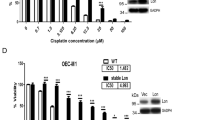
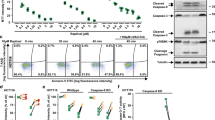
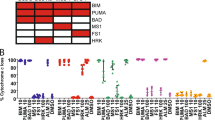
Abstract
Following the screening of a battery of distinct small-interfering RNAs that target various components of the apoptotic machinery, we found that knockdown of the voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) was particularly efficient in preventing cell death induced by cisplatin (CDDP) in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Both the downregulation of VDAC1 and its chemical inhibition with 4,4′-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid reduced the apoptosis-associated modifications induced by CDDP, including mitochondrial transmembrane potential dissipation and plasma membrane permeabilization. VDAC1 inhibition strongly reduced the CDDP-induced conformational activation of Bax, yet had no discernible effect on the activation of Bak, suggesting that VDAC1 acts downstream of Bak and upstream of Bax. Accordingly, knockdown of Bak abolished the activation of Bax, whereas Bax downregulation had no effect on Bak activation. In VDAC1-depleted cells, the failure of CDDP to activate Bax could be reversed by means of the Bcl-2/Bcl-XL antagonist ABT-737, which concomitantly restored CDDP cytotoxicity. Altogether, these results delineate a novel pathway for the induction of mitochondrial membrane permeabilization (MMP) in the course of CDDP-induced cell death that involves a hierarchical contribution of Bak, VDAC1 and Bax. Moreover, our data suggest that VDAC1 may act as a facultative regulator/effector of MMP, depending on the initial cytotoxic event.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ΔΨm:
-
mitochondrial transmembrane potential
- BH3:
-
Bcl-2 homology domain 3
- BRCA1:
-
breast cancer 1, early onset
- CDDP:
-
cisplatin
- Cyt c:
-
cytochrome c
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
- DIDS:
-
4,4′-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid
- DiOC6(3):
-
3,3′dihexiloxalocarbocyanine iodide
- ERCC1:
-
excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 1
- H2O2:
-
hydrogen peroxide
- HE:
-
hydroethidine
- IMS:
-
intermembrane space
- LDH:
-
lactate dehydrogenase
- MMP:
-
mitochondrial membrane permeabilization
- NAC:
-
N-acetylcysteine
- NSCLC:
-
non-small cell lung cancer
- OM:
-
mitochondrial outer membrane
- PARP-1:
-
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- siRNA:
-
small-interfering RNA
- tBHP:
-
tert-butylhydroperoxide
- VDAC1:
-
voltage-dependent anion channel 1
- WST-1:
-
4-[3-(4-iodophenyl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2H-5-tetrazolio]-1,3-benzene disulfonate.
References
Baines CP, Kaiser RA, Sheiko T, Craigen WJ, Molkentin JD . (2007). Voltage-dependent anion channels are dispensable for mitochondrial-dependent cell death. Nat Cell Biol 9: 550–555.
Bartz SR, Zhang Z, Burchard J, Imakura M, Martin M, Palmieri A et al. (2006). Small interfering RNA screens reveal enhanced cisplatin cytotoxicity in tumor cells having both BRCA network and TP53 disruptions. Mol Cell Biol 26: 9377–9386.
Belzacq AS, Vieira HL, Kroemer G, Brenner C . (2002). The adenine nucleotide translocator in apoptosis. Biochimie 84: 167–176.
Berndtsson M, Hagg M, Panaretakis T, Havelka AM, Shoshan MC, Linder S . (2007). Acute apoptosis by cisplatin requires induction of reactive oxygen species but is not associated with damage to nuclear DNA. Int J Cancer 120: 175–180.
Brenner C, Cadiou H, Vieira HL, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Xie Z et al. (2000). Bcl-2 and Bax regulate the channel activity of the mitochondrial adenine nucleotide translocator. Oncogene 19: 329–336.
Brenner C, Grimm S . (2006). The permeability transition pore complex in cancer cell death. Oncogene 25: 4744–4756.
Castedo M, Perfettini JL, Andreau K, Roumier T, Piacentini M, Kroemer G . (2003). Mitochondrial apoptosis induced by the HIV-1 envelope. Ann NY Acad Sci 1010: 19–28.
Chandra D, Choy G, Daniel PT, Tang DG . (2005). Bax-dependent regulation of Bak by voltage-dependent anion channel 2. J Biol Chem 280: 19051–19061.
Cheng EH, Sheiko TV, Fisher JK, Craigen WJ, Korsmeyer SJ . (2003). VDAC2 inhibits BAK activation and mitochondrial apoptosis. Science 301: 513–517.
Cosaert J, Quoix E . (2002). Platinum drugs in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 87: 825–833.
Criollo A, Galluzzi L, Chiara Maiuri M, Tasdemir E, Lavandero S, Kroemer G . (2007). Mitochondrial control of cell death induced by hyperosmotic stress. Apoptosis 12: 3–18.
de La Motte Rouge T, Galluzzi L, Olaussen KA, Zermati Y, Tasdemir E, Robert T et al. (2007). A novel epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor promotes apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells resistant to erlotinib. Cancer Res 67: 6253–6262.
Galluzzi L, Kroemer G . (2007). Mitochondrial apoptosis without VDAC. Nat Cell Biol 9: 487–489.
Galluzzi L, Zamzami N, de La Motte Rouge T, Lemaire C, Brenner C, Kroemer G . (2007). Methods for the assessment of mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in apoptosis. Apoptosis 12: 803–813.
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE, Didelot C, Kroemer G . (2006). Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 13: 1423–1433.
Griffiths GJ, Dubrez L, Morgan CP, Jones NA, Whitehouse J, Corfe BM et al. (1999). Cell damage-induced conformational changes of the pro-apoptotic protein Bak in vivo precede the onset of apoptosis. J Cell Biol 144: 903–914.
Grimm S, Brdiczka D . (2007). The permeability transition pore in cell death. Apoptosis 12: 841–855.
Kepp O, Rajalingam K, Kimmig S, Rudel T . (2007). Bak and Bax are non-redundant during infection- and DNA damage-induced apoptosis. EMBO J 26: 825–834.
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C . (2007). Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev 87: 99–163.
Lalier L, Cartron PF, Juin P, Nedelkina S, Manon S, Bechinger B et al. (2007). Bax activation and mitochondrial insertion during apoptosis. Apoptosis 12: 887–896.
Lorenzo HK, Susin SA, Penninger J, Kroemer G . (1999). Apoptosis inducing factor (AIF): a phylogenetically old, caspase-independent effector of cell death. Cell Death Differ 6: 516–524.
Mandic A, Hansson J, Linder S, Shoshan MC . (2003). Cisplatin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and nucleus-independent apoptotic signaling. J Biol Chem 278: 9100–9106.
Marzo I, Brenner C, Zamzami N, Jurgensmeier JM, Susin SA, Vieira HL et al. (1998). Bax and adenine nucleotide translocator cooperate in the mitochondrial control of apoptosis. Science 281: 2027–2031.
Modjtahedi N, Giordanetto F, Madeo F, Kroemer G . (2006). Apoptosis-inducing factor: vital and lethal. Trends Cell Biol 16: 264–272.
Olaussen KA, Dunant A, Fouret P, Brambilla E, Andre F, Haddad V et al. (2006). DNA repair by ERCC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer and cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 355: 983–991.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. (2005). An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 435: 677–681.
Perfettini JL, Kroemer RT, Kroemer G . (2004). Fatal liaisons of p53 with Bax and Bak. Nat Cell Biol 6: 386–388.
Ravagnan L, Roumier T, Kroemer G . (2002). Mitochondria, the killer organelles and their weapons. J Cell Physiol 192: 131–137.
Reed JC . (2006). Proapoptotic multidomain Bcl-2/Bax-family proteins: mechanisms, physiological roles, and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Death Differ 13: 1378–1386.
Rudin CM, Yang Z, Schumaker LM, VanderWeele DJ, Newkirk K, Egorin MJ et al. (2003). Inhibition of glutathione synthesis reverses Bcl-2-mediated cisplatin resistance. Cancer Res 63: 312–318.
Seve P, Dumontet C . (2005). Chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents 5: 73–88.
Shafir I, Feng W, Shoshan-Barmataz V . (1998). Voltage-dependent anion channel proteins in synaptosomes of the torpedo electric organ: immunolocalization, purification, and characterization. J Bioenerg Biomembr 30: 499–510.
Shimizu S, Ide T, Yanagida T, Tsujimoto Y . (2000a). Electrophysiological study of a novel large pore formed by Bax and the voltage-dependent anion channel that is permeable to cytochrome c. J Biol Chem 275: 12321–12325.
Shimizu S, Matsuoka Y, Shinohara Y, Yoneda Y, Tsujimoto Y . (2001). Essential role of voltage-dependent anion channel in various forms of apoptosis in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol 152: 237–250.
Shimizu S, Narita M, Tsujimoto Y . (1999). Bcl-2 family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by the mitochondrial channel VDAC. Nature 399: 483–487.
Shimizu S, Shinohara Y, Tsujimoto Y . (2000b). Bax and Bcl-xL independently regulate apoptotic changes of yeast mitochondria that require VDAC but not adenine nucleotide translocator. Oncogene 19: 4309–4318.
Shoshan-Barmatz V, Hadad N, Feng W, Shafir I, Orr I, Varsanyi M et al. (1996). VDAC/porin is present in sarcoplasmic reticulum from skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett 386: 205–210.
Siddik ZH . (2003). Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene 22: 7265–7279.
Tarze A, Deniaud A, Le Bras M, Maillier E, Molle D, Larochette N et al. (2007). GAPDH, a novel regulator of the pro-apoptotic mitochondrial membrane permeabilization. Oncogene 26: 2606–2620.
Thinnes FP, Schmid A, Benz R, Hilschmann N . (1990). Studies on human porin. III. Does the voltage-dependent anion channel ‘Porin 31HL’ form part of the chloride channel complex, which is observed in different cells and thought to be affected in cystic fibrosis? Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 371: 1047–1050.
Wang GQ, Gastman BR, Wieckowski E, Goldstein LA, Gambotto A, Kim TH et al. (2001). A role for mitochondrial Bak in apoptotic response to anticancer drugs. J Biol Chem 276: 34307–34317.
Yagoda N, von Rechenberg M, Zaganjor E, Bauer AJ, Yang WS, Fridman DJ et al. (2007). RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 447: 864–868.
Zamzami N, Kroemer G . (2004). Methods to measure membrane potential and permeability transition in the mitochondria during apoptosis. Methods Mol Biol 282: 103–115.
Zamzami N, Kroemer G . (2005). p53 in apoptosis control: an introduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331: 685–687.
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M, Decaudin D, Macho A, Hirsch T et al. (1995). Sequential reduction of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and generation of reactive oxygen species in early programmed cell death. J Exp Med 182: 367–377.
Zermati Y, Mouhamad S, Stergiou L, Besse B, Galluzzi L, Boehrer S et al. (2007). Non-apoptotic role for Apaf-1 in the DNA damage response. Mol Cell 28: 624–637.
Zhang K, Chew M, Yang EB, Wong KP, Mack P . (2001). Modulation of cisplatin cytotoxicity and cisplatin-induced DNA cross-links in HepG2 cells by regulation of glutathione-related mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol 59: 837–843.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by a special grant from Ligue National contre le cancer (équipe labellisée), as well as by grants from Agence Nationale de Recherche, Agence Nationale pour la Recherche sur le Sida, Cancéropôle Ile-de-France, Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale, Institut National du Cancer, European Commission (ApoSys, RIGHT, Active p53, Trans-Death, DeathTrain, ChemoRes) and Sidaction. NT is recipient of an FRM PhD fellowship. OK is recipient of an EMBO PhD fellowship. LS is funded by a DeathTrain PhD fellowship. EM is recipient of a DeathTrain PhD student fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tajeddine, N., Galluzzi, L., Kepp, O. et al. Hierarchical involvement of Bak, VDAC1 and Bax in cisplatin-induced cell death. Oncogene 27, 4221–4232 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.63
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.63
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A highly annotated database of genes associated with platinum resistance in cancer
Oncogene (2021)
-
Cellular pharmacology studies of anticancer agents: recommendations from the EORTC-PAMM group
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2018)
-
CoQ0-induced mitochondrial PTP opening triggers apoptosis via ROS-mediated VDAC1 upregulation in HL-60 leukemia cells and suppresses tumor growth in athymic nude mice/xenografted nude mice
Archives of Toxicology (2018)
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling requires glycine to promote angiogenesis
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
A Single Talent Immunogenic Membrane Antigen and Novel Prognostic Predictor: voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) in Pancreatic Cancer
Scientific Reports (2016)