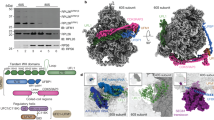
Abstract
Ribosomes translating secretory and membrane proteins are targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane and attach to the protein-conducting channel and ribosome-associated membrane proteins (RAMPs). Recently, a new RAMP, ERj1p, has been identified that recruits BiP to ribosomes and regulates translational activity. Here we present the cryo-EM structure of a ribosome–ERj1p complex, revealing how ERj1p coordinates the ribosome at the membrane and how allosteric effects may mediate ERj1p's regulatory activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brightman, S.E., Blatch, G.L. & Zetter, B.R. Gene 153, 249–254 (1995).
Kroczynska, B., Evangelista, C.M., Samant, S.S., Elguindi, E.C. & Blond, S.Y. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 11432–11443 (2004).
Dudek, J. et al. EMBO J. 21, 2958–2967 (2002).
Chevalier, M., Rhee, H., Elguindi, E.C. & Blond, S.Y. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 19620–19627 (2000).
Halic, M. et al. Nature 427, 808–814 (2004).
Dudek, J. et al. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol., advance online publication 23 October 2005 (10.1038/nsmb1002).
Zupicich, J., Brenner, S.E. & Skarnes, W.C. Genome Biol. 2, Research 0050 (2001).
Spahn, C.M. et al. Cell 107, 373–386 (2001).
Beckmann, R. et al. Cell 107, 361–372 (2001).
Ferbitz, L. et al. Nature 431, 590–596 (2004).
Nakatogawa, H. & Ito, K. Cell 108, 629–636 (2002).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the VolkswagenStiftung (R.B.), Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (R.Z., J.D. and grant Sfb449 to M.B. and R.B.) and from the US National Institutes of Health (R01 NS 43258 and R01 GM 60635 to P.A.P.). The technical assistance of A. Müller is gratefully acknowledged. The cryo-EM data were collected, in part, on the JEOL 3000SFF electron microscope at the National Center for Macromolecular Imaging (Houston, USA), which is supported by the US National Institutes of Health though the National Center for Research Resources's P41 program (grant RR02250). We thank A. Paredes for his microscopy work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blau, M., Mullapudi, S., Becker, T. et al. ERj1p uses a universal ribosomal adaptor site to coordinate the 80S ribosome at the membrane. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12, 1015–1016 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb998
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb998
This article is cited by
-
Visualizing maturation factor extraction from the nascent ribosome by the AAA-ATPase Drg1
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2022)
-
Dual topology of co-chaperones at the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
Hsp70 at the membrane: driving protein translocation
BMC Biology (2018)
-
Inhibitors of protein translocation across membranes of the secretory pathway: novel antimicrobial and anticancer agents
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2018)
-
Diversity and selectivity in mRNA translation on the endoplasmic reticulum
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2015)