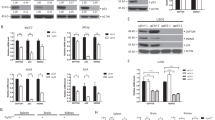
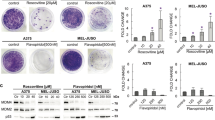
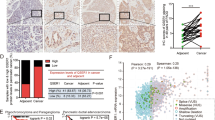
Abstract
Nutlin-3 is a selective inhibitor of the p53-Mdm2 interaction, and inhibits growth in most tumor cells with wild-type p53. However, it only induces apoptosis in subsets of tumor cells. We report that the apoptotic response induced by Nutlin-3 correlates with its antitumor effects in xenograft models in athymic mice. We have investigated signals that sensitize cells to undergo apoptosis induced by Nutlin-3. We demonstrate that adenovirus E1A increases Nutlin-3-induced apoptosis through pRb inhibition in mouse embryonic fibroblast cells in a p53-dependent manner. Consistent with this, pRb depletion by siRNA transfection with Nutlin-3 synergistically increases apoptosis in HCT116 human colon cancer cells, which are insensitive to induction of apoptosis by Nutlin-3 alone. As pRb is a key negative regulator of E2F, we asked whether E2F transcriptional activity determines the apoptotic response of cancer cells to Nutlin-3. We demonstrate that transcriptional activity of E2F correlates with the apoptotic response to Nutlin-3 in various tumor cells and depletion of E2F-1 suppresses Nutlin-3-induced apoptosis in cells possessing high transcriptional activity of E2F, including retinoblastoma cells harboring mutated Rb with wild-type p53. Furthermore, we report that expression of the p53 homologue p73, a target of E2F-1, is markedly increased by Nutlin-3 in Rb-mutated tumor cells harboring wild-type p53. Depletion of p73 by siRNA transfection suppresses Nutlin-3-induced apoptosis in these cells. Taken together, our results demonstrate that E2F-1 transcriptional activity is a critical determinant of Mdm2 antagonist-induced apoptosis and p73 is important for E2F-1-mediated apoptosis induced by Nutlin-3, especially in tumor cells with mutated Rb. Furthermore, our results suggest that tumor cells, including Rb mutated cells, which harbor wild-type p53 and high E2F transcriptional activity, could be a good target for Mdm2 antagonist therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosini G, Sambol EB, Carvajal D, Vassilev LT, Singer S, Schwartz GK . (2007). Mouse Double minute antagonist Nutlin-3a enhances chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in cancer cells with mutant p53 by activating E2F1. Oncogene 24: 3473–3481.
Bates S, Phillips AC, Clark PA, Stott F, Peters G, Ludwig RL et al. (1998). p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature 395: 124–125.
Brockmann D, Esche H . (1995). Regulation of viral and cellular gene expression by E1A proteins encoded by the oncogenic adenovirus type 12. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 119: 81–112.
Chen L, Lu W, Agrawal S, Zhou W, Zhang R, Chen J . (1999). Ubiquitous induction of p53 in tumor cells by antisense inhibition of MDM2 expression. Mol Med 5: 21–34.
Coll-Mulet L, Iglesias-Serret D, Santidrian AF, Cosialls AM, De Frias M, Castano E et al. (2006). MDM2 antagonists activate p53 and synergize with genotoxic drugs in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 107: 4109–4114.
Dyson N . (1998). The regulation of E2F by pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev 12: 2245–2262.
Holmberg C, Helin K, Sehested M, Karlström O . (1998). E2F-1-induced p53-independent apoptosis in transgenic mice. Oncogene 17: 143–155.
Irwin M, Marin MC, Phillips AC, Seelan RS, Smith DI, Liu W et al. (2000). Role for the p53 homologue p73 in E2F-1-induced apoptosis. Nature 407: 645–648.
Kojima K, Konopleva M, Samudio IJ, Shikami M, Cabreira-Hansen M, McQueen T et al. (2005). Mdm2 antagonists induce p53-dependent apoptosis in AML: implications for leukemia therapy. Blood 106: 3150–3159.
Lau LMS, Nugent JK, Zhao X, Irwin MS . (2008). Hdm2 antagonist Nutlin-3 disrupts p73-Hdm2 binding and enhances p73 function. Oncogene 27: 997–1003.
Laurie NA, Donovan SL, Shih CS, Zhang J, Mills N, Fuller C et al. (2006). Inactivation of the p53 pathway in retinoblastoma. Nature 444: 61–66.
Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T, Housman DE . (1993). p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell 74: 954–967.
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ . (1992). The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell 69: 1237–1245.
Nicholson SA, Okby NT, Khan MA, Welsh JA, McMenamin MG, Travis WD et al. (2001). Alterations of p14ARF, p53, and p73 genes involved in the E2F-1-mediated apoptotic pathways in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res 61: 5636–5643.
Patton JT, Mayo LD, Singhi AD, Gudkov AV, Stark GR, Jackson MW . (2006). Levels of HdmX expression dictate the sensitivity of normal and transformed cells to Nutlin-3. Cancer Res 66: 3169–3176.
Pützer BM, Stiewe T, Parssanedjad K, Rega S, Esche H . (2000). E1A is sufficient by itself to induce apoptosis independent of p53 and other adenoviral gene products. Cell Death Differ 7: 177–188.
Qin XQ, Livingston DM, Kaelin Jr WG, Adams PD . (1994). Deregulated transcription factor E2F-1 expression leads to S-phase entry and p53-mediated apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 10918–10922.
Samuelson AV, Lowe SW . (1997). Selective induction of p53 and chemosensitivity in RB-deficient cells by E1A mutants unable to bind the RB-related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 12094–12099.
Secchiero P, Barbarotto E, Tiribelli M, Zerbinati C, Di Iasio MG, Gonelli A et al. (2006). Functional integrity of the p53-mediated apoptotic pathway induced by the nongenotoxic agent nutlin-3 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Blood 107: 4122–4129.
Semizarov D, Kroeger P, Fesik S . (2004). siRNA-mediated gene silencing: a global genome view. Nucleic Acids Res 32: 3836–3845.
Shan B, Lee WH . (1994). Deregulated expression of E2F-1 induces S-phase entry and leads to apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 14: 8166–8173.
Stanelle J, Pützer BM . (2006). E2F1-induced apoptosis: turning killers into therapeutics. Trends Mol Med 12: 177–185.
Stiewe T, Pützer BM . (2000). Role of the p53-homologue p73 in E2F1-induced apoptosis. Nat Genet 26: 464–469.
Stuhmer T, Chatterjee M, Hildebrandt M, Herrmann P, Gollasch H, Gerecke C et al. (2005). Nongenotoxic activation of the p53 pathway as a therapeutic strategy for multiple myeloma. Blood 106: 3609–3617.
Tovar C, Rosinski J, Filipovic Z, Higgins B, Kolinsky K, Hilton H et al. (2006). Small-molecule MDM2 antagonists reveal aberrant p53 signaling in cancer: implications for therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 1888–1893.
Van Maerken T, Speleman F, Vermeulen J, Lambertz I, De Clercq S, De Smet E et al. (2006). Small-molecule MDM2 antagonists as a new therapy concept for neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 66: 9646–9655.
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z et al. (2004). In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 303: 844–848.
Vousden KH . (2000). p53: death star. Cell 103: 691–694.
Vousden KH, Lu X . (2002). Live or let die: the cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 594–604.
Wade M, Wong ET, Tang M, Stommel JM, Wahl GM . (2006). HdmX modulates the outcome of p53 activation in human tumor cells. J Biol Chem 281: 33036–33044.
Zindy F, Eischen CM, Randle DH, Kamijo T, Cleveland JL, Sherr CJ et al. (1998). Myc signaling via the ARF tumor suppressor regulates p53-dependent apoptosis and immortalization. Genes Dev 12: 2424–2433.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Andy Finch (UCSF), Dr Martin McMahon (UCSF) and Ms Amy Young in the McCormick laboratory for sharing reagents; Daiichi Sankyo members: Ms Megumi Minami, Dr Takahiko Seki and Dr Takeshi Jimbo for technical supports, and Dr Hiroyuki Fujiwara and Ms Etsuko Seno for help in plasmid constructions. We acknowledge Dr Gerard Evan (UCSF), Dr Mike Fried (UCSF) and Dr Hideyuki Saya (Keio University) for reading the manuscript carefully and for providing many insightful comments. We also thank the UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center Genome core facilities for real-time Q-PCR analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitagawa, M., Aonuma, M., Lee, S. et al. E2F-1 transcriptional activity is a critical determinant of Mdm2 antagonist-induced apoptosis in human tumor cell lines. Oncogene 27, 5303–5314 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.164
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.164
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Resistance mechanisms to inhibitors of p53-MDM2 interactions in cancer therapy: can we overcome them?
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2021)
-
rs35301225 polymorphism in miR-34a promotes development of human colon cancer by deregulation of 3′UTR in E2F1 in Chinese population
Cancer Cell International (2017)
-
Molecular mechanisms of nutlin-3 involve acetylation of p53, histones and heat shock proteins in acute myeloid leukemia
Molecular Cancer (2014)
-
Protein grafting of p53TAD onto a leucine zipper scaffold generates a potent HDM dual inhibitor
Nature Communications (2014)
-
Insights into p53 transcriptional function via genome-wide chromatin occupancy and gene expression analysis
Cell Death & Differentiation (2012)