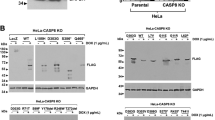
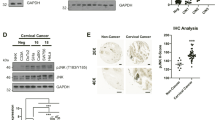
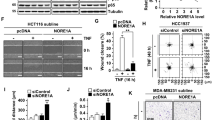
Abstract
Notch-1 inhibits apoptosis in some transformed cells through incompletely understood mechanisms. Notch-1 can increase nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activity through a variety of mechanisms. Overexpression of cleaved Notch-1 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells activates NF-κB via interaction with the I kappa B kinase (IKK) signalosome. Concomitant activation of the Notch and NF-κB pathways has been described in a large series of cervical cancer specimens. Here, we show that wild-type, spontaneously expressed Notch-1 stimulates NF-κB activity in CaSki cervical cancer cells by associating with the IKK signalosome through IKKα. A significant fraction of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-stimulated IκB kinase activity in CaSki cells is Notch-1-dependent. In addition, Notch-1 is found in the nucleus in association with IKKα at IKKα-stimulated promoters and is required for association of IKKα with these promoters under basal and TNF-α-stimulated conditions. Notch-1–IKKα complexes are found in normal human keratinocytes as well, suggesting that IKK regulation is a physiological function of Notch-1. Both Notch-1 and IKKα knockdown sensitize CaSki cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis to equivalent extents. Our data indicate that Notch-1 regulates NF-κB in cervical cancer cells at least in part via cytoplasmic and nuclear IKK-mediated pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera C, Hoya-Arias R, Haegeman G, Espinosa L, Bigas A . (2004). Recruitment of IkappaBalpha to the hes1 promoter is associated with transcriptional repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 16537–16542.
Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC, Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD, Baldwin AS . (2003). A nucleosomal function for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Nature 423: 659–663.
Bash J, Zong WX, Banga S, Rivera A, Ballard DW, Ron Y et al. (1999). Rel/NF-kappaB can trigger the Notch signaling pathway by inducing the expression of Jagged1, a ligand for Notch receptors. EMBO J 18: 2803–2811.
Daniel B, Rangarajan A, Mukherjee G, Vallikad E, Krishna S . (1997). The link between integration and expression of human papillomavirus type 16 genomes and cellular changes in the evolution of cervical intraepithelial neoplastic lesions. J Gen Virol 78: 1095–1101.
Fernandez-Majada V, Aguilera C, Villanueva A, Vilardell F, Robert-Moreno A, Aytes A et al. (2007). Nuclear IKK activity leads to dysregulated Notch-dependent gene expression in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 276–281.
Gray GE, Mann RS, Mitsiadis E, Henrique D, Carcangiu ML, Banks A et al. (1999). Human ligands of the Notch receptor. Am J Pathol 154: 785–794.
Guan E, Wang J, Laborda J, Norcross M, Baeuerle PA, Hoffman T . (1996). T cell leukemia-associated human Notch/translocation-associated Notch homologue has I kappa B-like activity and physically interacts with nuclear factor-kappa B proteins in T cells. J Exp Med 183: 2025–2032.
Hoberg JE, Popko AE, Ramsey CS, Mayo MW . (2006). I{kappa}B Kinase {alpha}-mediated derepression of SMRT potentiates acetylation of RelA/p65 by p300. Mol Cell Biol 26: 457–471.
Hoberg JE, Yeung F, Mayo MW . (2004). SMRT derepression by the IkappaB kinase alpha: a prerequisite to NF-kappaB transcription and survival. Mol Cell 16: 245–255.
Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM . (2004). The IKK NF-kappa B system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3: 17–26.
Kim SH, Song SH, Kim SG, Chun KS, Lim SY, Na HK et al. (2004). Celecoxib induces apoptosis in cervical cancer cells independent of cyclooxygenase using NF-kappaB as a possible target. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130: 551–560.
Lathion S, Schaper J, Beard P, Raj K . (2003). Notch1 can contribute to viral-induced transformation of primary human keratinocytes. Cancer Res 63: 8687–8694.
Lin A, Karin M . (2003). NF-kappaB in cancer: a marked target. Semin Cancer Biol 13: 107–114.
Manna SK, Mukhopadhyay A, Aggarwal BB . (2000). IFN-alpha suppresses activation of nuclear transcription factors NF-kappa B and activator protein 1 and potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis. J Immunol 165: 4927–4934.
Miele L . (2006). Notch signaling. Clin Cancer Res 12: 1074–1079.
Miele L, Golde T, Osborne B . (2006). Notch signaling in cancer. Curr Mol Med 6: 905–918.
Nair A, Venkatraman M, Maliekal TT, Nair B, Karunagaran D . (2003). NF-kappaB is constitutively activated in high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and squamous cell carcinomas of the human uterine cervix. Oncogene 22: 50–58.
Nickoloff BJ, Osborne BA, Miele L . (2003). Notch signaling as a therapeutic target in cancer: a new approach to the development of cell fate modifying agents. Oncogene 22: 6598–6608.
Nickoloff BJ, Qin JZ, Chaturvedi V, Denning MF, Bonish B, Miele L . (2002). Jagged-1 mediated activation of notch signaling induces complete maturation of human keratinocytes through NF-kappaB and PPARgamma. Cell Death Differ 9: 842–855.
Osipo C, Golde TE, Osborne BA, Miele LA . (2008). Off the beaten pathway: the complex cross talk between Notch and NF-kappaB. Lab Invest 88: 11–17.
Perkins ND . (2007). Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 49–62.
Prochaska HJ, Santamaria AB . (1988). Direct measurement of NAD(P)H:quinone reductase from cells cultured in microtiter wells: a screening assay for anticarcinogenic enzyme inducers. Anal Biochem 169: 328–336.
Prusty BK, Husain SA, Das BC . (2005). Constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kB: preferential homodimerization of p50 subunits in cervical carcinoma. Front Biosci 10: 1510–1519.
Ramdass B, Maliekal TT, Lakshmi S, Rehman M, Rema P, Nair P et al. (2006). Coexpression of Notch1 and NF-kappaB signaling pathway components in human cervical cancer progression. Gynecol Oncol 104: 352–361.
Rangarajan A, Syal R, Selvarajah S, Chakrabarti O, Sarin A, Krishna S . (2001). Activated Notch1 signaling cooperates with papillomavirus oncogenes in transformation and generates resistance to apoptosis on matrix withdrawal through PKB/Akt. Virology 286: 23–30.
Shin HM, Minter LM, Cho OH, Gottipati S, Fauq AH, Golde TE et al. (2006). Notch1 augments NF-kappaB activity by facilitating its nuclear retention. EMBO J 25: 129–138.
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, Monks A, McMahon J, Vistica D et al. (1990). New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst 82: 1107–1112.
Talora C, Sgroi DC, Crum CP, Dotto GP . (2002). Specific down-modulation of Notch1 signaling in cervical cancer cells is required for sustained HPV-E6/E7 expression and late steps of malignant transformation. Genes Dev 16: 2252–2263.
Vacca A, Felli MP, Palermo R, Di Mario G, Calce A, Di Giovine M et al. (2006). Notch3 and pre-TCR interaction unveils distinct NF-kappaB pathways in T-cell development and leukemia. EMBO J 25: 1000–1008.
Venkatraman M, Anto RJ, Nair A, Varghese M, Karunagaran D . (2005). Biological and chemical inhibitors of NF-kappaB sensitize SiHa cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Mol Carcinog 44: 51–59.
Vilimas T, Mascarenhas J, Palomero T, Mandal M, Buonamici S, Meng F et al. (2007). Targeting the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in Notch1-induced T-cell leukemia. Nat Med 13: 70–77.
Vooijs M, Schroeter EH, Pan Y, Blandford M, Kopan R . (2004). Ectodomain shedding and intramembrane cleavage of mammalian Notch proteins is not regulated through oligomerization. J Biol Chem 279: 50864–50873.
Wang J, Shelly L, Miele L, Boykins R, Norcross MA, Guan E . (2001). Human Notch-1 inhibits NF-kappa B activity in the nucleus through a direct interaction involving a novel domain. J Immunol 167: 289–295.
Wei LH, Lai KP, Chen CA, Cheng CH, Huang YJ, Chou CH et al. (2005). Arsenic trioxide prevents radiation-enhanced tumor invasiveness and inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 through downregulation of nuclear factor kappaB. Oncogene 24: 390–398.
Weijzen S, Rizzo P, Braid M, Vaishnav R, Jonkheer SM, Zlobin A et al. (2002). Activation of Notch-1 signaling maintains the neoplastic phenotype in human Ras-transformed cells. Nat Med 8: 979–986.
Weijzen S, Zlobin A, Braid M, Miele L, Kast WM . (2003). HPV16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins regulate Notch-1 expression and cooperate to induce transformation. J Cell Physiol 194: 356–362.
Woo SH, Park IC, Park MJ, An S, Lee HC, Jin HO et al. (2004). Arsenic trioxide sensitizes CD95/Fas-induced apoptosis through ROS-mediated upregulation of CD95/Fas by NF-kappaB activation. Int J Cancer 112: 596–606.
Yamamoto Y, Gaynor RB . (2001). Therapeutic potential of inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway in the treatment of inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest 107: 135–142.
Yamamoto Y, Verma UN, Prajapati S, Kwak YT, Gaynor RB . (2003). Histone H3 phosphorylation by IKK-alpha is critical for cytokine-induced gene expression. Nature 423: 655–659.
Zagouras P, Stifani S, Blaumueller CM, Carcangiu ML, Artavanis-Tsakonas S . (1995). Alterations in Notch signaling in neoplastic lesions of the human cervix. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 6414–6418.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grants RO1 CA084065 and 1 PO1 AG025531, and the V+Whittier Foundation (WMK). WMK holds the Walter A Richter Cancer Research Chair. We are grateful to Anna Bigas for critical reading of this manuscript and to Raphael Kopan for helpful discussion of our data and for the gift of the Notch-1/Renilla construct used for quantitative immunoprecipitation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, L., Peng, Y., Yun, J. et al. Notch-1 associates with IKKα and regulates IKK activity in cervical cancer cells. Oncogene 27, 5833–5844 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.190
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.190
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Interactions of melatonin with various signaling pathways: implications for cancer therapy
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
Glycogene expression profiles based on microarray data from cervical carcinoma HeLa cells with partially silenced E6 and E7 HPV oncogenes
Infectious Agents and Cancer (2018)
-
MicroRNA-218-5p inhibits cell growth and metastasis in cervical cancer via LYN/NF-κB signaling pathway
Cancer Cell International (2018)
-
The ANK repeats of Notch-4/Int3 activate NF-κB canonical pathway in the absence of Rbpj and causes mammary tumorigenesis
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Notch signaling pathway networks in cancer metastasis: a new target for cancer therapy
Medical Oncology (2017)