem Biol 12: 469–475.
Dachs GU, Patterson AV, Firth JD, Ratcliffe PJ, Townsend KM, Stratford IJ et al. (1997). Targeting gene expression to hypoxic tumor cells. Nat Med 3: 515–520.
De Laurenzi V, Melino G . (2001). Gene disruption of tissue transglutaminase. Mol Cell Biol 21: 148–155.
Dirmeier R, O’Brien K, Engle M, Dodd A, Spears E, Poyton RO . (2004). Measurement of oxidative stress in cells exposed to hypoxia and other changes in oxygen concentration. Methods Enzymol 381: 589–603.
Fesus L, Piacentini M . (2002). Transglutaminase 2: an enigmatic enzyme with diverse functions. Trends Biochem Sci 27: 534–539.
Filiano AJ, Bailey CDC, Tucholski J, Gundemir S, Johnson GVW . (2008). Transglutaminase 2 protects against ischemic insult, interacts with HIF1β, and attenuates HIF1 signaling. FASEB J 22: 2662–2675.
Giaccia A, Siim BG, Johnson RS . (2003). HIF-1 as a target for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2: 803–811.
Hasegawa G, Suwa M, Ichikawa Y, Ohtsuka T, Kumagai S, Kikuchi M et al. (2003). A novel function of tissue-type transglutaminase: protein disulphide isomerase. Biochem J 373: 793–803.
Herman JF, Mangala LS, Mehta K . (2006). Implications of increased tissue transglutaminase (TG2) expression in drug-resistant breast cancer (MCF-7) cells. Oncogene 25: 3049–3058.
Hui AS, Bauer AL, Striet JB, Schnell PO, Czyzyk-Krzeska MF . (2006). Calcium signaling stimulates translation of HIF-alpha during hypoxia. FASEB J 20: 466–475.
Jeon JH, Kim CW, Shin DM, Kim K, Cho SY, Kwon JC et al. (2003a). Differential incorporation of biotinylated polyamines by transglutaminase 2. FEBS Lett 534: 180–184.
Jeon JH, Choi KH, Cho SY, Kim CW, Shin DM, Kwon JC et al. (2003b). Transglutaminase 2 inhibits Rb binding of human papillomavirus E7 by incorporating polyamine. EMBO J 22: 5273–5282.
Jeon JH, Lee HJ, Jang GY, Kim CW, Shin DM, Cho SY et al. (2004). Different inhibition characteristics of intracellular transglutaminase activity by cystamine and cysteamine. Exp Mol Med 36: 576–581.
Kaidi A, Qualtrough D, Williams AC, Paraskeva C . (2006). Direct transcriptional up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 promotes colorectal tumor cell survival and enhances HIF-1 transcriptional activity during hypoxia. Cancer Res 66: 6683–6691.
Kuhlicke J, Frick JS, Morote-Garcia JC, Rosenberger P, Eltzschig HK . (2007). Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1 coordinates induction of Toll-like receptors TLR2 and TLR6 during hypoxia. PLos ONE 2: e1364.
Lee KN, Birckbichler PJ, Patterson Jr MK . (1989). GTP hydrolysis by guinea pig liver transglutaminase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 162: 1370–1375.
Livak KJ, Schmitten TD . (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25: 402–408.
Lorand L, Graham RM . (2003). Transglutaminases: crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 140–156.
Maxwell PH . (2005). The HIF pathway in cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol 16: 523–530.
Mehta K, Fok J, Miller FR, Koul D, Sahin AA . (2004). Prognostic significance of tissue transglutaminase in drug resistant and metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10: 8068–8076.
Mishra S, Murphy LJ . (2004). Tissue transglutaminase has intrinsic kinase activity: identification of transglutaminase 2 as an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 kinase. J Biol Chem 279: 23863–23868.
Park SS, Kim JM, Kim DS, Kim IH, Kim SY . (2006). Transglutaminase 2 mediates polymer formation of IκBα through C-terminal glutamine cluster. J Biol Chem 281: 34965–34972.
Perkins ND . (2007). Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 49–62.
Piret JP, Mottet D, Raes M, Michiels C . (2002). Is HIF-1alpha a pro- or an anti-apoptotic protein? Biochem Pharmacol 64: 889–892.
Pouyssegur J, Dayan F, Mazure NM . (2006). Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature 441: 437–443.
Reed JC . (2006). Drug insight: cancer therapy strategies based on restoration of endogenous cell death mechanisms. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3: 388–398.
Semenza GL . (2003). Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 721–732.
Shin DM, Jeon JH, Kim CW, Cho SY, Kwon JC, Lee HJ et al. (2004). Cell type-specific activation of intracellular transglutaminase 2 by oxidative stress or ultraviolet irradiation: implications of transglutaminase 2 in age-related cataractogenesis. J Biol Chem 279: 15032–15039.
Shin DM, Jeon JH, Kim CW, Cho SY, Lee HJ, Jang GY et al. (2008). TGFβ mediates activation of transglutaminase 2 in response to oxidative stress that leads to protein aggregation. FASEB J 22: 2498–2507.
Sohn J, Kim TI, Yoon YH, Kim JY, Kim SY . (2003). Novel transglutaminase inhibitors reverse the inflammation of allergic conjunctivitis. J Clin Invest 111: 121–128.
Verma A, Mehta K . (2007). Tissue transglutaminase-mediated chemoresistance in cancer cells. Drug Resist Updat 10: 144–151.
Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maxwell PH, Harris AL, Ratcliffe PJ . (2000). Identification of novel hypoxia dependent and independent target genes of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumour suppressor by mRNA differential expression profiling. Oncogene 19: 6297–6305.
Yamaguchi H, Wang HG . (2006). Tissue transglutaminase serves as an inhibitor of apoptosis by cross-linking caspase 3 in thapsigargin-treated cells. Mol Cell Biol 26: 569–579.
Yuan L, Choi K, Khosla C, Zheng X, Higashikubo R, Chicoine MR et al. (2005). Tissue transglutaminase 2 inhibition promotes cell death and chemosensitivity in glioblastomas. Mol Cancer Ther 4: 1293–1302.
Zagzag D, Zhong H, Scalzitti JM, Laughner E, Simons JW, Semenza GL . (2000). Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in brain tumors: association with angiogenesis, invasion, and progression. Cancer 88: 2606–2618.
Zhang R, Tremblay TL, McDermid A, Thibault P, Stanimirovic D . (2003a). Identification of differentially expressed proteins in human glioblastoma cell lines and tumors. Glia 42: 194–208.
Zhang Z, Vezza R, Plappert T, McNamara P, Lawson JA, Austin S et al. (2003b). COX-2-dependent cardiac failure in Gh/tTG transgenic mice. Circ Res 92: 1153–1161.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr YD Kim for critical comments on this paper. We also thank Dr Shigetaka Kitajima (Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Japan) for providing cIAP2 reporter construct. This work was supported by the grants from Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (R11-2002-097-09005-0 and R01-2005-000-10364-0) and also by the Research Program for New Drug Target Discovery (M10748000296-07N4800-29610). GYJ, SYC, EMJ, SHL and YC were supported by the graduate program of BK21, Korea Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, GY., Jeon, JH., Cho, SY. et al. Transglutaminase 2 suppresses apoptosis by modulating caspase 3 and NF-κB activity in hypoxic tumor cells. Oncogene 29, 356–367 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.342
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.342
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Canonical and truncated transglutaminase-2 regulate mucin-1 expression and androgen independency in prostate cancer cell lines
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Transglutaminase 2 crosslinks the glutathione S-transferase tag, impeding protein–protein interactions of the fused protein
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
Pivotal Role of Peptides in Gastric Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Therapy
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2021)
-
Transglutaminase 2 mediates transcriptional regulation through BAF250a polyamination
Genes & Genomics (2021)
-
Amplification of transglutaminase 2 enhances tumor-promoting inflammation in gastric cancers
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2020)