Abstract
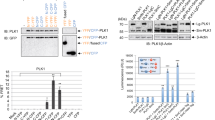
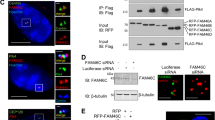
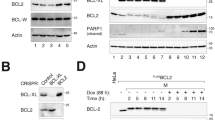
Bcl-xL, an anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member protein, contributes to the resistance against chemotherapies such as tubulin-binder treatment in many human tumors. Although Bcl-xL is phosphorylated after tubulin-binder treatment, the role of the phosphorylation and its responsible kinase(s) are poorly understood. Here, we identified Plk1 (polo-like kinase 1) as a Bcl-xL kinase. Same location of Bcl-xL and Plk1 was revealed by immunocytochemical analyses at M-phase in situ. Plk1 phosphorylates Bcl-xL in vitro, and we identified Plk1 phosphorylation sites in Bcl-xL. When all of these phosphorylation sites were substituted to alanines, the anti-apoptotic activity of the Bcl-xL mutant against the apoptosis induced by pironetin, but not against ultraviolet-induced apoptosis, was increased. These observations suggest that Plk1 is a regulator of Bcl-xL phosphorylation and controls the anti-apoptotic activity of Bcl-xL during pironetin-induced apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr FA, Silljé HH, Nigg EA . (2004). Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 429–440.
Basu A, Haldar S . (2003). Identification of a novel Bcl-xL phosphorylation site regulating the sensitivity of taxol- or 2-methoxyestradiol-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett 538: 41–47.
Boise LH, González-García M, Postema CE, Ding L, Lindsten T, Turka LA et al. (1993). bcl-x, a bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell 74: 597–608.
Chang BS, Minn AJ, Muchmore SW, Fesik SW, Thompson CB . (1997). Identification of a novel regulatory domain in Bcl-xL and Bcl-2. EMBO J 16: 968–977.
Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ . (1998). BCL-2 family: regulators of cell death. Annu Rev Immunol 16: 395–419.
Chen J, Dai G, Wang YQ, Wang S, Pan FY, Xue B et al. (2006). Polo-like kinase 1 regulates mitotic arrest after UV irradiation through dephosphorylation of p53 and inducing p53 degradation. FEBS Lett 580: 3626–3630.
Cheng EH, Levine B, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Hardwick JM . (1996). Bax-independent inhibition of apoptosis by Bcl-xL . Nature 379: 554–556.
Cittelly DM, Nesic-Taylor O, Perez-Polo JR . (2007). Phosphorylation of Bcl-xL after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci Res 85: 1894–1911.
Cory S, Adams JM . (2002). The BCL2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 647–656.
Deverman BE, Cook BL, Manson SR, Niederhoff RA, Langer EM, Rosová I et al. (2002). Bcl-xL deamidation is a critical switch in the regulation of the response to DNA damage. Cell 111: 51–62.
Du L, Lyle CS, Chambers TC . (2005). Characterization of vinblastine-induced Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 phosphorylation: evidence for a novel protein kinase and a coordinated phosphorylation/dephosphorylation cycle associated with apoptosis induction. Oncogene 24: 107–117.
Elia AE, Rellos P, Haire LF, Chao JW, Ivins FJ, Hoepker K et al. (2003). The molecular basis for phosphodependent substrate targeting and regulation of Plks by the Polo-box domain. Cell 115: 83–95.
Feng Y, Hodge DR, Palmieri G, Chase DL, Longo DL, Ferris DK . (1999). Association of polo-like kinase with α-, β- and γ-tubulins in a stable complex. Biochem J 339: 435–442.
Gumireddy K, Reddy MV, Cosenza SC, Nathan RB, Baker SJ, Papathi N et al. (2005). ON01910, a non-ATP-competitive small molecule inhibitor of Plk1, is a potent anticancer agent. Cancer Cell 7: 275–286.
Jeong SY, Gaume B, Lee YJ, Hsu YT, Ryu SW, Yoon SH et al. (2004). Bcl-xL sequesters its C-terminal membrane anchor in soluble, cytosolic homodimers. EMBO J 23: 2146–2155.
Kaufmann T, Schlipf S, Sanz J, Neubert K, Stein R, Borner C . (2003). Characterization of the signal that directs Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Cell Biol 160: 53–64.
Kawatani M, Imoto M . (2003). Deletion of the BH1 domain of Bcl-2 accelerates apoptosis by acting in a dominant negative fashion. J Biol Chem 278: 19732–19742.
Kondoh M, Usui T, Nishikiori T, Mayumi T, Osada H . (1999). Apoptosis induction via microtubule disassembly by an antitumour compound, pironetin. Biochem J 340: 411–416.
Liu X, Erikson RL . (2003). Polo-like kinase (Plk) 1 depletion induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 5789–5794.
Muchmore SW, Sattler M, Liang H, Meadows RP, Harlan JE, Yoon HS et al. (1996). X-ray and NMR structure of human Bcl-xL, an inhibitor of programmed cell death. Nature 381: 335–341.
Nakajima H, Toyoshima-Morimoto F, Taniguchi E, Nishida E . (2003). Identification of a consensus motif for Plk (Polo-like kinase) phosphorylation reveals Myt1 as a Plk1 substrate. J Biol Chem 278: 25277–25280.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. (2005). An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 435: 677–681.
Petros AM, Olejniczak ET, Fesik SW . (2004). Structural biology of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1644: 83–94.
Poruchynsky MS, Wang EE, Rudin CM, Blagosklonny MV, Fojo T . (1998). Bcl-xL is phosphorylated in malignant cells following microtubule disruption. Cancer Res 58: 3331–3338.
Ree AH, Bratland Å, Nome RV, Stokke T, Fodstad Ø . (2003). Repression of mRNA for the PLK cell cycle gene after DNA damage requires BRCA1. Oncogene 22: 8952–8955.
Reed JC . (2002). Apoptosis-based therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1: 111–121.
Schinzel A, Kaufmann T, Borner C . (2004). Bcl-2 family members: intracellular targeting, membrane-insertion, and changes in subcellular localization. Biochim Biophys Acta 1644: 95–105.
Simizu S, Osada H . (2000). Mutations in the Plk gene lead to instability of Plk protein in human tumour cell lines. Nat Cell Biol 2: 852–854.
Simizu S, Takagi S, Tamura Y, Osada H . (2005). RECK-mediated suppression of tumor cell invasion is regulated by glycosylation in human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 65: 7455–7461.
Simizu S, Tamura Y, Osada H . (2004). Dephosphorylation of Bcl-2 by protein phosphatase 2A results in apoptosis resistance. Cancer Sci 95: 266–270.
Tamura Y, Simizu S, Osada H . (2004). The phosphorylation status and anti-apoptotic activity of Bcl-2 are regulated by ERK and protein phosphatase 2A on the mitochondria. FEBS Lett 569: 249–255.
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S . (2000). Bcl-2 family: life-or-death switch. FEBS Lett 466: 6–10.
Usui T, Watanabe H, Nakayama H, Tada Y, Kanoh N, Kondoh M et al. (2004). The anticancer natural product pironetin selectively targets Lys352 of α-tubulin. Chem Biol 11: 799–806.
Watanabe N, Arai H, Iwasaki J, Shiina M, Ogata K, Hunter T et al. (2005). Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) phosphorylation destabilizes somatic Wee1 via multiple pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 11663–11668.
Watanabe N, Arai H, Nishihara Y, Taniguchi M, Watanabe N, Hunter T et al. (2004). M-phase kinases induce phospho-dependent ubiquitination of somatic Wee1 by SCFβ-TrCP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 4419–4424.
Wyllie AH, Kerr JF, Currie AR . (1980). Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 68: 251–306.
Zheng JY, Tsai YC, Kadimcherla P, Zhang R, Shi J, Oyler GA et al. (2008). The C-terminal transmembrane domain of Bcl-xL mediates changes in mitochondrial morphology. Biophys J 94: 286–297.
Acknowledgements
We thank Y Ichikawa and R Nakazawa (Bioarchitect Research Group, RIKEN) for the DNA sequencing, and I Kagawa, M Kumai, E Oka and F Sakai (Research Resources Center, RIKEN) for the peptide synthesis, phospho-Ser62-specific rabbit polyclonal antibody production and affinity purification. This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and by the Chemical Biology Project (RIKEN). YT and ST are recipients of the Junior Research Associate fellowship of RIKEN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamura, Y., Simizu, S., Muroi, M. et al. Polo-like kinase 1 phosphorylates and regulates Bcl-xL during pironetin-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 28, 107–116 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.368
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.368
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulation of apoptosis by an intrinsically disordered region of Bcl-xL
Nature Chemical Biology (2018)
-
Polo-like Kinase 1 as a potential therapeutic target in Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma
BMC Cancer (2016)
-
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Discovery and development of the Polo-like kinase inhibitor volasertib in cancer therapy
Leukemia (2015)
-
Polo-box domain: a versatile mediator of polo-like kinase function
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2010)