Abstract
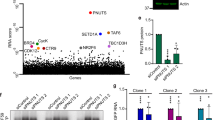
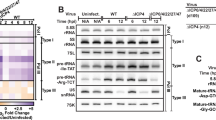
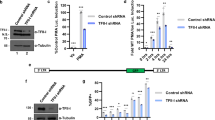
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein K13 interacts with a cytosolic IκB kinase (IKK) complex to activate nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). We recently reported that K13 antagonizes KSHV lytic regulator RTA (replication and transcription activator) and blocks lytic replication, but spares RTA-induced viral interleukin-6 (vIL6). Here we report that K13 is also present in the nuclear compartment, a property not shared by its structural homologs. K13 interacts with and activates the nuclear IKK complex, and binds to the IκBα promoter. K13 mutants that are retained in the cytosol lack NF-κB activity. However, neither the IKKs nor NF-κB activation is required for nuclear localization of K13. Instead, this ability is dependent on a nuclear localization signal located in its N-terminal 40 amino acids. Finally, K13, along with p65/RelA, binds to the promoters of a number of KSHV lytic genes, including RTA, ORF57 and vGPCR, but not to the promoter of the vIL6 gene. Thus, K13 has an unexpected nuclear role in viral and cellular gene regulation and its differential binding to the promoters of lytic genes may not only contribute to the inhibition of KSHV lytic replication, but may also account for the escape of vIL6 from K13-induced transcriptional suppression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
An J, Sun Y, Sun R, Rettig MB . (2003). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encoded vFLIP induces cellular IL-6 expression: the role of the NF-kappaB and JNK/AP1 pathways. Oncogene 22: 3371–3385.
Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC, Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD, Baldwin AS . (2003). A nucleosomal function for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Nature 423: 659–663.
Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D . (1988). Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell 53: 211–217.
Brown HJ, Song MJ, Deng H, Wu T-T, Cheng G, Sun R . (2003). NF-{kappa}B inhibits gammaherpesvirus lytic replication. J Virol 77: 8532–8540.
Chaudhary PM, Jasmin A, Eby MT, Hood L . (1999). Modulation of the NF-kappa B pathway by virally encoded death effector domains-containing proteins. Oncogene 18: 5738–5746.
Chugh P, Matta H, Schamus S, Zachariah S, Kumar A, Richardson JA et al. (2005). Constitutive NF-kappaB activation, normal Fas-induced apoptosis, and increased incidence of lymphoma in human herpes virus 8 K13 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 12885–12890.
Davis M, Hatzubai A, Andersen JS, Ben-Shushan E, Fisher GZ, Yaron A et al. (2002). Pseudosubstrate regulation of the SCF(beta-TrCP) ubiquitin ligase by hnRNP-U. Genes Dev 16: 439–451.
Ear T, Cloutier A, McDonald PP . (2005). Constitutive nuclear expression of the I kappa B kinase complex and its activation in human neutrophils. J Immunol 175: 1834–1842.
Field N, Low W, Daniels M, Howell S, Daviet L, Boshoff C et al. (2003). KSHV vFLIP binds to IKK-{gamma} to activate IKK. J Cell Sci 116: 3721–3728.
Ghosh S, Karin M . (2002). Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell 109 (Suppl): S81–S96.
Gloire G, Dejardin E, Piette J . (2006). Extending the nuclear roles of IkappaB kinase subunits. Biochem Pharmacol 72: 1081–1089.
Gorlich D, Kutay U . (1999). Transport between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15: 607–660.
Grossmann C, Podgrabinska S, Skobe M, Ganem D . (2006). Activation of NF-kappaB by the latent vFLIP gene of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is required for the spindle shape of virus-infected endothelial cells and contributes to their proinflammatory phenotype. J Virol 80: 7179–7185.
Guasparri I, Keller SA, Cesarman E . (2004). KSHV vFLIP is essential for the survival of infected lymphoma cells. J Exp Med 199: 993–1003.
Han Z, Swaminathan S . (2006). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic gene ORF57 is essential for infectious virion production. J Virol 80: 5251–5260.
Harhaj EW, Good L, Xiao G, Uhlik M, Cvijic ME, Rivera-Walsh I et al. (2000). Somatic mutagenesis studies of NF-kappa B signaling in human T cells: evidence for an essential role of IKK gamma in NF-kappa B activation by T-cell costimulatory signals and HTLV-I Tax protein. Oncogene 19: 1448–1456.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . (2004). Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 18: 2195–2224.
Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Richardson P, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, Hayashi T et al. (2002). NF-kappa B as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. J Biol Chem 277: 16639–16647.
Kirshner JR, Lukac DM, Chang J, Ganem D . (2000). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus open reading frame 57 encodes a posttranscriptional regulator with multiple distinct activities. J Virol 74: 3586–3597.
Kumar A, Eby MT, Sinha S, Jasmin A, Chaudhary PM . (2001). Ectodermal dysplasia receptor activates the nuclear factor kappa B, c-Jun N-terminal kinase and cell death pathways and binds to ectodysplasin A. J Biol Chem 276: 2668–2677.
Lange A, Mills RE, Lange CJ, Stewart M, Devine SE, Corbett AH . (2007). Classical nuclear localization signals: definition, function, and interaction with importin alpha. J Biol Chem 282: 5101–5105.
Liu L, Eby MT, Rathore N, Sinha SK, Kumar A, Chaudhary PM . (2002). The human herpes virus 8-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein physically associates with and persistently activates the Ikappa B kinase complex. J Biol Chem 277: 13745–13751.
Matta H, Chaudhary PM . (2004). Activation of alternative NF-kappa B pathway by human herpes virus 8-encoded Fas-associated death domain-like IL-1 beta-converting enzyme inhibitory protein (vFLIP). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 9399–9404.
Matta H, Mazzacurati L, Schamus S, Yang T, Sun Q, Chaudhary PM . (2007a). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) oncoprotein K13 bypasses TRAFs and directly interacts with the I{kappa}B kinase complex to selectively activate NF-{kappa}B without JNK activation. J Biol Chem 282: 24858–24865.
Matta H, Sun Q, Moses G, Chaudhary PM . (2003). Molecular genetic analysis of human herpes virus 8-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein-induced NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 278: 52406–52411.
Matta H, Surabhi RM, Zhao J, Punj V, Sun Q, Schamus S et al. (2007b). Induction of spindle cell morphology in human vascular endothelial cells by human herpesvirus 8-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein K13. Oncogene 26: 1656–1660.
Nakamura H, Lu M, Gwack Y, Souvlis J, Zeichner SL, Jung JU . (2003). Global changes in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated virus gene expression patterns following expression of a tetracycline-inducible Rta transactivator. J Virol 77: 4205–4220.
Nekorchuk M, Han Z, Hsieh TT, Swaminathan S . (2007). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 protein enhances mRNA accumulation independently of effects on nuclear RNA export. J Virol 81: 9990–9998.
Renard P, Percherancier Y, Kroll M, Thomas D, Virelizier JL, Arenzana-Seisdedos F et al. (2000). Inducible NF-kappaB activation is permitted by simultaneous degradation of nuclear IkappaBalpha. J Biol Chem 275: 15193–15199.
Schulz TF . (2006). The pleiotropic effects of Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus. J Pathol 208: 187–198.
Sun Q, Matta H, Chaudhary PM . (2003a). The human herpes virus 8-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein protects against growth factor withdrawal-induced apoptosis via NF-κB activation. Blood 101: 1956–1961.
Sun Q, Matta H, Lu G, Chaudhary PM . (2006). Induction of IL-8 expression by human herpesvirus 8 encoded vFLIP K13 via NF-kappaB activation. Oncogene 25: 2717–2726.
Sun Q, Zachariah S, Chaudhary PM . (2003b). The human herpes virus 8-encoded viral FLICE-inhibitory protein induces cellular transformation via NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 278: 52437–52445.
Thome M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Fickenscher H, Meinl E, Neipel F et al. (1997). Viral FLICE-inhibitory proteins (FLIPs) prevent apoptosis induced by death receptors. Nature 386: 517–521.
Tran K, Merika M, Thanos D . (1997). Distinct functional properties of IkappaB alpha and IkappaB beta. Mol Cell Biol 17: 5386–5399.
Verma UN, Yamamoto Y, Prajapati S, Gaynor RB . (2004). Nuclear role of I kappa B kinase-gamma/NF-kappa B essential modulator (IKK gamma/NEMO) in NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression. J Biol Chem 279: 3509–3515.
Wang SE, Wu FY, Chen H, Shamay M, Zheng Q, Hayward GS . (2004). Early activation of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus RTA, RAP, and MTA promoters by the tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate-induced AP1 pathway. J Virol 78: 4248–4267.
West JT, Wood C . (2003). The role of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus-8 regulator of transcription activation (RTA) in control of gene expression. Oncogene 22: 5150–5163.
Yamamoto Y, Verma UN, Prajapati S, Kwak YT, Gaynor RB . (2003). Histone H3 phosphorylation by IKK-alpha is critical for cytokine-induced gene expression. Nature 423: 655–659.
Zhao J, Punj V, Matta H, Mazzacurati L, Schamus S, Yang Y et al. (2007). K13 blocks KSHV lytic replication and deregulates vIL6 and hIL6 expression: a model of lytic replication induced clonal selection in viral oncogenesis. PLoS ONE 2: e1067.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Inder Verma for providing the IKK-deficient MEFs, Dr Shao-Cong Sun for NEMO-deficient Jurkat cells and Dr Mary Collins for a K13 monoclonal antibody. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (CA85177 and CA124621), the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society and the Mario Lemieux Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matta, H., Punj, V., Schamus, S. et al. A nuclear role for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded K13 protein in gene regulation. Oncogene 27, 5243–5253 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.150
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.150
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Beyond NF-κB activation: nuclear functions of IκB kinase α
Journal of Biomedical Science (2013)
-
Modulation of NF-κB signalling by microbial pathogens
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2011)
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein (vFLIP) K13 suppresses CXCR4 expression by upregulating miR-146a
Oncogene (2010)
-
Integrated microarray and multiplex cytokine analyses of Kaposi's Sarcoma Associated Herpesvirus viral FLICE Inhibitory Protein K13 affected genes and cytokines in human blood vascular endothelial cells
BMC Medical Genomics (2009)