Abstract
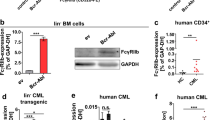
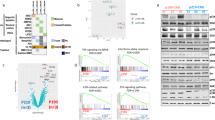
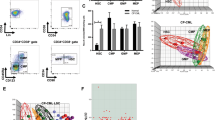
Bcr-Abl oncogene is responsible for the initial phase of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), which is effectively treated by the Bcr-Abl inhibitor imatinib. Over time patients become resistant to treatment and progress to blast crisis, an event that is driven by additional genetic and epigenetic aberrations. Recently, we showed that Riz1 expression decreases in blast crisis and that re-expression of Riz1 inhibits IGF-1 expression. IGF-1 signaling is required in many stages of hematopoiesis and inappropriate activation of autocrine IGF-1 signaling may facilitate transformation to blast crisis. We observed that in 8 out of 11 matched CML patient biopsies the IGF-1 expression is elevated in blast crisis. We examined mechanisms used by CML blast crisis cell lines to activate IGF-1 expression. We found that Bcr-Abl activates autocrine IGF-1 signaling using Hck and Stat5b. Inhibition of these signaling components using small molecule drugs or shRNA decreases proliferation and enhances apoptosis. Together, our study suggests that aberrant IGF-1 signaling is an important event in blast crisis transformation and it provides a mechanism to explain the activity of IGF-1R and Hck inhibitors in blocking CML blast crisis phenotypes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Akahane K, Tojo A, Urabe A, Takaku F . (1987). Pure erythropoietic colony and burst formations in serum-free culture and their enhancement by insulin-like growth factor I. Exp Hematol 15: 797–802.
Barnes DJ, Melo JV . (2002). Cytogenetic and molecular genetic aspects of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Acta Haematol 108: 180–202.
Baserga R, Peruzzi F, Reiss K . (2003). The IGF-1 receptor in cancer biology. Int J Cancer 107: 873–877.
Chen J, Wu A, Sun H, Drakas R, Garofalo C, Cascio S et al. (2005). Functional significance of type 1 insulin-like growth factor-mediated nuclear translocation of the insulin receptor substrate-1 and beta-catenin. J Biol Chem 280: 29912–29920.
Coluccia AM, Vacca A, Dunach M, Mologni L, Redaelli S, Bustos VH et al. (2007). Bcr-Abl stabilizes beta-catenin in chronic myeloid leukemia through its tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO J 26: 1456–1466.
Coppola D, Ferber A, Miura M, Sell C, D'Ambrosio C, Rubin R et al. (1994). A functional insulin-like growth factor I receptor is required for the mitogenic and transforming activities of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol 14: 4588–4595.
Corey SJ, Anderson SM . (1999). Src-related protein tyrosine kinases in hematopoiesis. Blood 93: 1–14.
Danhauser-Riedl S, Warmuth M, Druker BJ, Emmerich B, Hallek M . (1996). Activation of Src kinases p53/56lyn and p59hck by p210bcr/abl in myeloid cells. Cancer Res 56: 3589–3596.
Danielpour D, Song K . (2006). Cross-talk between IGF-I and TGF-beta signaling pathways. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17: 59–74.
Deutsch E, Maggiorella L, Wen B, Bonnet ML, Khanfir K, Frascogna V et al. (2004). Tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1024 exerts antileukaemic effects on STI571-resistant Bcr-Abl expressing cells and decreases AKT phosphorylation. Br J Cancer 91: 1735–1741.
Di Noto R, Luciano L, Lo Pardo C, Ferrara F, Frigeri F, Mercuro O et al. (1997). JURL-MK1 (c-kithigh/CD30−/CD40−) and KURL-MK2 (c-kitlow/CD30+/CD40+) cell lines: ‘two-sided’ model for investigating leukemic megakaryocytopoiesis. Leukemia 11: 1554–1564.
Doepfner KT, Spertini O, Arcaro A . (2007). Autocrine insulin-like growth factor-I signaling promotes growth and survival of human acute myeloid leukemia cells via the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Leukemia 21: 1921–1930.
Drexler HG, MacLeod RAF, Uphoff CC . (1999). Leukemia cell lines: in vitro models for the study of Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia. Leuk Res 23: 207–215.
Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Kantarjian H, Resta DJ, Reese SF, Ford JM et al. (2001). Activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med 344: 1038–1042.
Gouilleux F, Wakao H, Mundt M, Groner B . (1994). Prolactin induces phosphorylation of Tyr694 of Stat5 (MGF), a prerequisite for DNA binding and induction of transcription. EMBO J 13: 4361–4369.
Guilhot F, Apperley J, Kim DW, Bullorsky EO, Baccarani M, Roboz GJ et al. (2007). Dasatinib induces significant hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with imatinib-resistant or -intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia in accelerated phase. Blood 109: 4143–4150.
Hanke JH, Gardner JP, Dow RL, Changelian PS, Brissette WH, Weringer EJ et al. (1996). Discovery of a novel, potent, and Src family-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Study of Lck- and FynT-dependent T cell activation. J Biol Chem 271: 695–701.
Herrington J, Smit LS, Schwartz J, Carter-Su C . (2000). The role of STAT proteins in growth hormone signaling. Oncogene 19: 2585–2597.
Hizuka N, Sukegawa I, Takano K, Asakawa KK, Horikawa R, Tsushima T et al. (1987). Characterization of insulin-like growth factor I receptors on human erythroleukemia cell line (K-562 cells). Endocrinol Jpn 34: 81–88.
Hoelbl A, Kovacic B, Kerenyi MA, Simma A, Warsch W, Cui Y et al. (2006). Clarifying the role of Stat5 in lymphoid development and Abelson-induced transformation. Blood 107: 4898–4906.
Hu Y, Liu Y, Pelletier S, Buchdunger E, Warmuth M, Fabbro D et al. (2004). Requirement of Src kinases Lyn, Hck and Fgr for BCR-ABL1-induced B-lymphoblastic leukemia but not chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 36: 453–461.
Hu Y, Swerdlow S, Duffy TM, Weinmann R, Lee FY, Li S . (2006). Targeting multiple kinase pathways in leukemic progenitors and stem cells is essential for improved treatment of Ph+ leukemia in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 16870–16875.
Ilaria Jr RL, Van Etten RA . (1996). P210 and P190 (BCR/ABL) induce the tyrosine phosphorylation and DNA binding activity of multiple specific STAT family members. J Biol Chem 271: 31704–31710.
Jamieson CH, Ailles LE, Dylla SJ, Muijtjens M, Jones C, Zehnder JL et al. (2004). Granulocyte-macrophage progenitors as candidate leukemic stem cells in blast-crisis CML. N Engl J Med 351: 657–667.
Jiang X, Lopez A, Holyoake T, Eaves A, Eaves C . (1999). Autocrine production and action of IL-3 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in chronic myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 12804–12809.
Johnson EW, Jones LA, Kozak RW . (1992). Expression and function of insulin-like growth factor receptors on anti-CD3-activated human T lymphocytes. J Immunol 148: 63–71.
Jones HE, Gee JM, Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM, Barrow D, Nicholson RI . (2006). Growth factor receptor interplay and resistance in cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 13 (Suppl 1): S45–S51.
Kaleko M, Rutter WJ, Miller AD . (1990). Overexpression of the human insulin like growth factor I receptor promotes ligand-dependent neoplastic transformation. Mol Cell Biol 10: 464–473.
Klejman A, Schreiner SJ, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Slupianek A, Wilson M, Smithgall TE et al. (2002). The Src family kinase Hck couples BCR/ABL to STAT5 activation in myeloid leukemia cells. EMBO J 21: 5766–5774.
Kofoed EM, Hwa V, Little B, Woods KA, Buckway CK, Tsubaki J et al. (2003). Growth hormone insensitivity associated with a STAT5b mutation. N Engl J Med 349: 1139–1147.
Krystal GW, Honsawek S, Litz J, Buchdunger E . (2000). The selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571 inhibits small cell lung cancer growth. Clin Cancer Res 6: 3319–3326.
Kurtz A, Zapf J, Eckardt KU, Clemons G, Froesch ER, Bauer C . (1988). Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates erythropoiesis in hypophysectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 7825–7829.
LeRoith D, Adamo M, Werner H, Roberts Jr CT . (1991). Insulin-like growth factors and their receptors as growth regulators in normal physiology and pathological states. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2: 134–139.
Lionberger JM, Wilson MB, Smithgall TE . (2000). Transformation of myeloid leukemia cells to cytokine independence by Bcr-Abl is suppressed by kinase-defective Hck. J Biol Chem 275: 18581–18585.
Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A . (1993). Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 75: 59–72.
Majka M, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak J, Ehrenman K, Pietrzkowski Z, Kowalska MA et al. (2001). Numerous growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines are secreted by human CD34(+) cells, myeloblasts, erythroblasts, and megakaryoblasts and regulate normal hematopoiesis in an autocrine/paracrine manner. Blood 97: 3075–3085.
Mayerhofer M, Valent P, Sperr WR, Griffin JD, Sillaber C . (2002). BCR/ABL induces expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its transcriptional activator, hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha, through a pathway involving phosphoinositide 3-kinase and the mammalian target of rapamycin. Blood 100: 3767–3775.
Merchav S, Tatarsky I, Hochberg Z . (1988a). Enhancement of erythropoiesis in vitro by human growth hormone is mediated by insulin-like growth factor I. Br J Haematol 70: 267–271.
Merchav S, Tatarsk I, Hochberg Z . (1988b). Enhancement of human granulopoiesis in vitro by biosynthetic insulin-like growth factor I/somatomedin C and human growth hormone. J Clin Invest 81: 791–797.
Meydan N, Grunberger T, Dadi H, Shahar M, Arpaia E, Lapidot Z et al. (1996). Inhibition of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by a Jak-2 inhibitor. Nature 379: 645–648.
Mori N, Morosetti R, Spira S, Lee S, Ben-Yehuda D, Schiller G et al. (1998). Chromosome band 1p36 contains a putative tumor suppressor gene important in the evolution of chronic myelocytic leukemia. Blood 92: 3405–3409.
Nam S, Williams A, Vultur A, List A, Bhalla K, Smith D et al. (2007). Dasatinib (BMS-354825) inhibits Stat5 signaling associated with apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Mol Cancer Ther 6: 1400–1405.
Nieborowska-Skorska M, Wasik MA, Slupianek A, Salomoni P, Kitamura T, Calabretta B et al. (1999). Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)5 activation by BCR/ABL is dependent on intact Src homology (SH)3 and SH2 domains of BCR/ABL and is required for leukemogenesis. J Exp Med 189: 1229–1242.
Parrizas M, Gazit A, Levitzki A, Wertheimer E, LeRoith D . (1997). Specific inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity and biological function by tyrphostins. Endocrinology 138: 1427–1433.
Pastural E, Takahashi N, Dong WF, Bainbridge M, Hull A, Pearson D et al. (2007). RIZ1 repression is associated with insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling activation in chronic myeloid leukemia cell line. Oncogene 26: 1586–1594.
Pepe MG, Ginzton NH, Lee PD, Hintz RL, Greenberg PL . (1987). Receptor binding and mitogenic effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factors I and II for human myeloid leukemic cells. J Cell Physiol 133: 219–227.
Playford MP, Bicknell D, Bodmer WF, Macaulay VM . (2000). Insulin-like growth factor 1 regulates the location, stability, and transcriptional activity of beta-catenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 12103–12108.
Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE . (2004). Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 505–518.
Ren R . (2005). Mechanisms of BCR-ABL in the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 172–183.
Sachdev D, Yee D . (2007). Disrupting insulin-like growth factor signaling as a potential cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 6: 1–12.
Sanders M, Sorba S, Dainiak N . (1993). Insulin-like growth factors stimulate erythropoiesis in serum-substituted umbilical cord blood cultures. Exp Hematol 21: 25–30.
Scherr M, Chaturvedi A, Battmer K, Dallmann I, Schultheis B, Ganser A et al. (2006). Enhanced sensitivity to inhibition of SHP2, STAT5, and Gab2 expression in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Blood 107: 3279–3287.
Schindler C, Darnell Jr JE . (1995). Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: the JAK-STAT pathway. Annu Rev Biochem 64: 621–651.
Schwartz GN, Warren MK, Sakano K, Szabo JM, Kessler SW, Pashapour A et al. (1996). Comparative effects of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) and IGF-II mutants specific for IGF-II/CIM6-P or IGF-I receptors on in vitro hematopoiesis. Stem Cells 14: 337–350.
Scott SA, Lakshmikuttyamma A, Sheridan DP, Sanche SE, Geyer CR, DeCoteau JF . (2007). Zebularine inhibits human acute myeloid leukemia cell growth in vitro in association with p15INK4B demethylation and reexpression. Exp Hematol 35: 263–273.
Sell C, Rubini M, Rubin R, Liu JP, Efstratiadis A, Baserga R . (1993). Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen is unable to transform mouse embryonic fibroblasts lacking type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 11217–11221.
Shimon I, Shpilberg O . (1995). The insulin-like growth factor system in regulation of normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Leuk Res 19: 233–240.
Siddiquee K, Zhang S, Guida WC, Blaskovich MA, Greedy B, Lawrence HR et al. (2007). Selective chemical probe inhibitor of Stat3, identified through structure-based virtual screening, induces antitumor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 7391–7396.
Specchia G, Liso V, Capalbo S, Fazioli F, Bettoni S, Bassan R et al. (1992). Constitutive expression of IL-1 beta, M-CSF and c-fms during the myeloid blastic phase of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Haematol 80: 310–316.
Steller MA, Zou Z, Schiller JT, Baserga R . (1996). Transformation by human papillomavirus 16 E6 and E7: role of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Cancer Res 56: 5087–5091.
Takahashi N, Pastural E, Lowsky R, Torlakovic E, Czader M, Garcia-Manero G et al. (2006). RIZ1 is downregulated during CML progression and displays tumor suppressor properties in CML cell lines. Blood 108: 2134.
Tazzari PL, Tabellini G, Bortul R, Papa V, Evangelisti C, Grafone T et al. (2007). The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor kinase inhibitor NVP-AEW541 induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells exhibiting autocrine insulin-like growth factor-I secretion. Leukemia 21: 886–896 [epub ahead of print].
Teglund S, McKay C, Schuetz E, van Deursen JM, Stravopodis D, Wang D et al. (1998). Stat5a and Stat5b proteins have essential and nonessential, or redundant, roles in cytokine responses. Cell 93: 841–850.
Valentinis B, Baserga R . (2001). IGF-I receptor signalling in transformation and differentiation. Mol Pathol 54: 133–137.
Valentinis B, Romano G, Peruzzi F, Morrione A, Prisco M, Soddu S et al. (1999). Growth and differentiation signals by the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in hemopoietic cells are mediated through different pathways. J Biol Chem 274: 12423–12430.
Wang Y, Jiang H . (2005). Identification of a distal STAT5-binding DNA region that may mediate growth hormone regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I gene expression. J Biol Chem 280: 10955–10963.
Wilson MB, Schreiner SJ, Choi HJ, Kamens J, Smithgall TE . (2002). Selective pyrrolo-pyrimidine inhibitors reveal a necessary role for Src family kinases in Bcr-Abl signal transduction and oncogenesis. Oncogene 21: 8075–8088.
Woelfle J, Chia DJ, Rotwein P . (2003). Mechanisms of growth hormone (GH) action. Identification of conserved Stat5 binding sites that mediate GH-induced insulin-like growth factor-I gene activation. J Biol Chem 278: 51261–51266.
Zadik Z, Estrov Z, Karov Y, Hahn T, Barak Y . (1993). The effect of growth hormone and IGF-I on clonogenic growth of hematopoietic cells in leukemic patients during active disease and during remission—a preliminary report. J Pediatr Endocrinol 6: 79–83.
Zhang X, Ren R . (1998). Bcr-Abl efficiently induces a myeloproliferative disease and production of excess interleukin-3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in mice: a novel model for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 92: 3829–3840.
Zhang Z, Meier KE . (2006). New assignments for multitasking signal transduction inhibitors. Mol Pharmacol 69: 1510–1512.
Zumkeller W, Burdach S . (1999). The insulin-like growth factor system in normal and malignant hematopoietic cells. Blood 94: 3653–3657.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Institute for Health Research. CRG is a CIHR-RPP New Investigator, AL is a Lymphoma Foundation of Canada Postdoctoral Fellow and EP is a CIHR Postdoctoral Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshmikuttyamma, A., Pastural, E., Takahashi, N. et al. Bcr-Abl induces autocrine IGF-1 signaling. Oncogene 27, 3831–3844 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.8
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Obesity and Leukemia: Biological Mechanisms, Perspectives, and Challenges
Current Obesity Reports (2023)
-
Inference of kinase-signaling networks in human myeloid cell line models by Phosphoproteomics using kinase activity enrichment analysis (KAEA)
BMC Cancer (2021)
-
NT157, an IGF1R-IRS1/2 inhibitor, exhibits antineoplastic effects in pre-clinical models of chronic myeloid leukemia
Investigational New Drugs (2021)
-
Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in tumorigenesis and drug resistance: a challenge for cancer therapy
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2020)
-
IGF-IR determines the fates of BCR/ABL leukemia
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2015)