Abstract
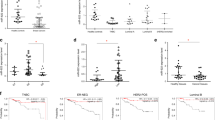
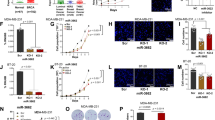
Predicting the impact of microRNAs (miRNAs) on target proteins is challenging because of their different regulatory effects at the transcriptional and translational levels. In this study, we applied a novel protein lysate microarray (LMA) technology to systematically monitor for target protein levels after high-throughput transfections of 319 pre-miRs into breast cancer cells. We identified 21 miRNAs that downregulated the estrogen receptor-α (ERα), as validated by western blotting and quantitative real time–PCR, and by demonstrating the inhibition of estrogen-stimulated cell growth. Five potent ERα-regulating miRNAs, miR-18a, miR-18b, miR-193b, miR-206 and miR-302c, were confirmed to directly target ERα in 3′-untranslated region reporter assays. The gene expression signature that they repressed highly overlapped with that of a small interfering RNA against ERα, and across all the signatures tested, was most closely associated with the repression of known estrogen-induced genes. Furthermore, miR-18a and miR-18b showed higher levels of expression in ERα-negative as compared with ERα-positive clinical tumors. In summary, we present systematic and direct functional evidence of miRNAs inhibiting ERα signaling in breast cancer, and demonstrate the high-throughput LMA technology as a novel, powerful technique in determining the relative impact of various miRNAs on key target proteins and associated cellular processes and pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Adams BD, Furneaux H, White BA . (2007). The micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA) miR-206 targets the human estrogen receptor-alpha (ERα) and represses ERα messenger RNA and protein expression in breast cancer cell lines. Mol Endocrinol 21: 1132–1147.
Baek D, Villen J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP . (2008). The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 455: 64–71.
Bartel DP . (2009). MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136: 215–233.
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS, Sander C . (2008). The microRNA org resource: targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res 36: D149–D153.
Blenkiron C, Goldstein LD, Thorne NP, Spiteri I, Chin SF, Dunning MJ et al. (2007). MicroRNA expression profiling of human breast cancer identifies new markers of tumor subtype. Genome Biol 8: R214.
Couse JF, Korach KS . (1999). Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev 20: 358–417.
Doisneau-Sixou SF, Sergio CM, Carroll JS, Hui R, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL . (2003). Estrogen and antiestrogen regulation of cell cycle progression in breast cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer 10: 179–186.
Efron B, Tibshirani R . (2007). On testing the significance of sets of genes. Ann Appl Stat 1: 107–129.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ . (2006). Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 259–269.
Frasor J, Stossi F, Danes JM, Komm B, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS . (2004). Selective estrogen receptor modulators: discrimination of agonistic versus antagonistic activities by gene expression profiling in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 64: 1522–1533.
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP . (2009). Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19: 92–105.
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ . (2008). miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 36: D154–D158.
Grimson A, Farh KK, Johnston WK, Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP, Bartel DP . (2007). MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell 27: 91–105.
Kenealy MR, Flouriot G, Sonntag-Buck V, Dandekar T, Brand H, Gannon F . (2000). The 3′-untranslated region of the human estrogen receptor-α gene mediates rapid messenger ribonucleic acid turnover. Endocrinology 141: 2805–2813.
Kondo N, Toyama T, Sugiura H, Fujii Y, Yamashita H . (2008). miR-206 Expression is down-regulated in estrogen receptor α-positive human breast cancer. Cancer Res 68: 5004–5008.
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ et al. (2005). Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37: 495–500.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP . (2005). Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120: 15–20.
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J et al. (2005). Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 433: 769–773.
Linsley PS, Schelter J, Burchard J, Kibukawa M, Martin MM, Bartz SR et al. (2007). Transcripts targeted by the microRNA-16 family cooperatively regulate cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol 27: 2240–2252.
Liu WH, Yeh SH, Lu CC, Yu SL, Chen HY, Lin CY et al. (2009). MicroRNA-18a prevents estrogen receptor-α expression, promoting proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology 136: 683–693.
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, Sensinger K, Wong L, Scott GK et al. (2006). Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer biopsies. Mol Cancer 5: 24.
Milano A, Dal Lago L, Sotiriou C, Piccart M, Cardoso F . (2006). What clinicians need to know about antioestrogen resistance in breast cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer 42: 2692–2705.
Naume B, Borgen E, Kvalheim G, Kåresen R, Qvist H, Sauer T et al. (2001). Detection of isolated tumor cells in bone marrow in early-stage breast carcinoma patients: comparison with preoperative clinical parameters and primary tumor characteristics. Clin Cancer Res 7: 4122–4129.
Reid G, Denger S, Kos M, Gannon F . (2002). Human estrogen receptor-α: regulation by synthesis, modification and degradation. Cell Mol Life Sci 59: 821–831.
Selbach M, Schwanhausser B, Thierfelder N, Fang Z, Khanin R, Rajewsky N . (2008). Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 455: 58–63.
Smyth GK . (2004). Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3: Article 3.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA et al. (2005). Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 15545–15550.
Sørlie T, Wang Y, Xiao C, Johnsen H, Naume B, Samaha RR et al. (2006). Distinct molecular mechanisms underlying clinically relevant subtypes of breast cancer: gene expression analyses across three different platforms. BMC Genomics 7: 127.
Wang X, El Naqa IM . (2008). Prediction of both conserved and nonconserved microRNA targets in animals. Bioinformatics 24: 325–332.
Verghese ET, Hanby AM, Speirs V, Hughes TA . (2008). Small is beautiful: microRNAs and breast cancer-where are we now? J Pathol 215: 214–221.
Zhao JJ, Lin J, Yang H, Kong W, He L, Ma X et al. (2008). MicroRNA-221/222 negatively regulates ERα and associates with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Biol Chem 283: 31079–31086.
Acknowledgements
The technical assistance of Pauliina Toivonen is gratefully acknowledged. We thank Agilent Technologies for their support on the miRNA expression arrays, and Hilde Johnsen (Department of Genetics, Norwegian Radium Hospital) for laboratory handling of miRNA expression arrays on tumors. We are grateful to the Department of Pathology, Norwegian Radium Hospital, for providing ER-IHC. This study was supported by the Academy of Finland Centre of Excellence on Translational Genome-Scale Biology, Academy of Finland postdoctoral researcher's grant (to SKL), Sigrid Juselius Foundation, Finnish Cancer Society, EU-FP6 projects RIGHT (LSHB-CT-2004-005276) and Moltools (LSHG-CT-2004-5033155), and EU-FP7 project ProspeR (HEALTH-F2-2007-201438).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leivonen, SK., Mäkelä, R., Östling, P. et al. Protein lysate microarray analysis to identify microRNAs regulating estrogen receptor signaling in breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 28, 3926–3936 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.241
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.241
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulation of ERα-dependent breast cancer metastasis by a miR-29a signaling
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
The Potential of Circulating miR-193b, miR-146b-3p and miR-483-3p as Noninvasive Biomarkers in Cutaneous Melanoma Patients
Molecular Biotechnology (2023)
-
Predictors of fulvestrant long-term benefit in hormone receptor-positive/HER2 negative advanced breast cancer
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Non-coding RNAs in polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology (2021)
-
MicroRNA in combination with HER2-targeting drugs reduces breast cancer cell viability in vitro
Scientific Reports (2021)